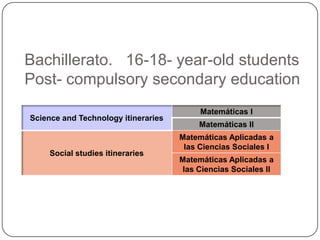
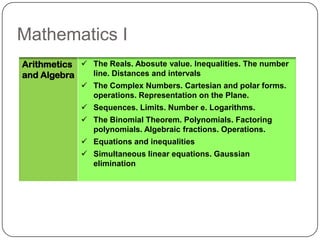
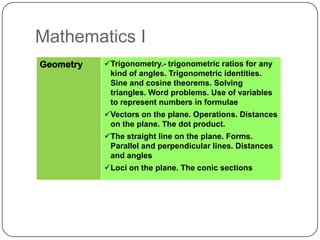
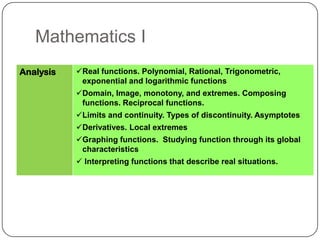
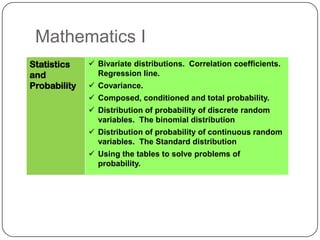
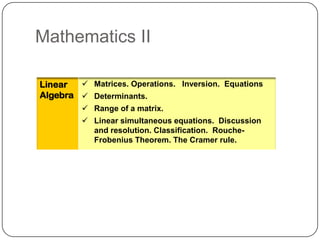
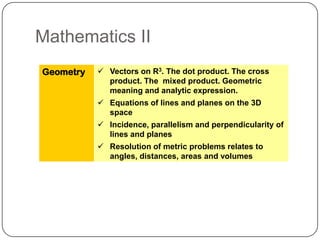
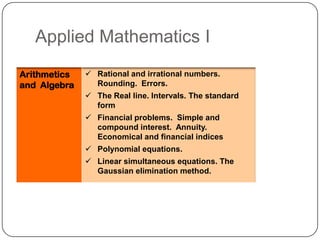
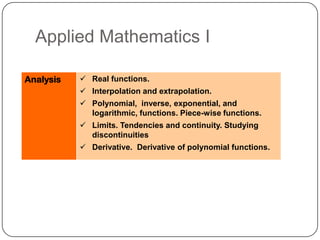
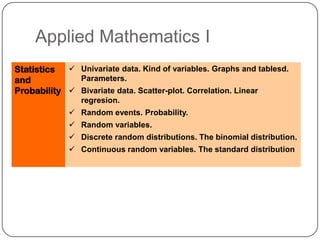
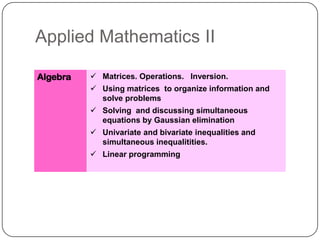
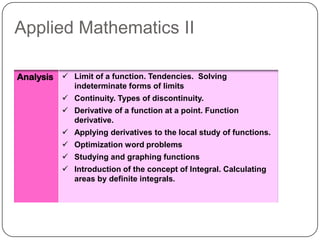
The document describes the mathematics curriculum for 16-18 year old students in Spain. It is divided into 4 sections: Mathematics I, Mathematics II, Applied Mathematics I, and Applied Mathematics II. The courses cover topics such as algebra, geometry, analysis, statistics, probability, matrices, and functions. Students can choose either science and technology or social studies itineraries.