Embed presentation
Downloaded 43 times


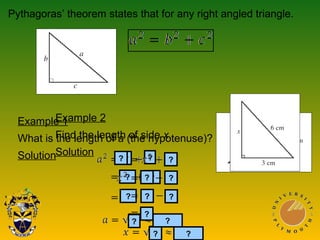

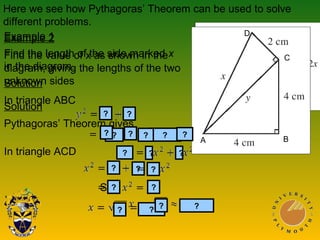

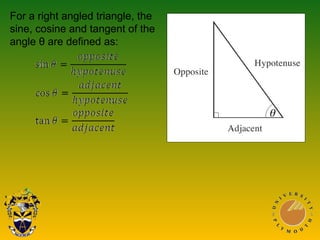
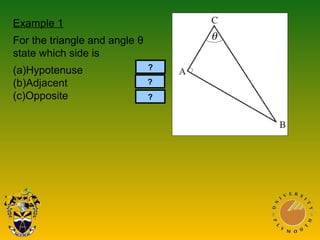
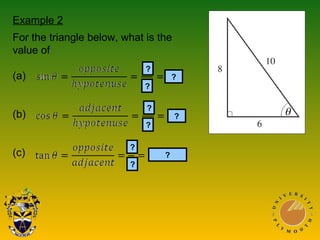

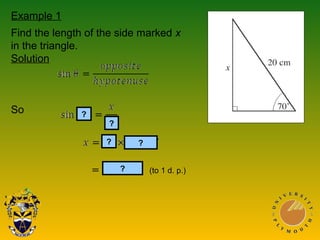
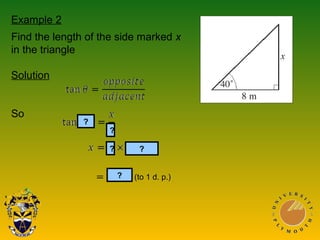
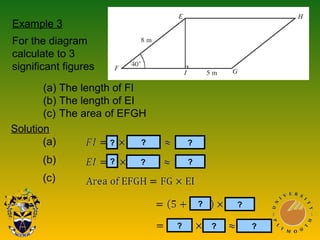

The document covers Pythagoras' theorem and trigonometric ratios, detailing methods to find side lengths in right-angled triangles. It includes various examples for understanding and applying the theorem, as well as definitions for sine, cosine, and tangent ratios. The content is structured across multiple presentations, providing step-by-step solutions to the problems.












