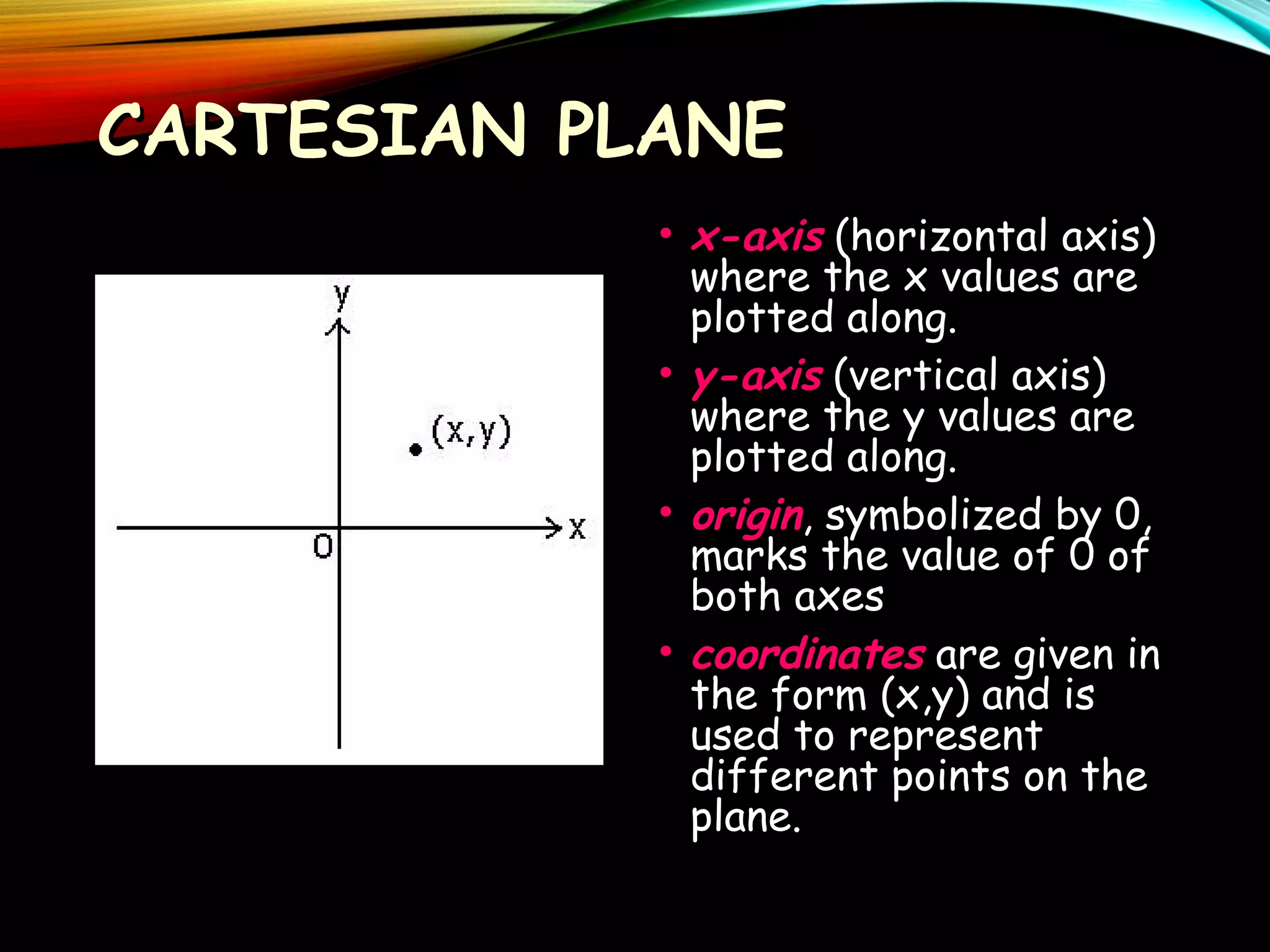
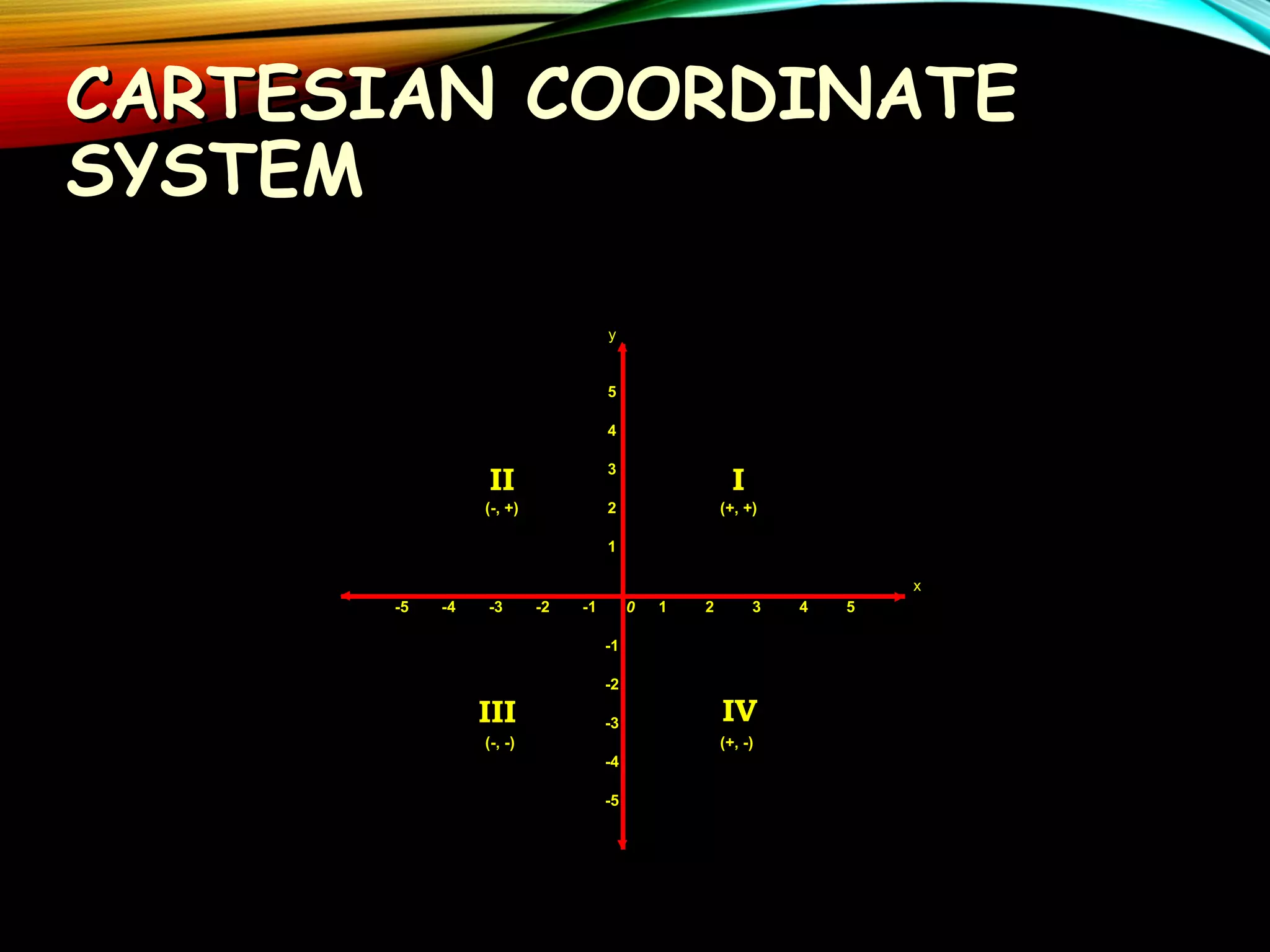
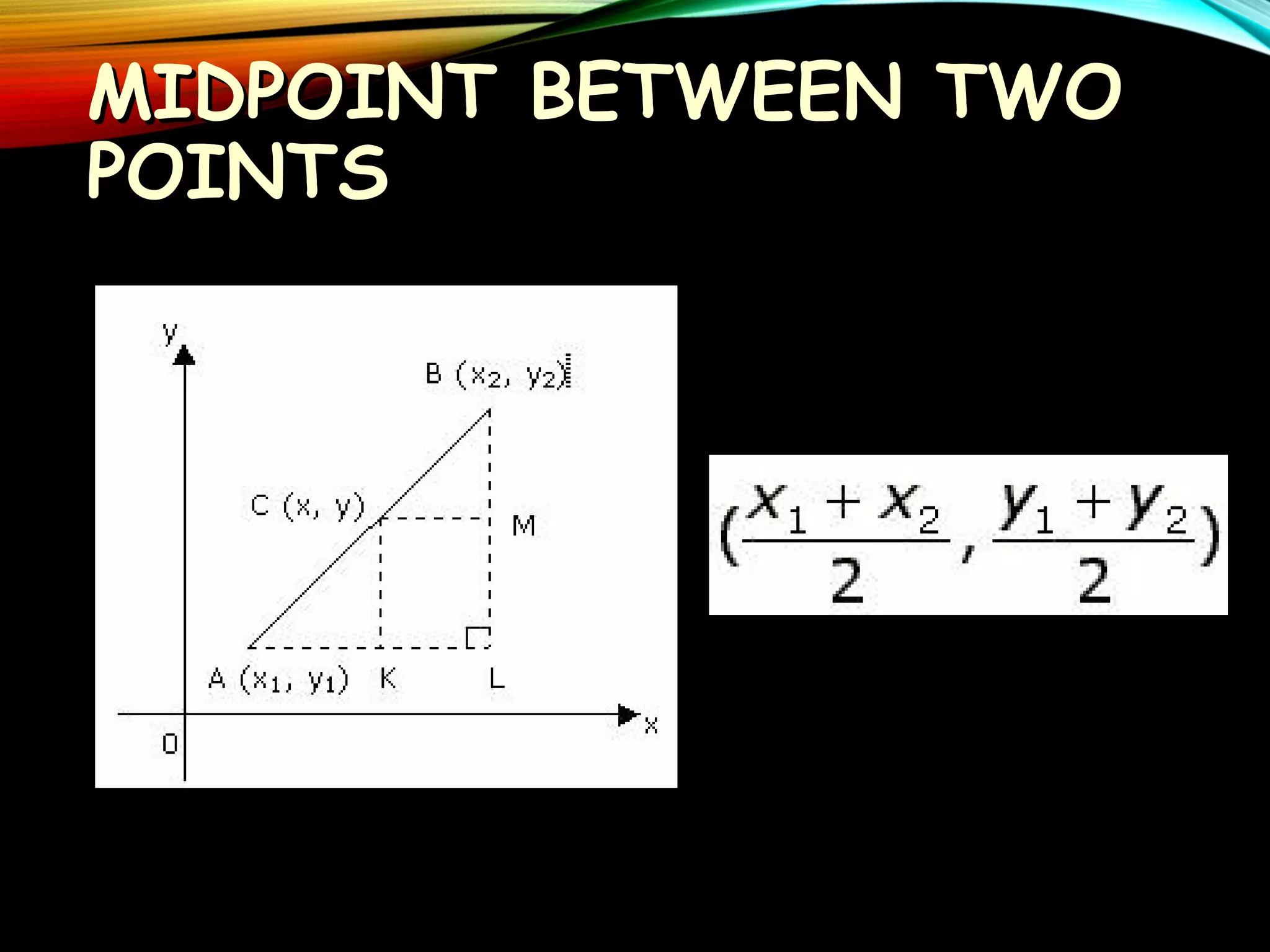
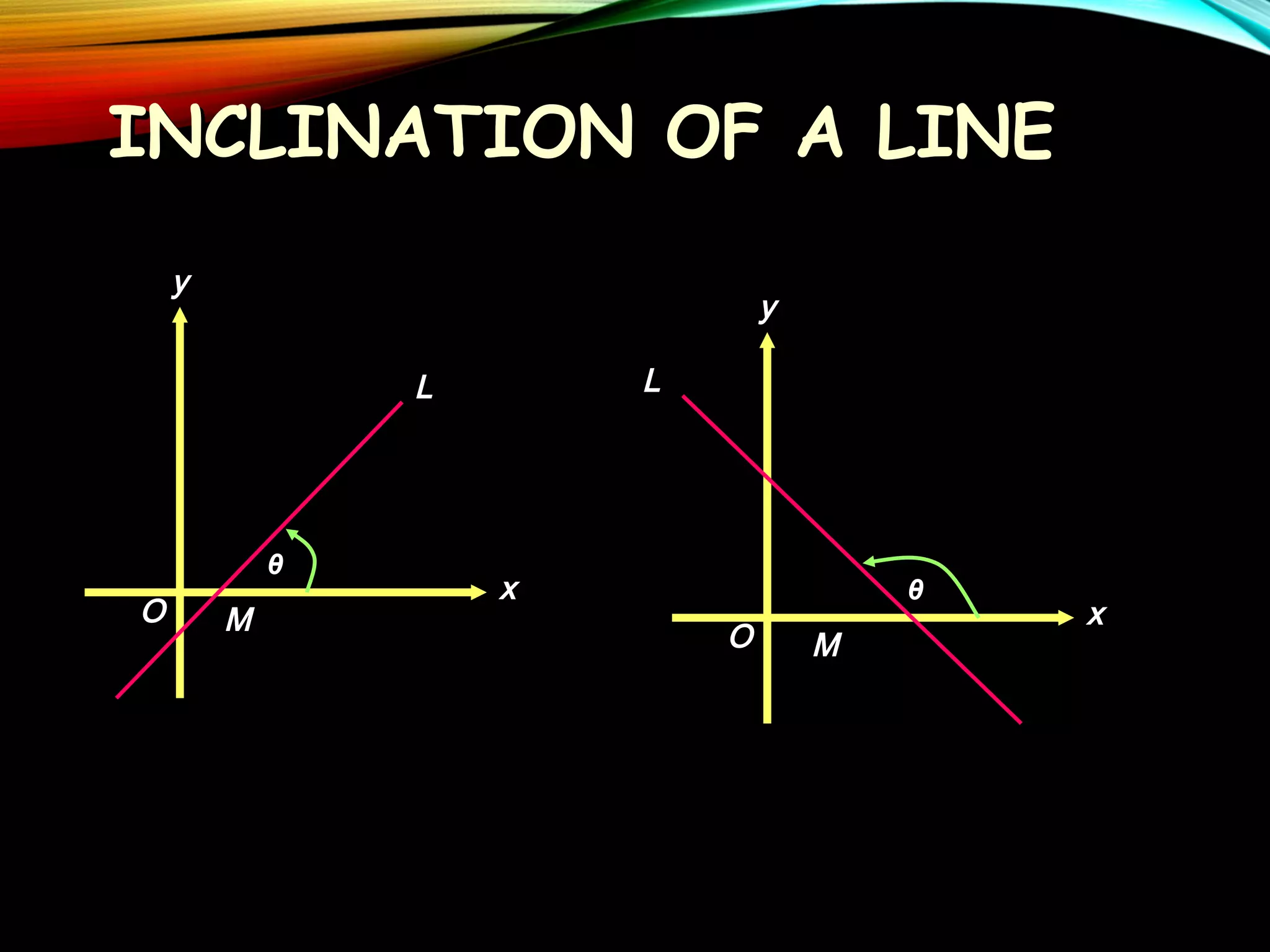
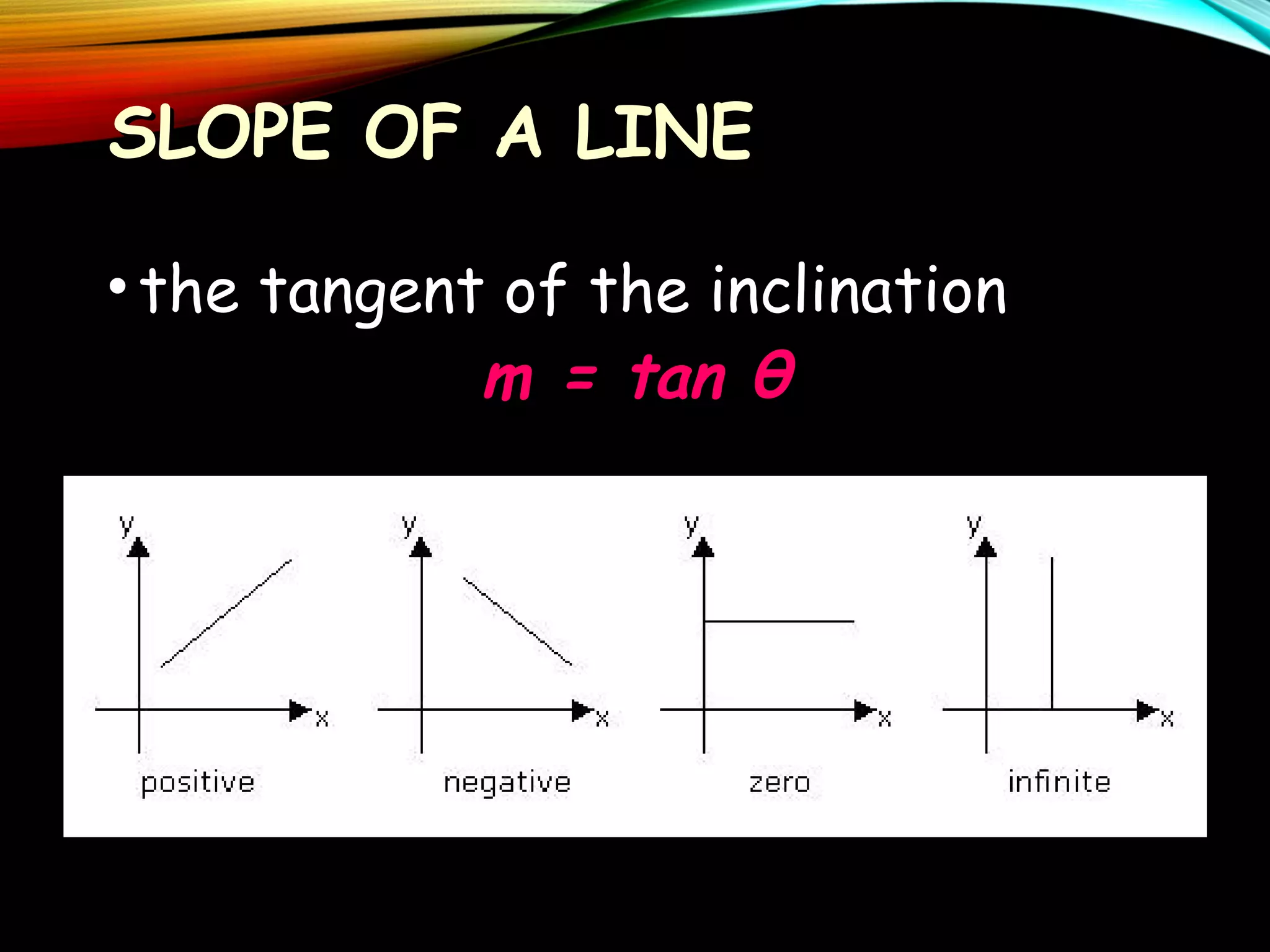
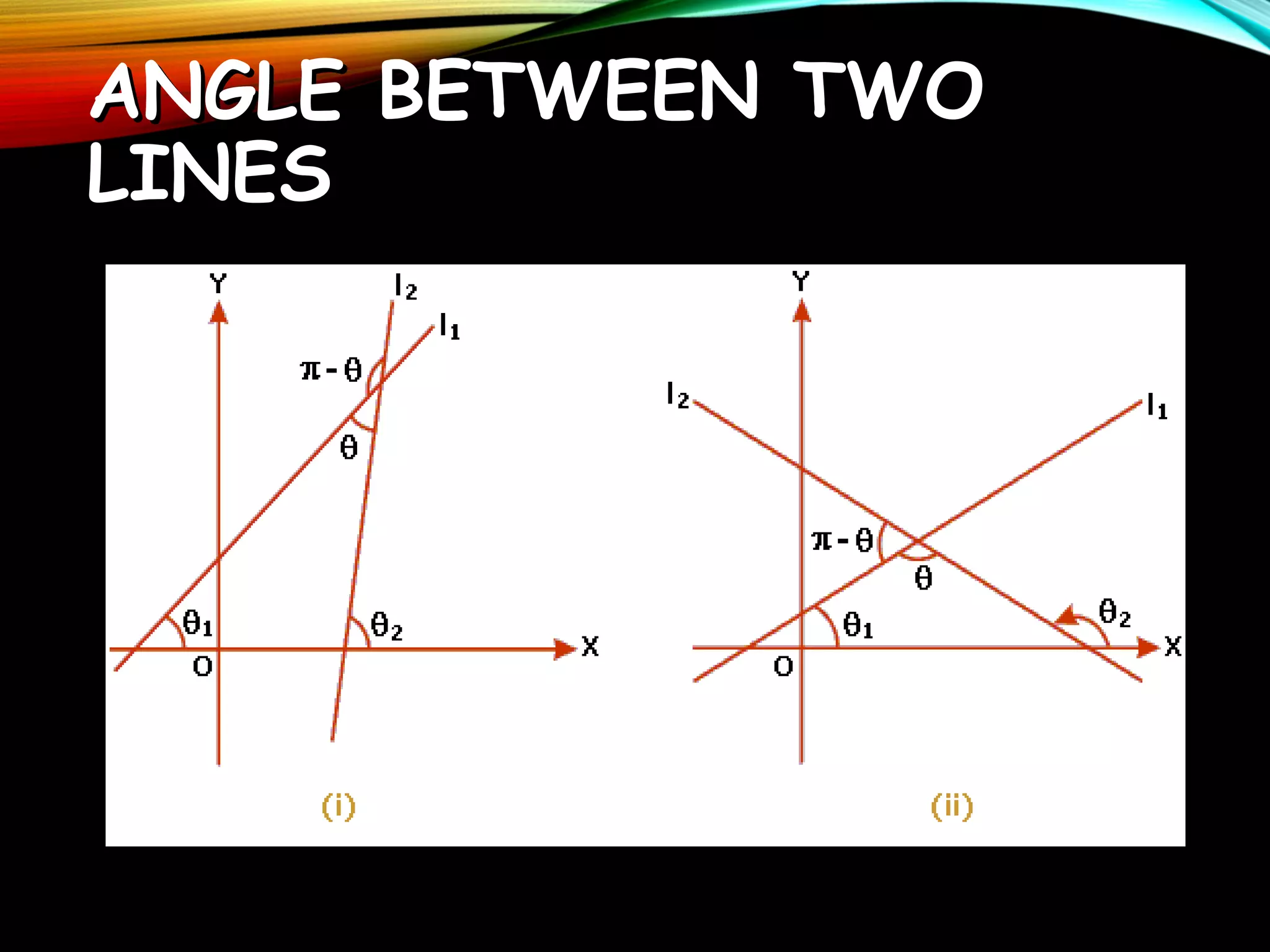
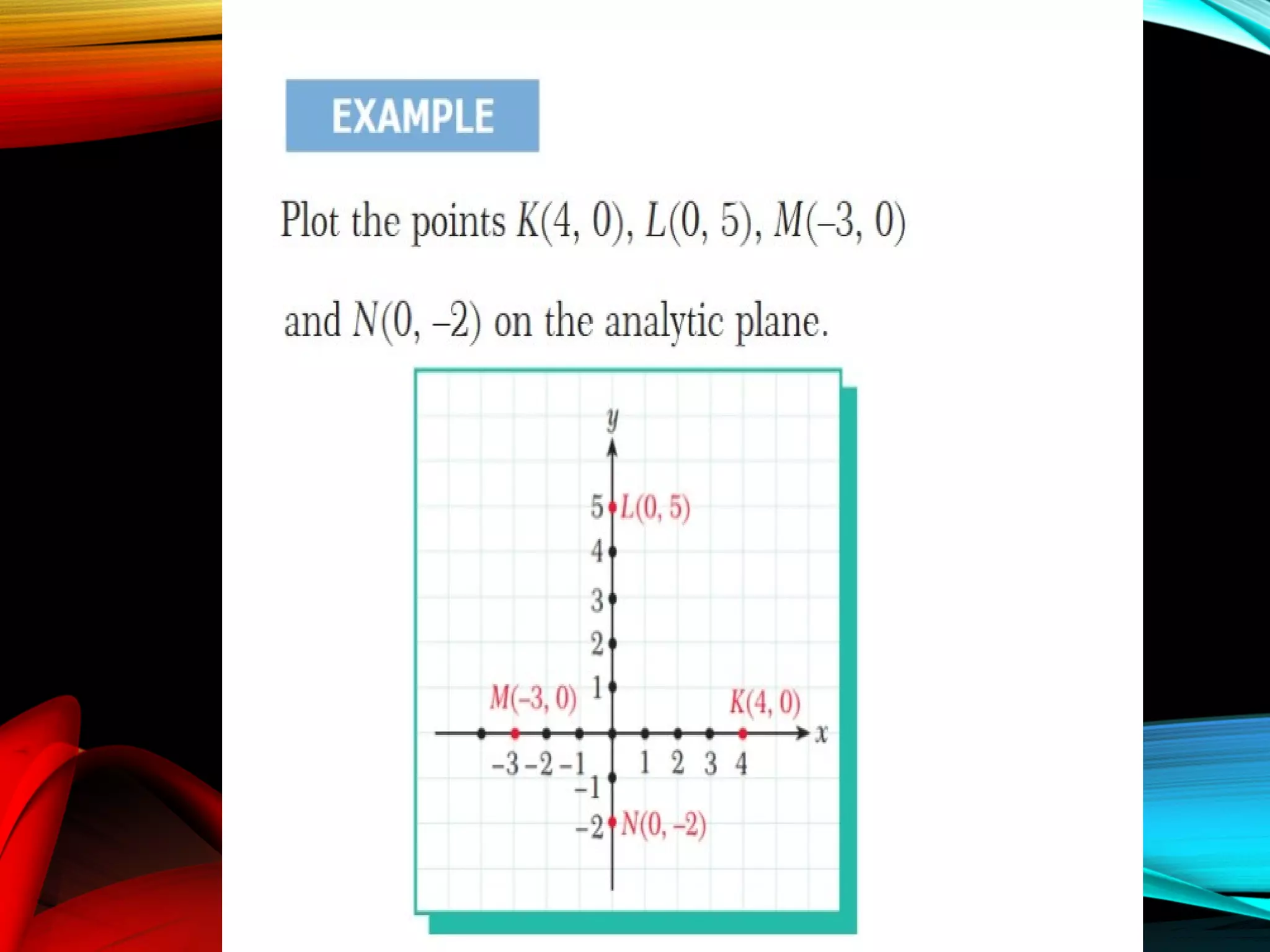
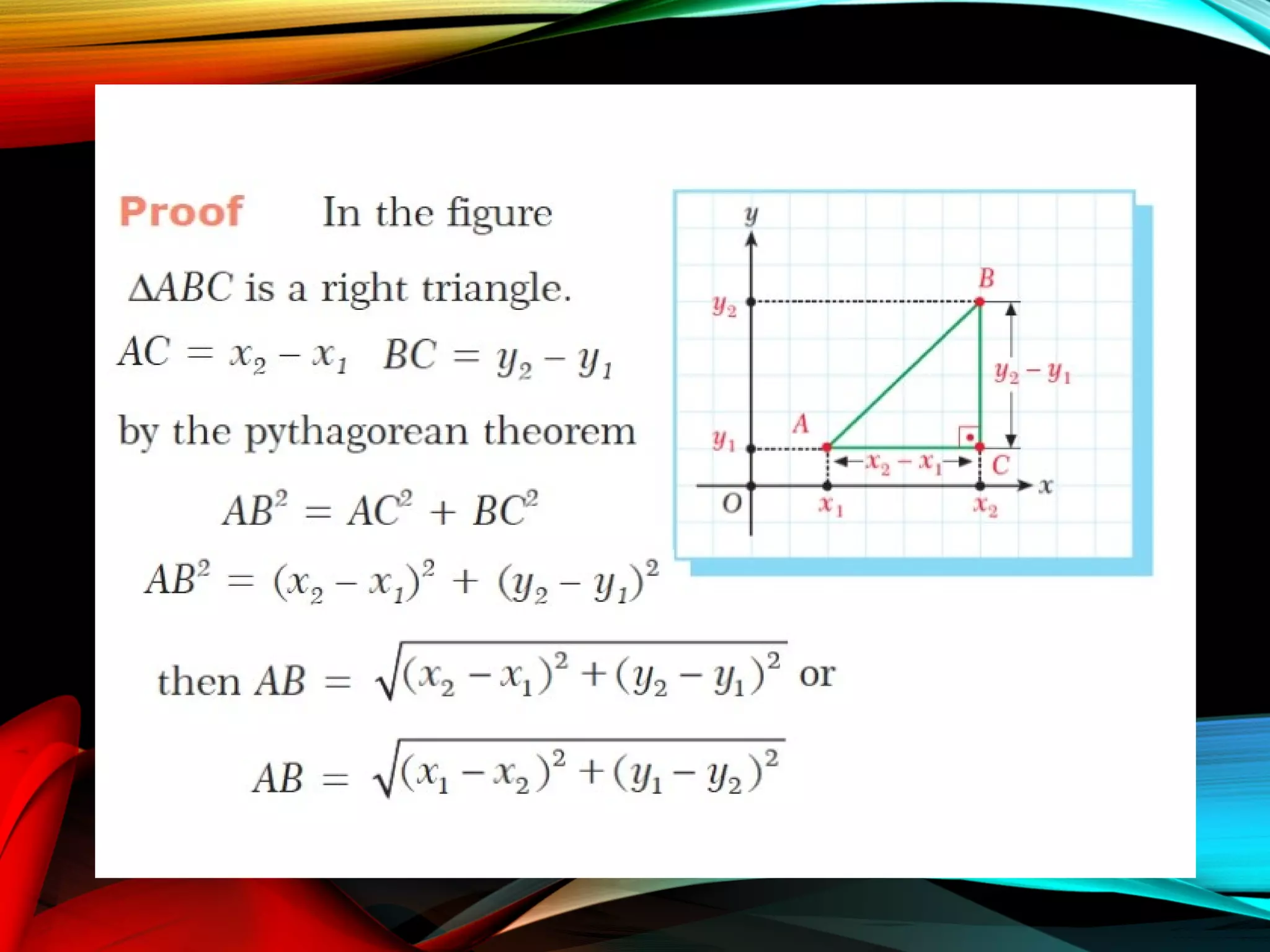
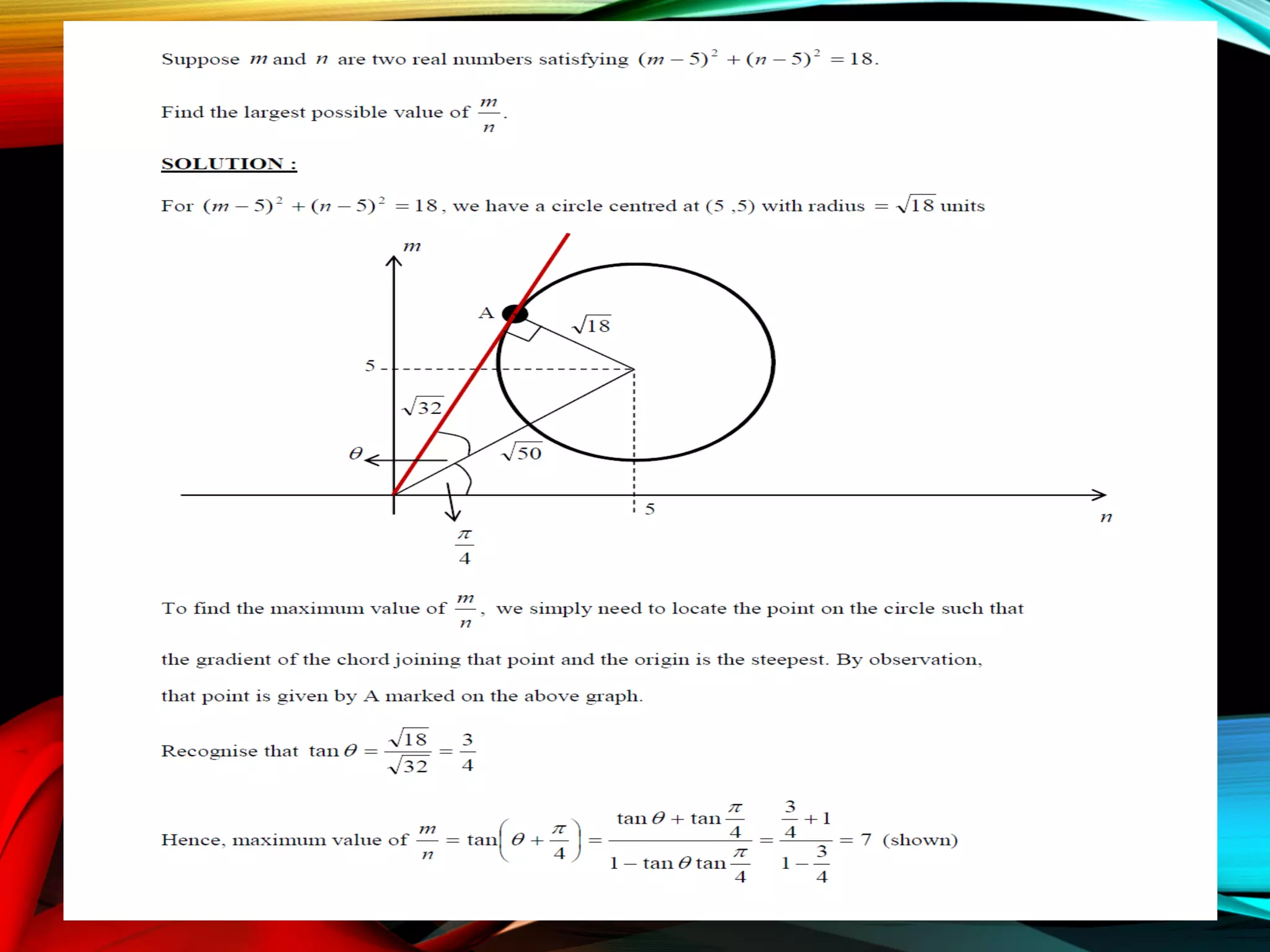
This document provides an overview of analytic geometry in 3 paragraphs or less. It introduces analytic geometry as a branch of mathematics that uses algebraic equations to describe geometric figures on a coordinate system. It was developed in the 1630s by Descartes and Fermat and allowed geometry and algebra to be linked by describing geometric concepts like points and lines with real numbers and equations. The key concept is using a coordinate system to assign unique real number coordinates to each point, allowing geometric shapes to be represented by algebraic equations.