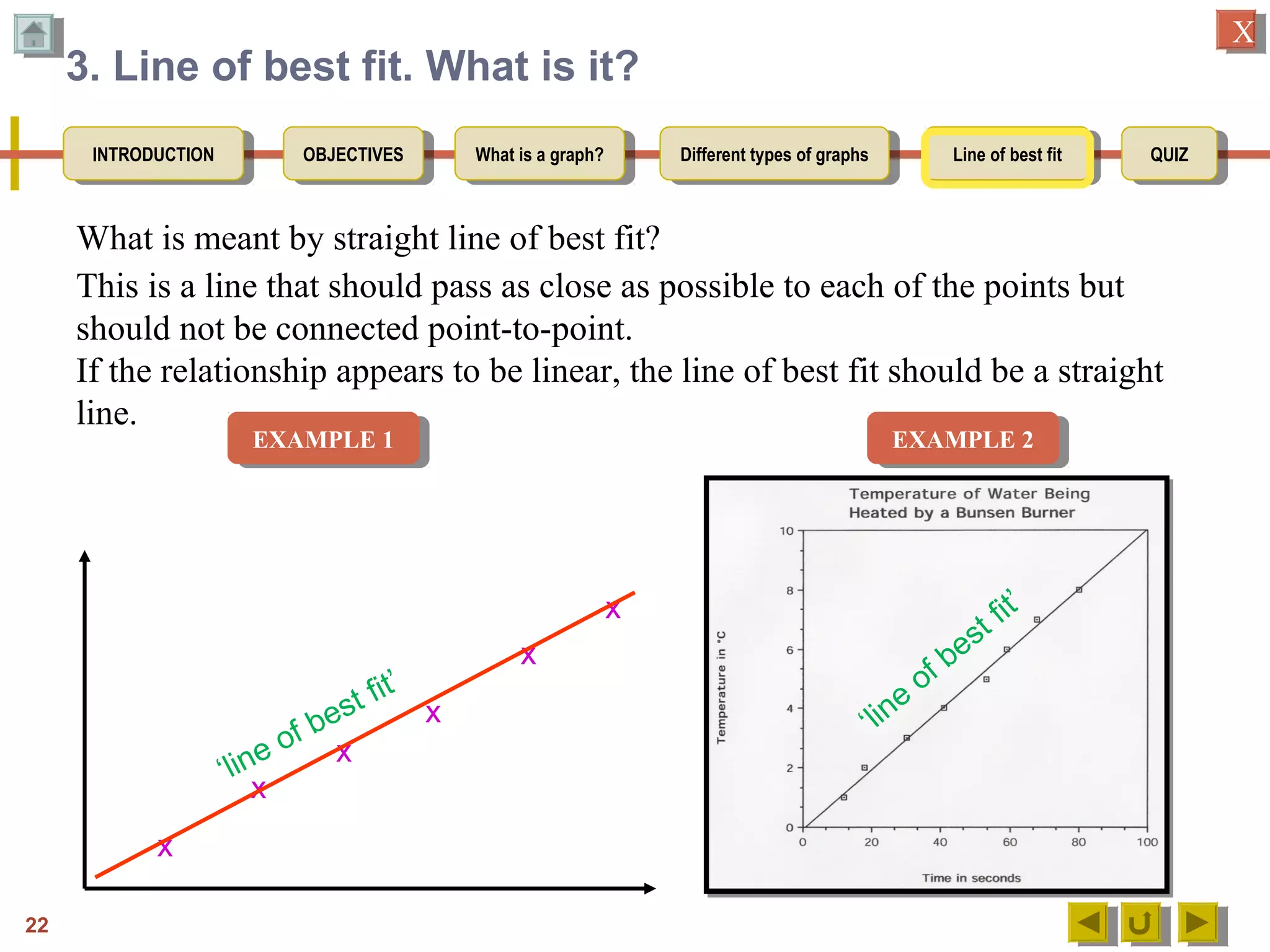
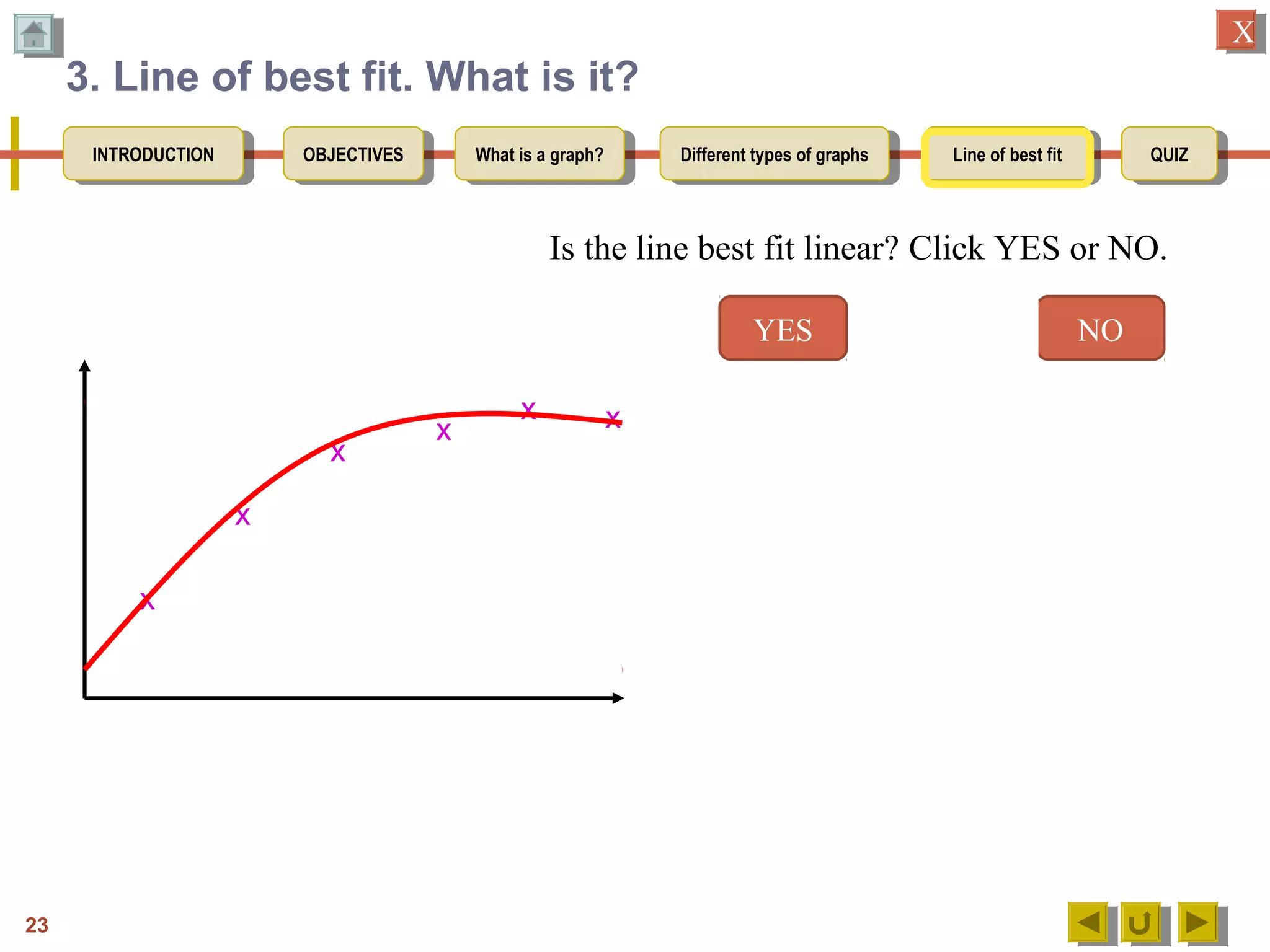
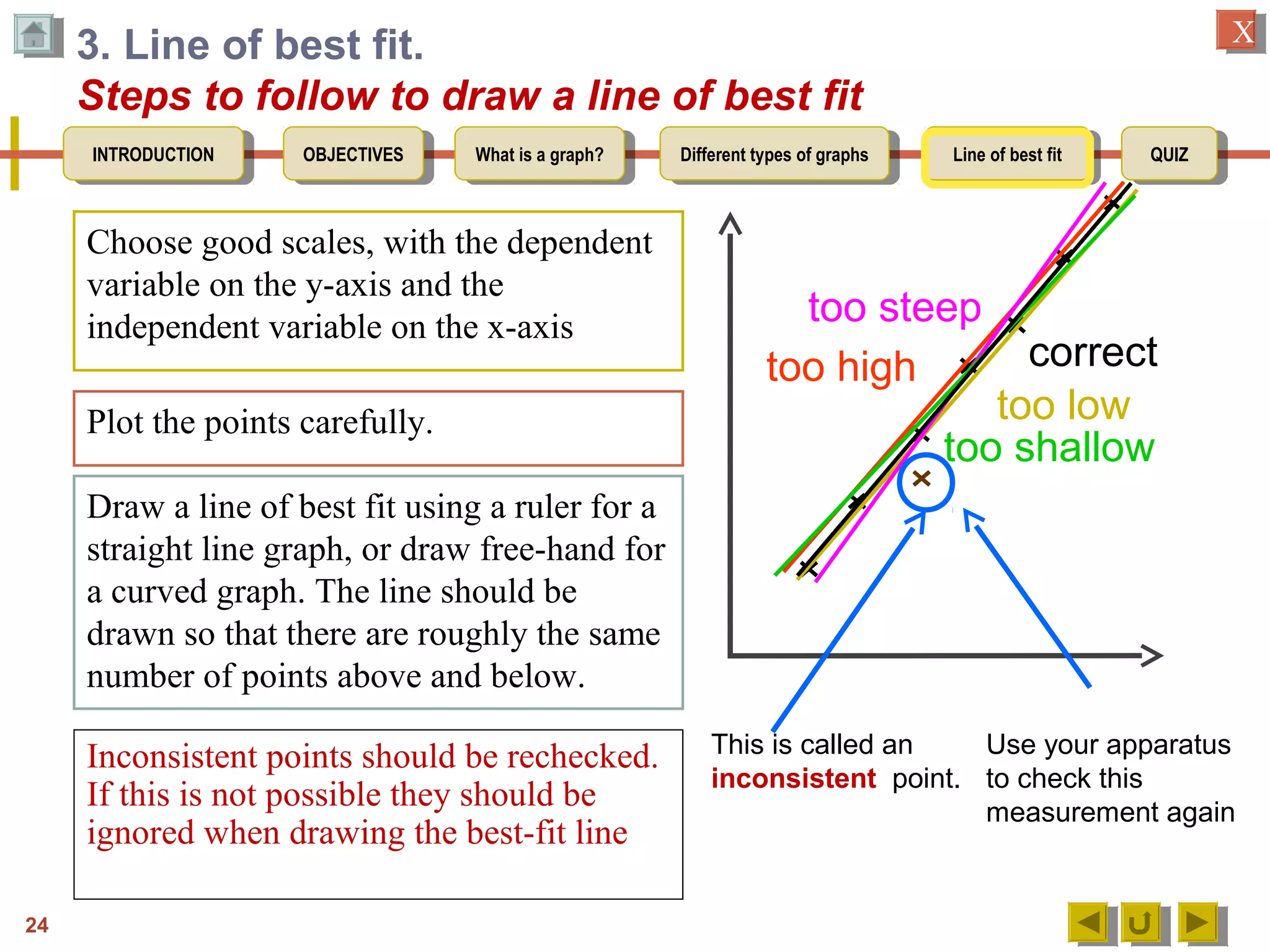
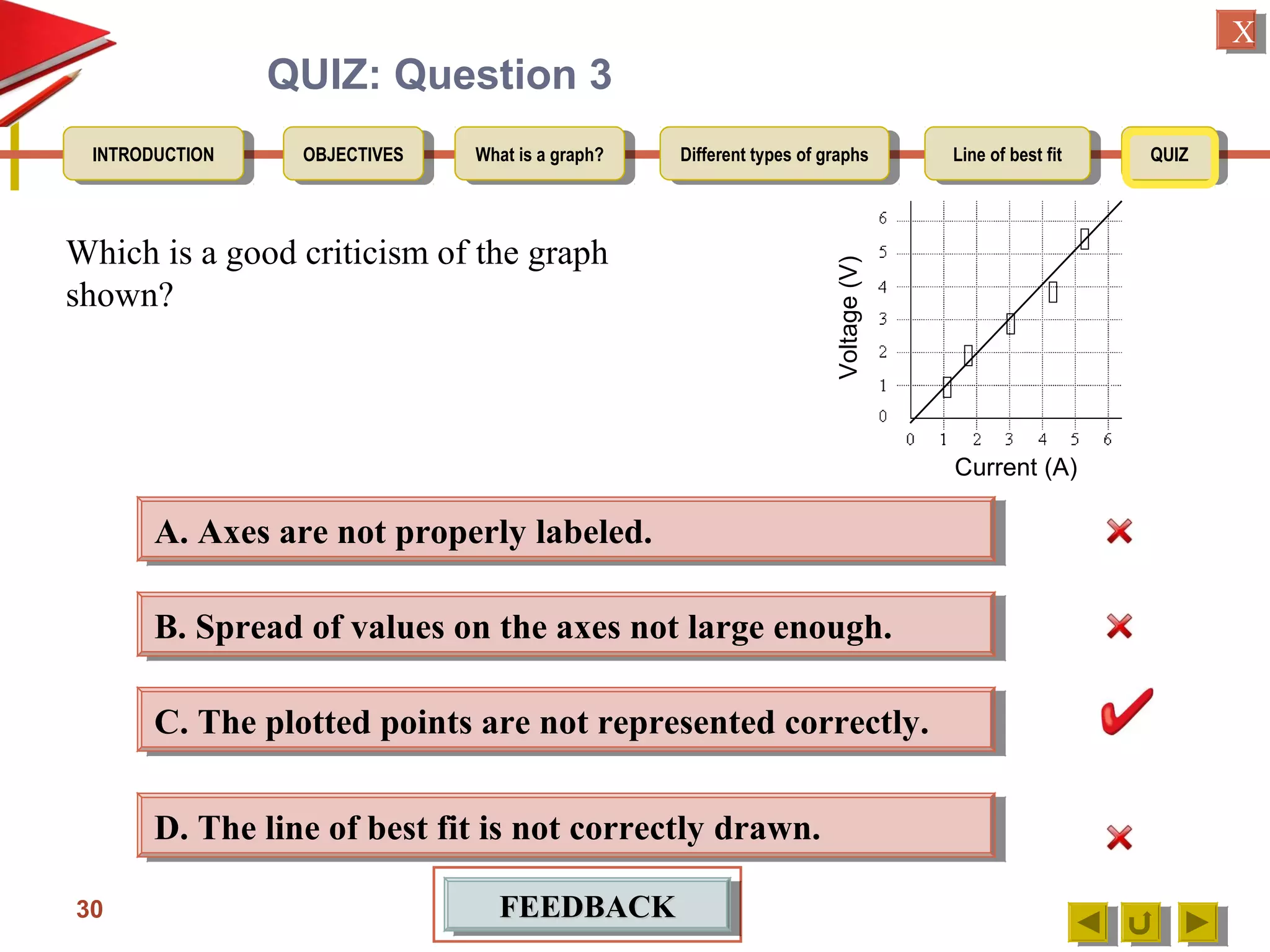
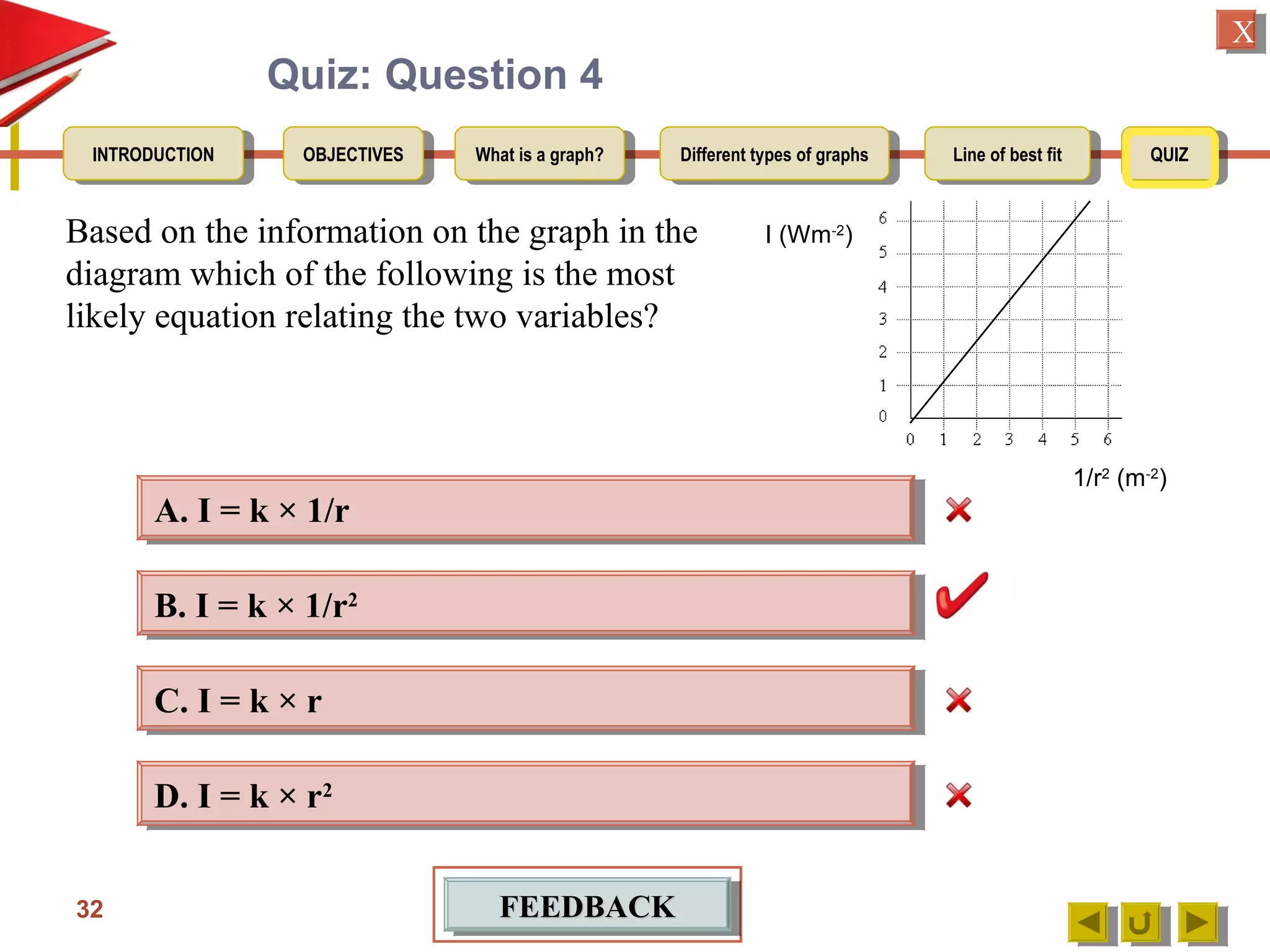
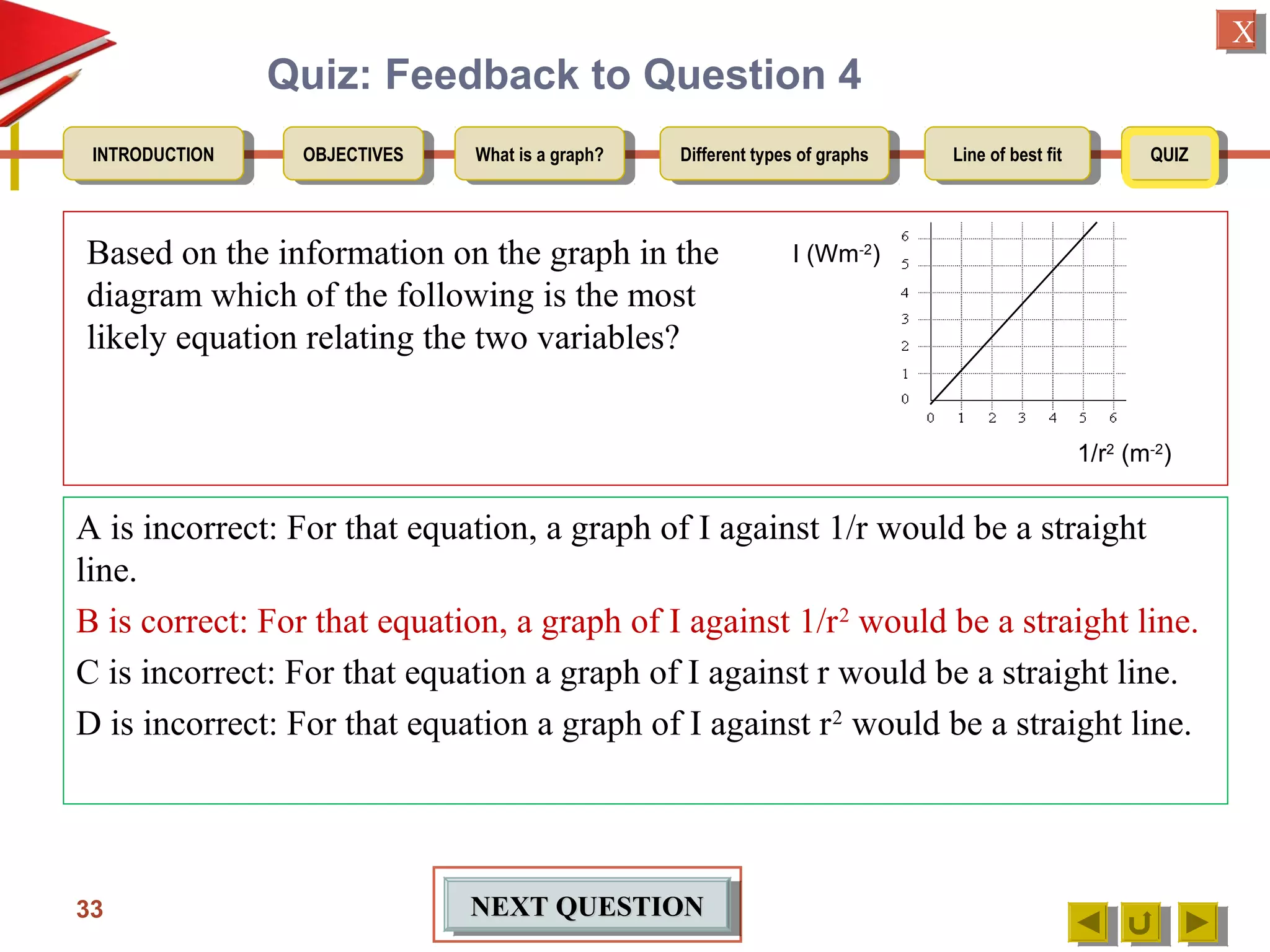
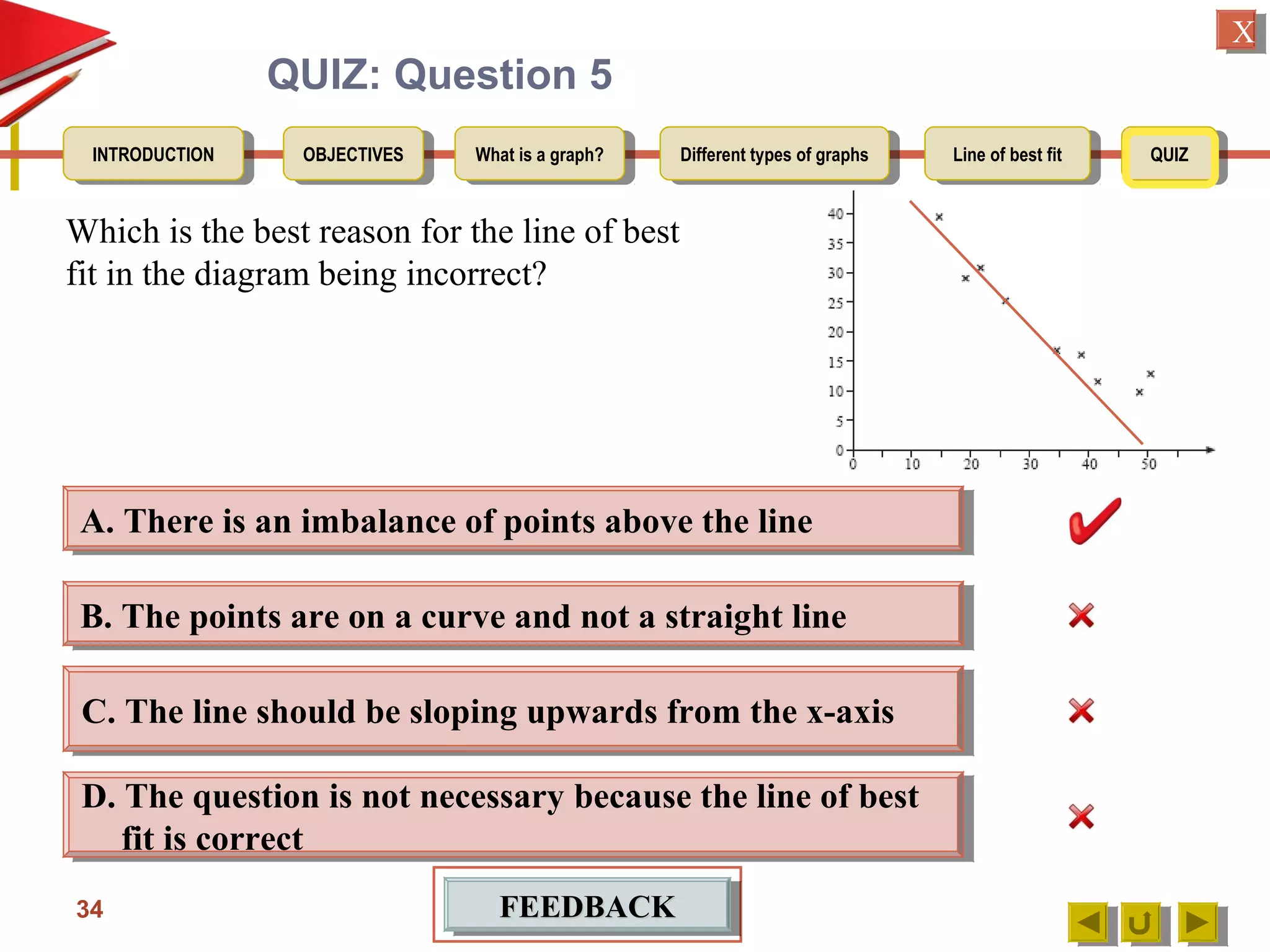
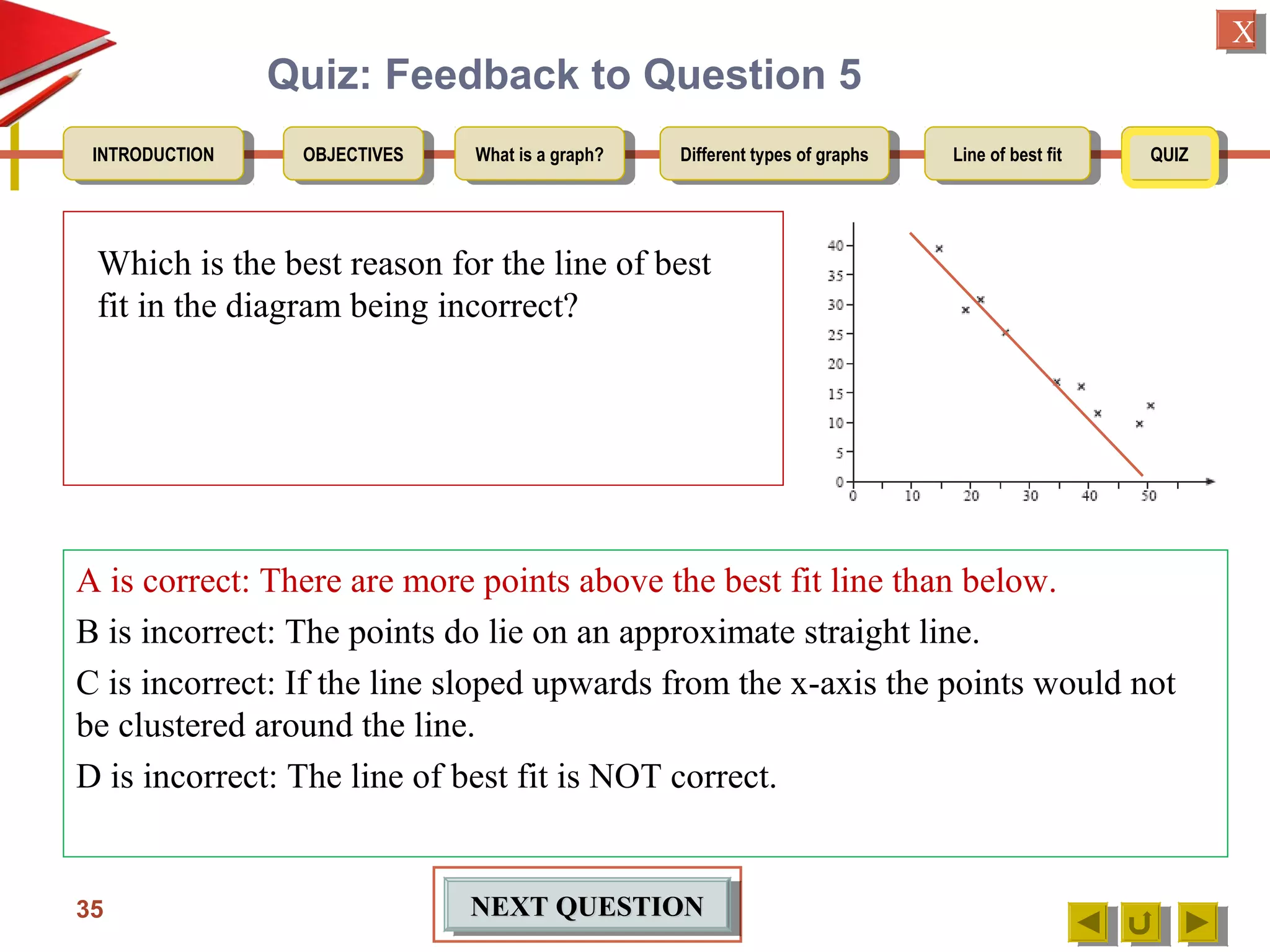
The document provides an introduction to graphs, including:
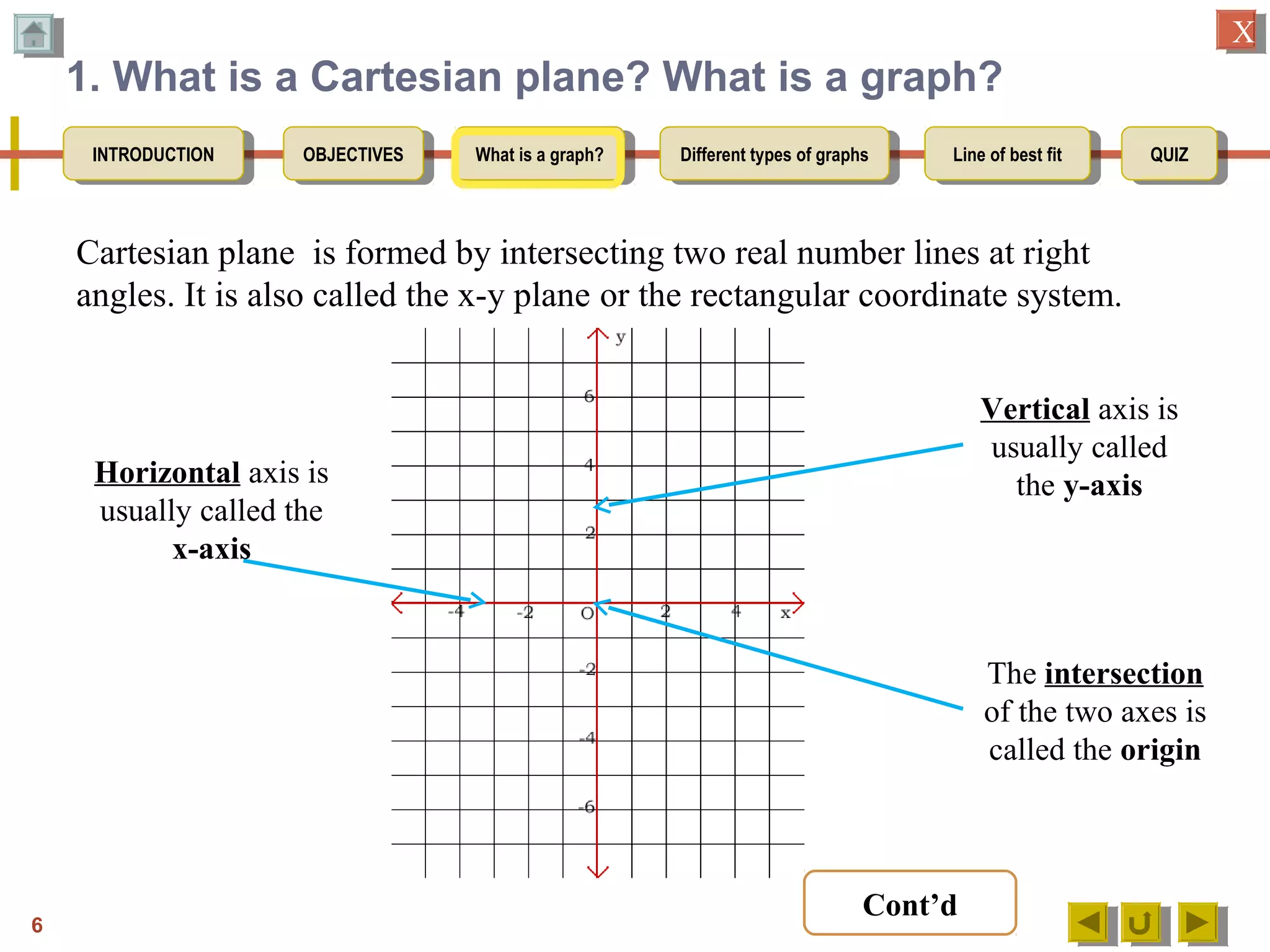
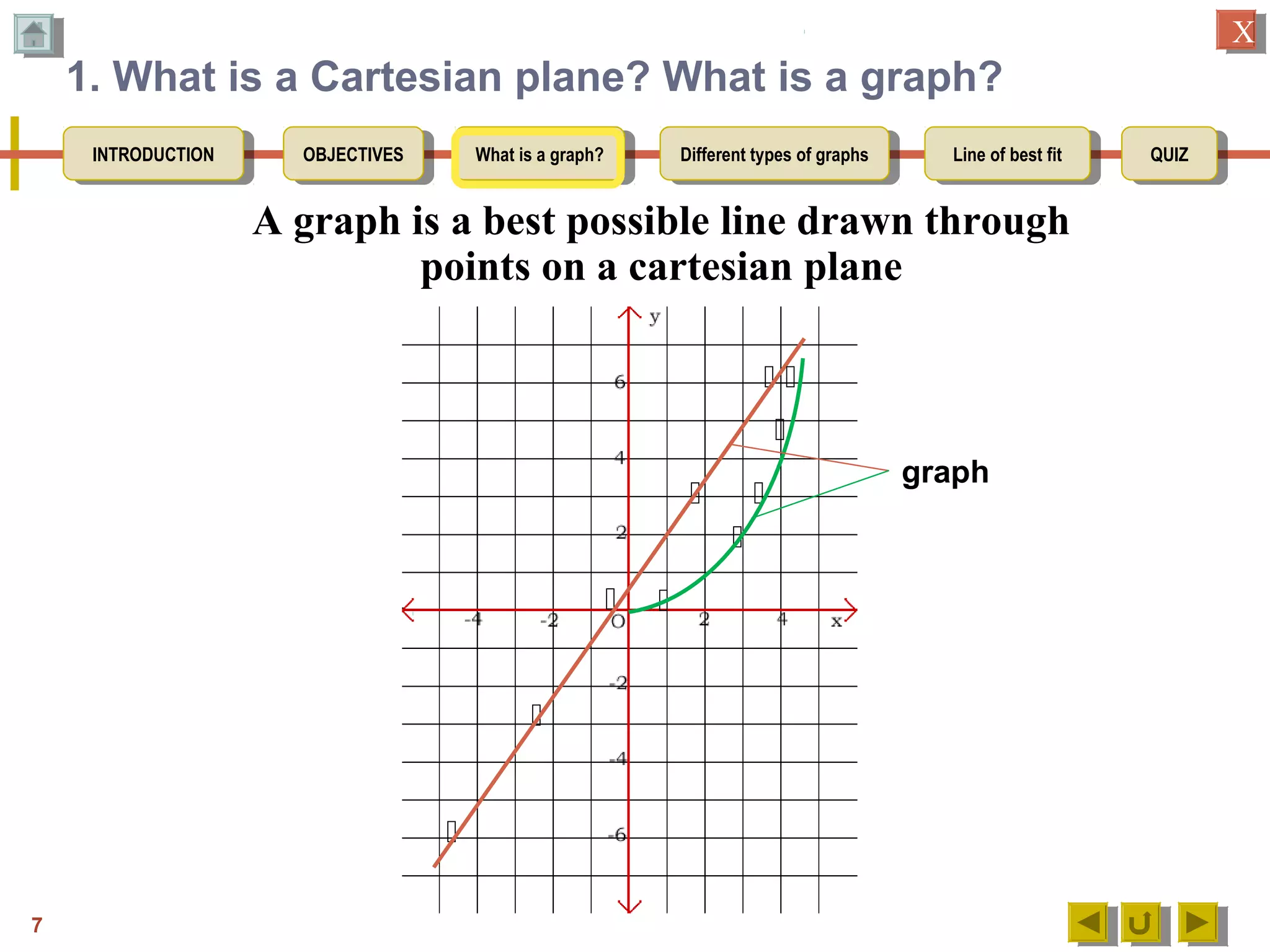
1. Defining a graph as a line drawn through points on a Cartesian plane.
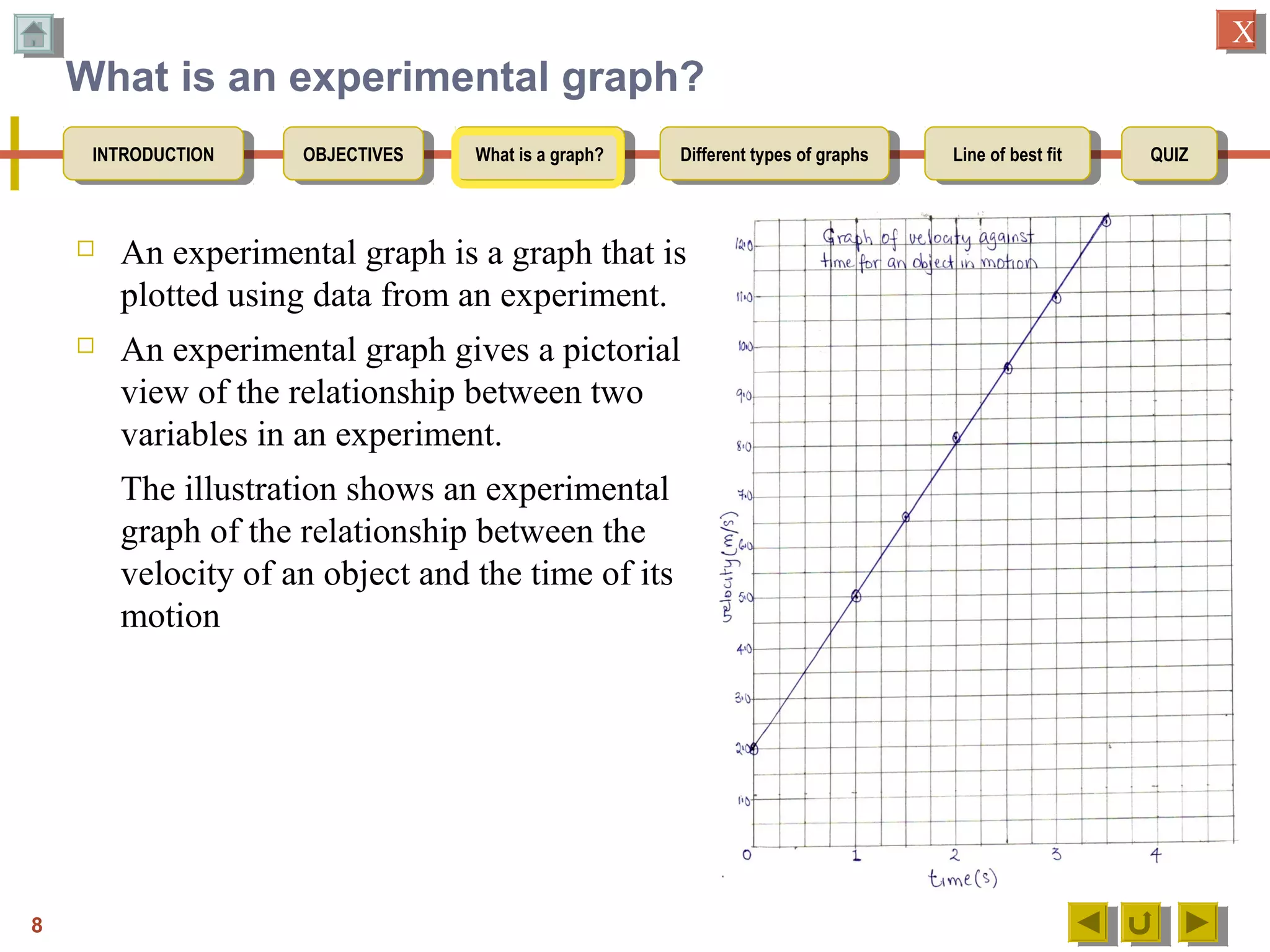
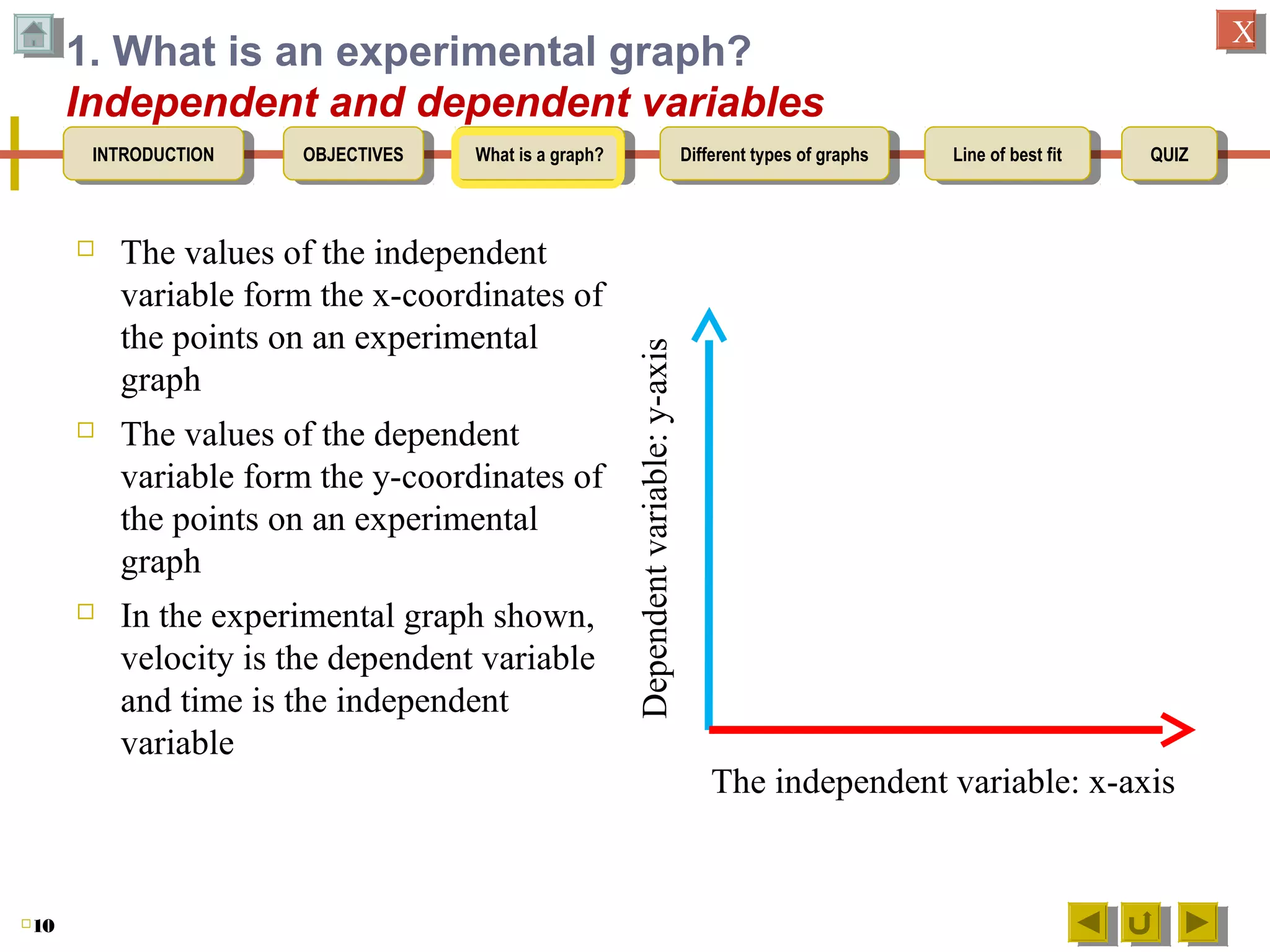
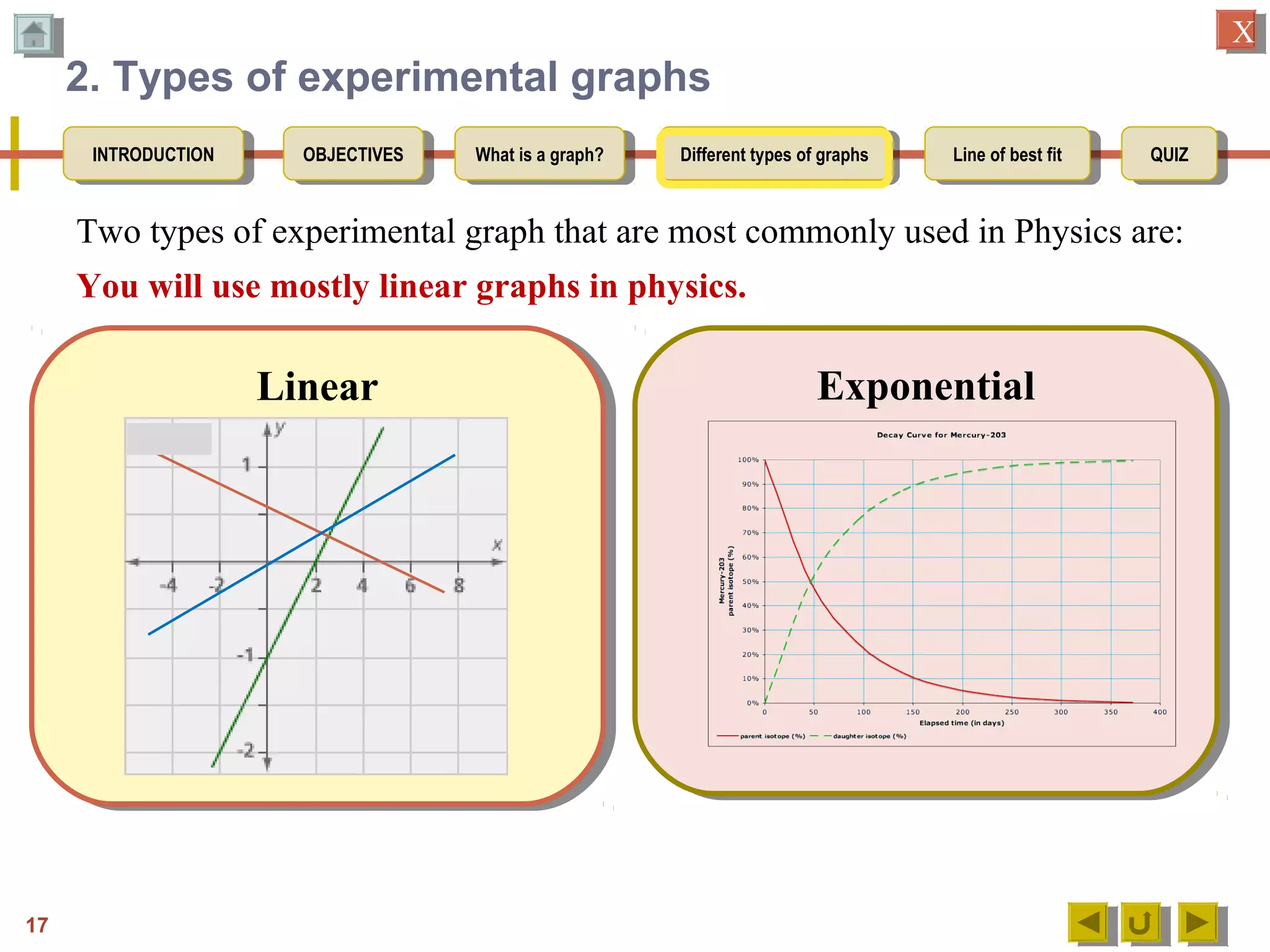
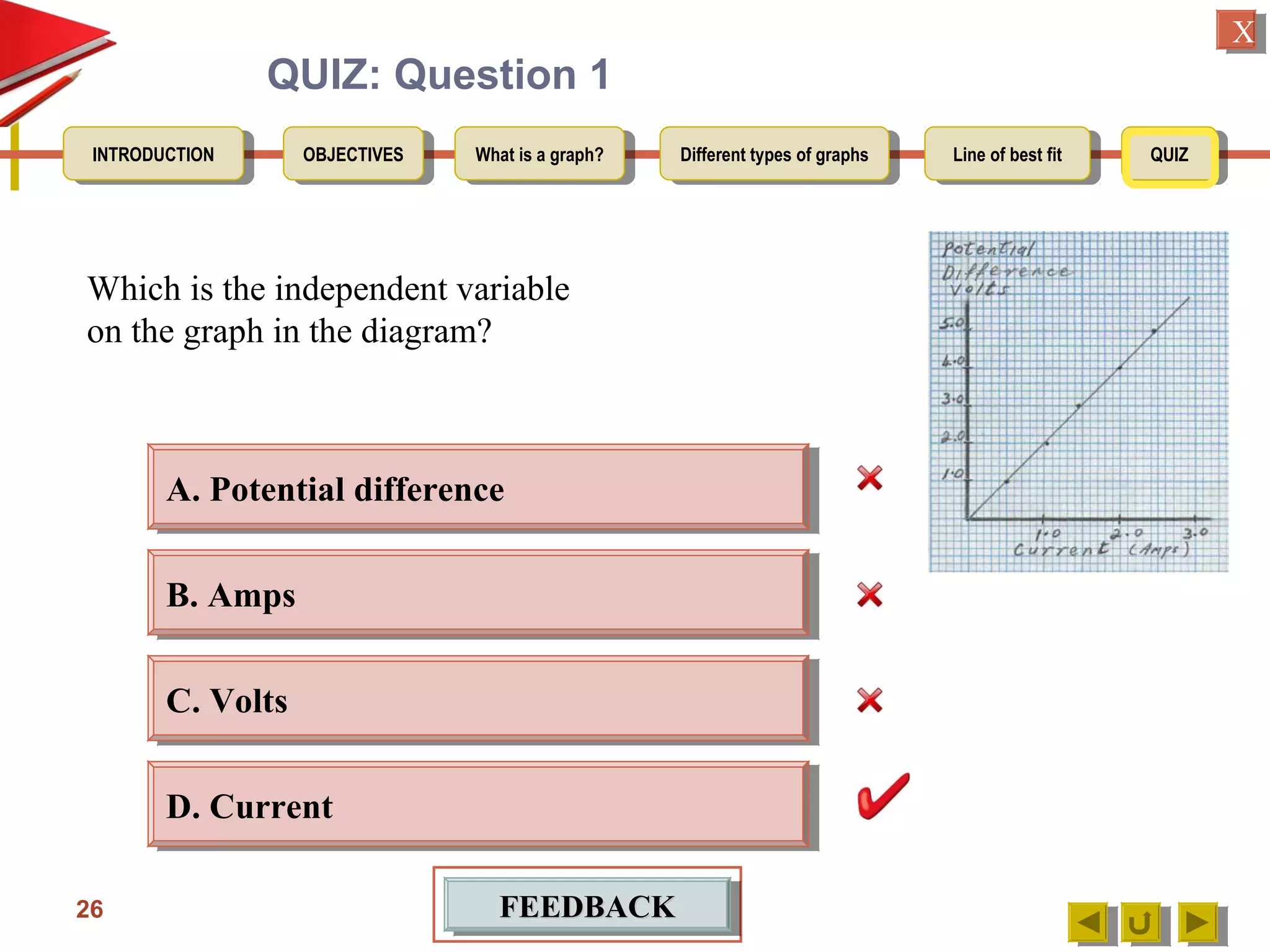
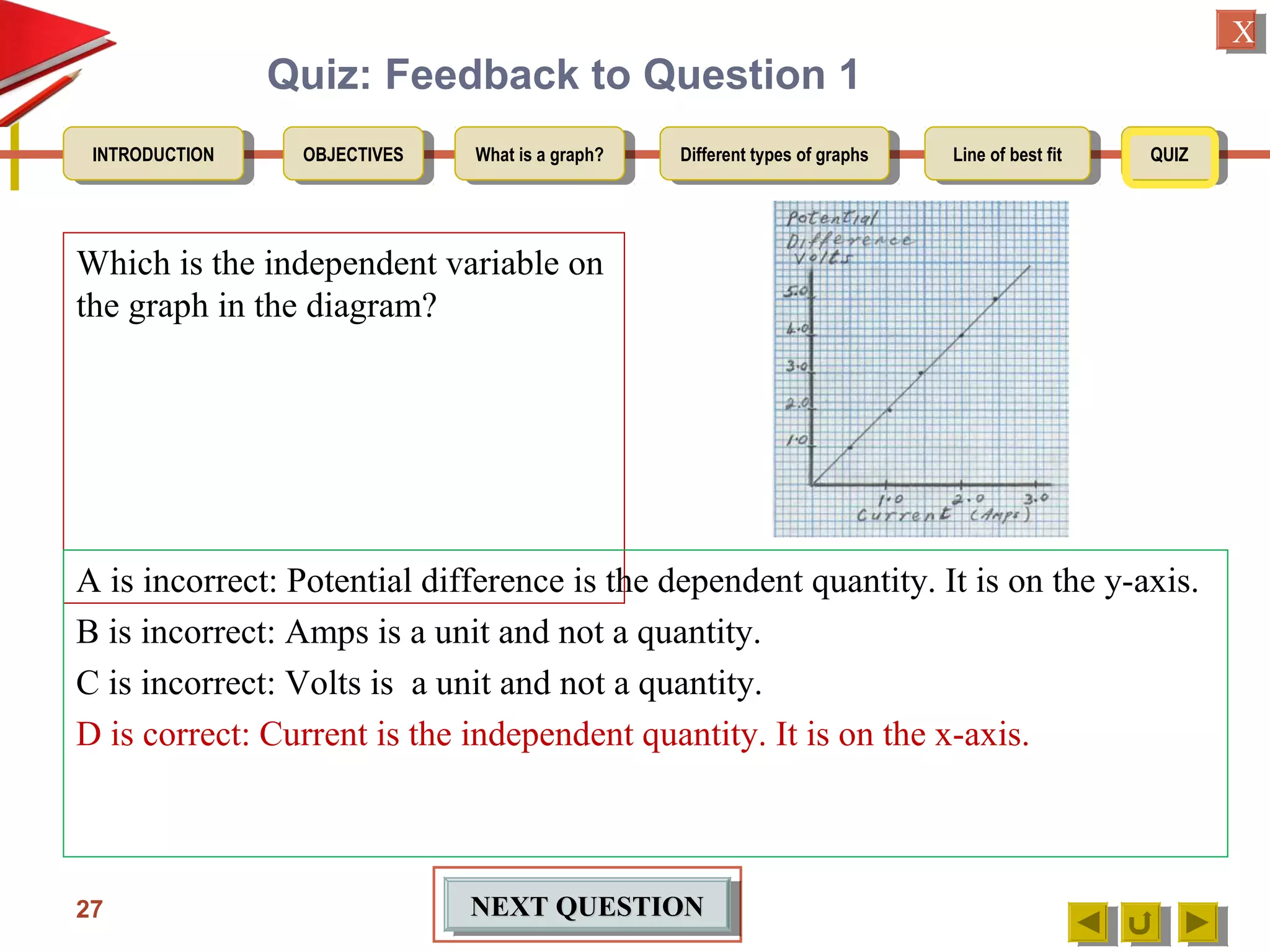
2. Explaining that an experimental graph shows the relationship between an independent and dependent variable from an experiment.
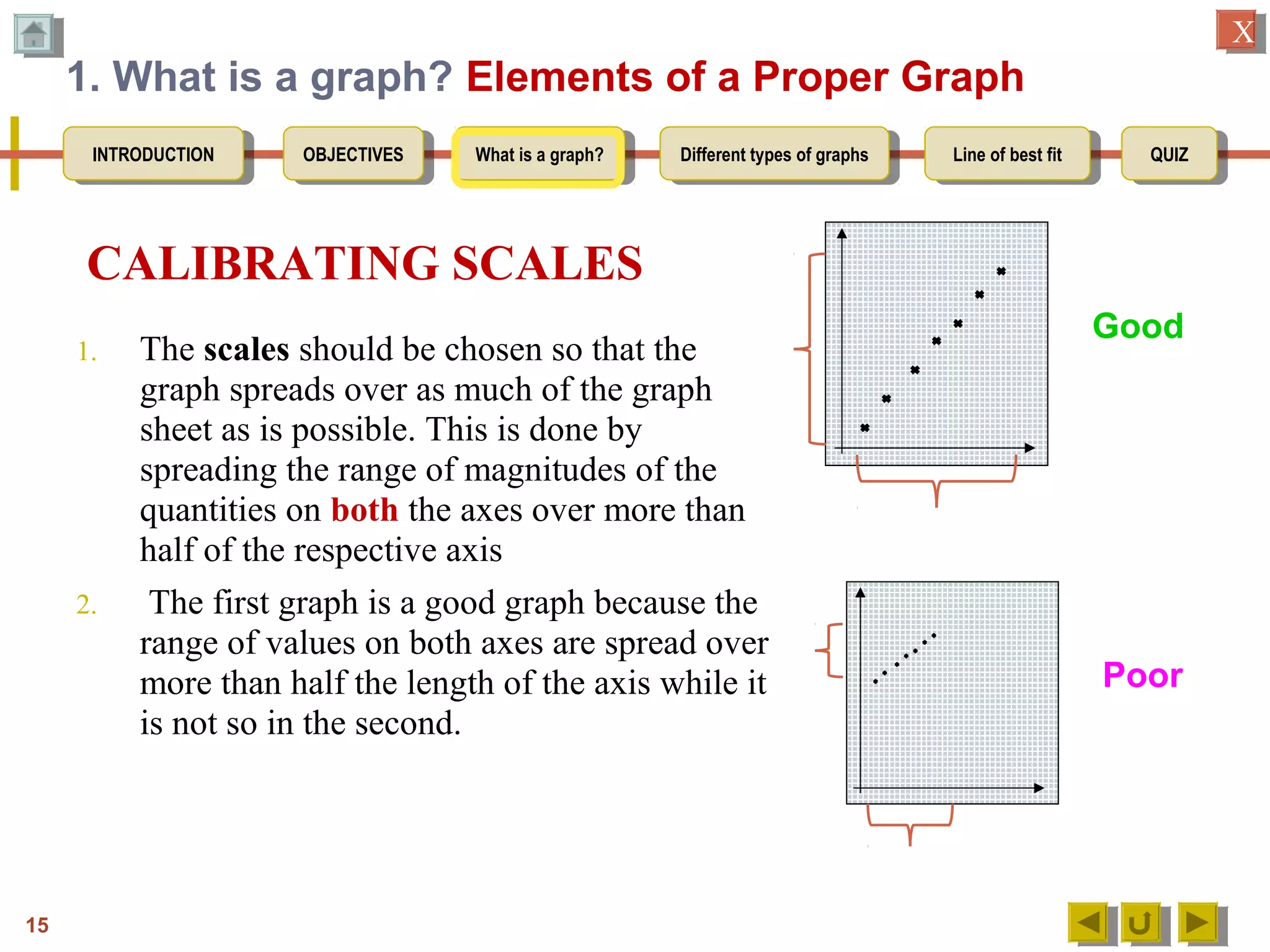
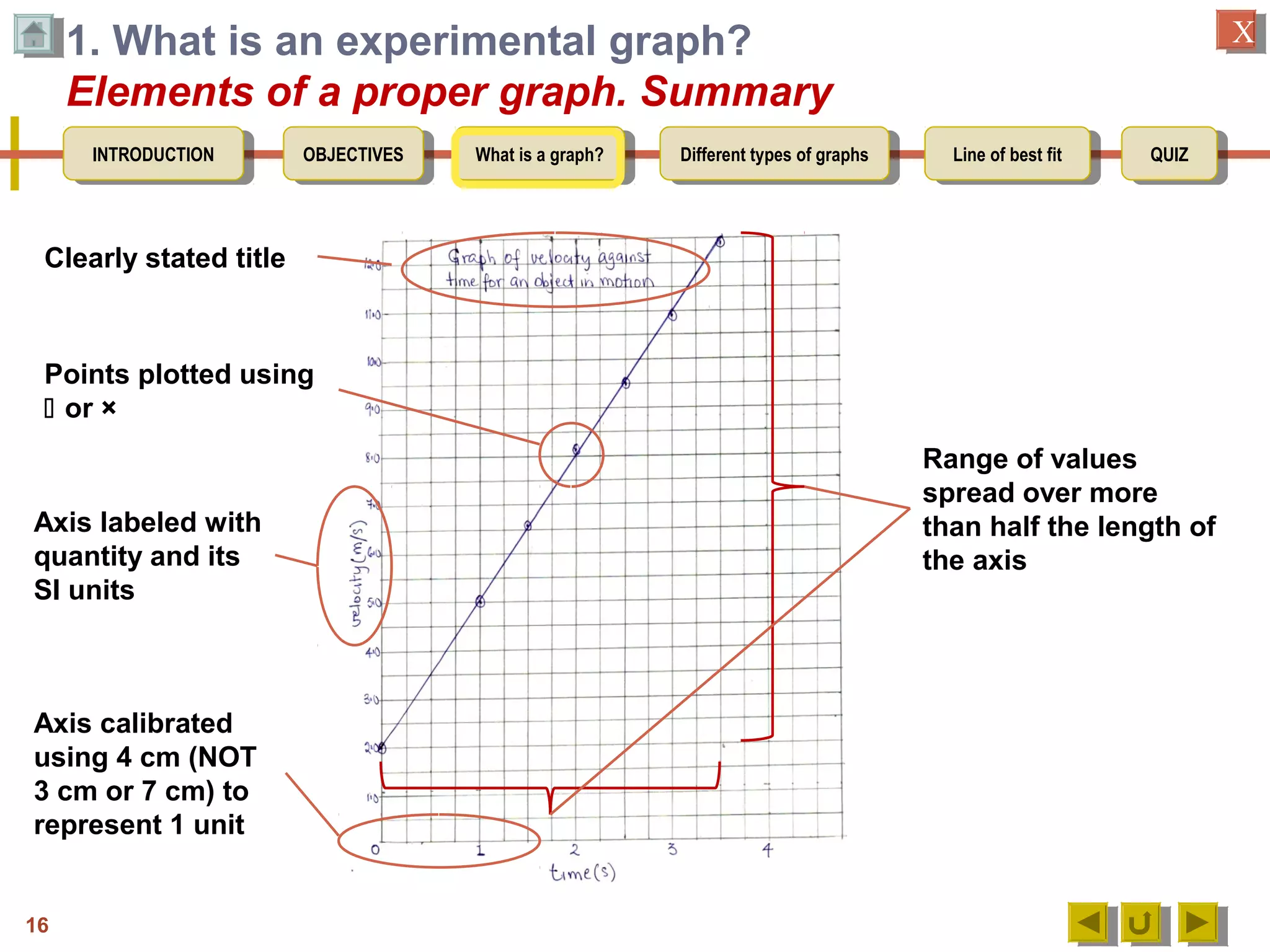
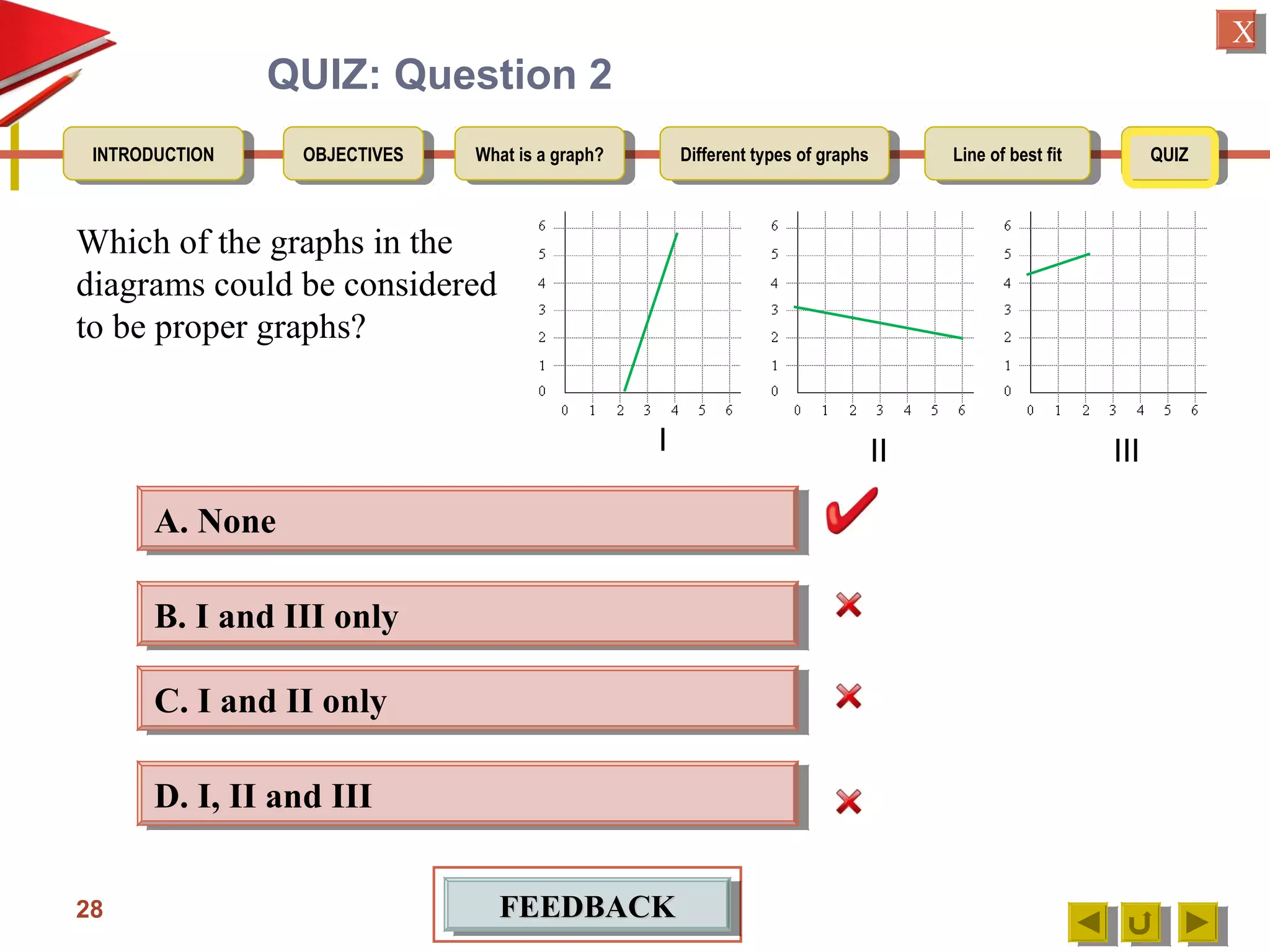
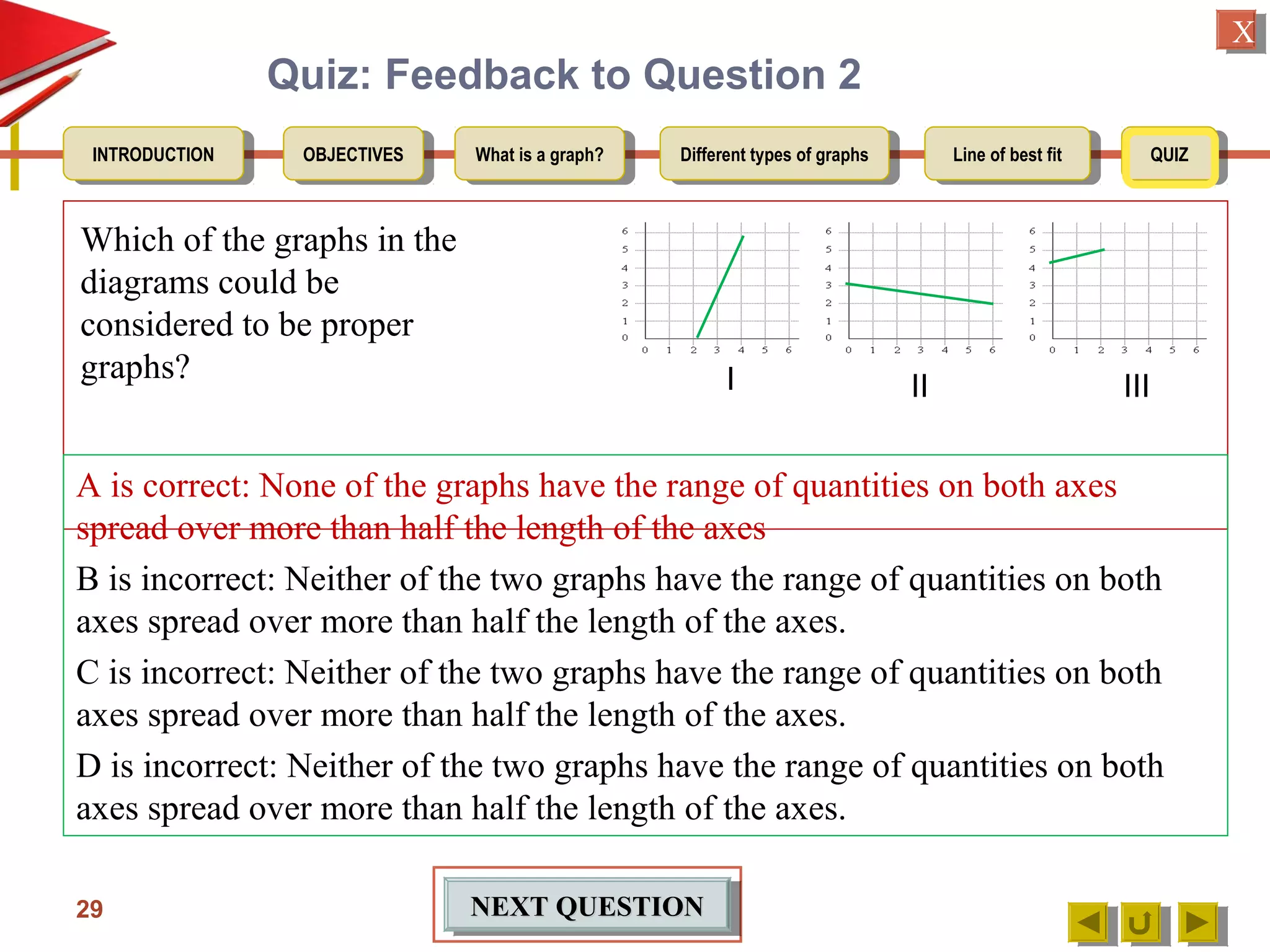
3. Detailing the key elements of a proper graph, including a title, labeled and calibrated axes, and points that take up over half the length of the axes.