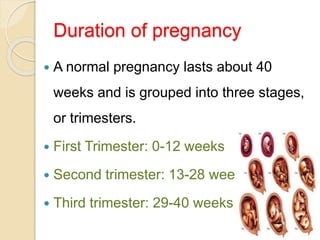
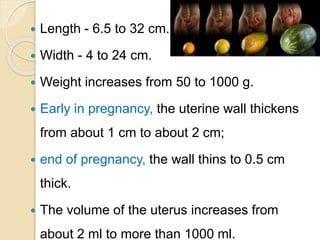
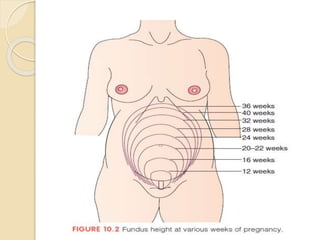
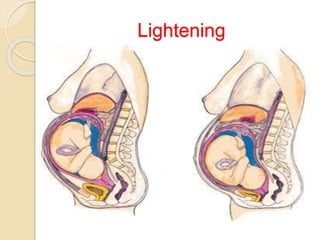
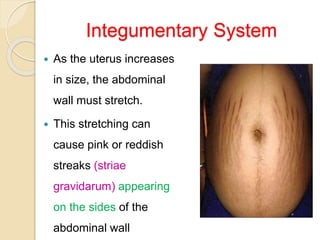
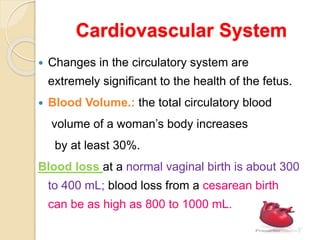
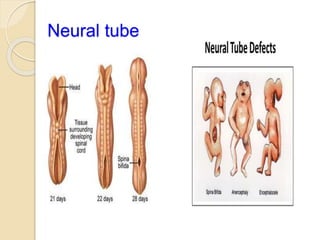
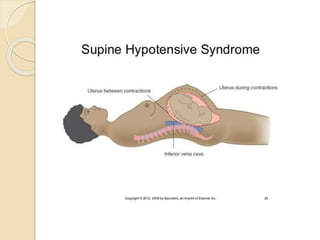
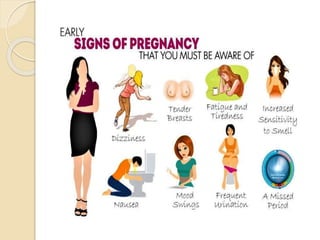
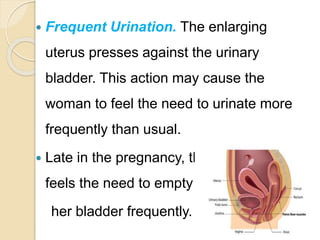
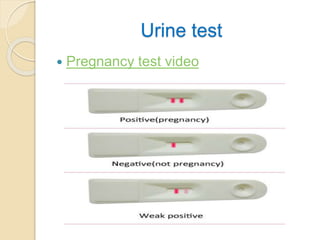
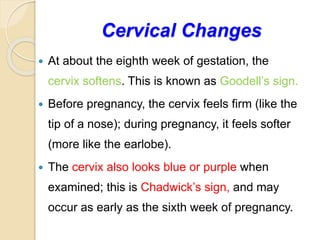
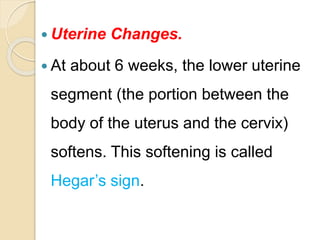
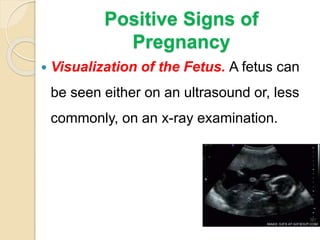
A normal pregnancy lasts about 40 weeks and is divided into three trimesters. The first trimester is weeks 0-12, the second is weeks 13-28, and the third is weeks 29-40. Signs of pregnancy include missed periods, breast changes, nausea, frequent urination, and darkening of the skin. Positive signs that confirm pregnancy are a positive urine test, visualization of the fetus by ultrasound, and detection of the fetal heartbeat with Doppler or fetoscope from 10 weeks onward.