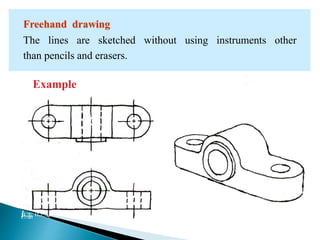
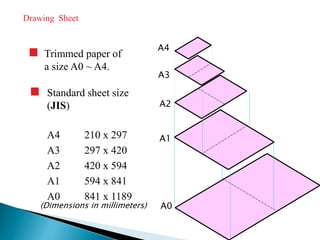
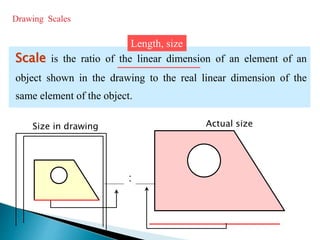
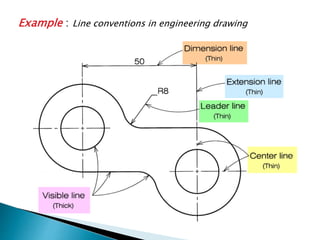
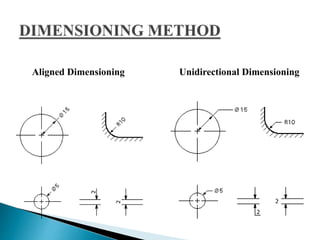
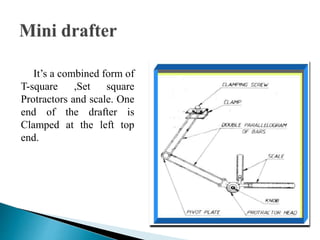
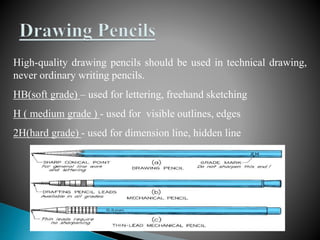
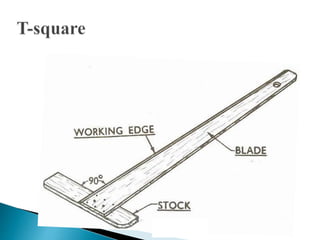
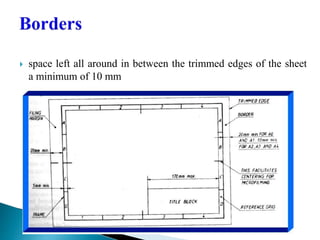
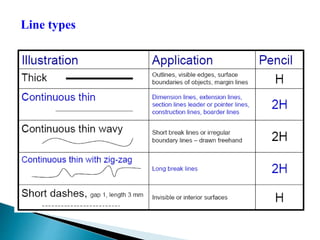
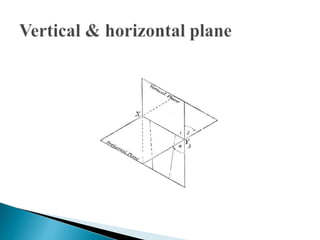
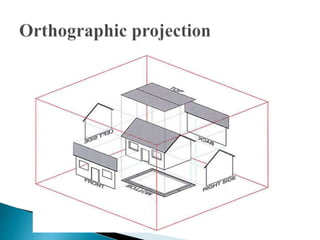
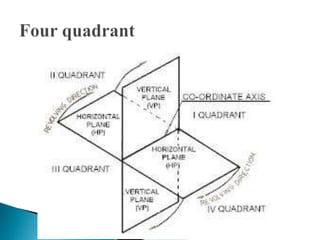
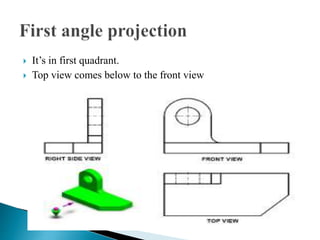
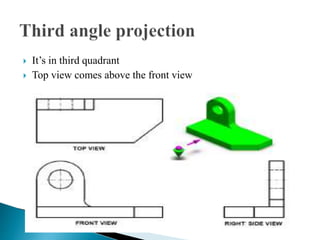
The document is an active learning assignment prepared by 4 students for their Electrical Engineering batch. It provides information on engineering drawing including: the definition of engineering drawing as a way to communicate engineers' ideas through graphical language; types of drawings like freehand and instrument drawings; drawing sheet sizes and scales; line types used in drawings; common drawing equipment; basic geometric shapes; orthographic projections; and engineering curves. Standard formatting of drawings is also discussed.