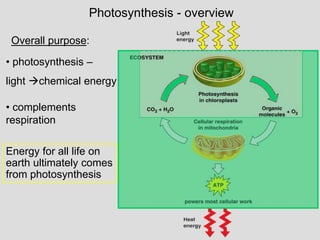
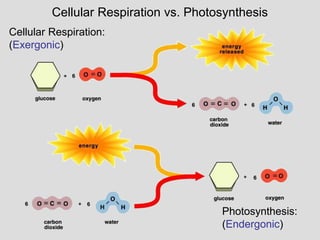
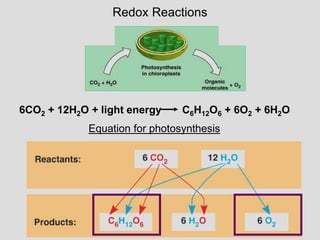
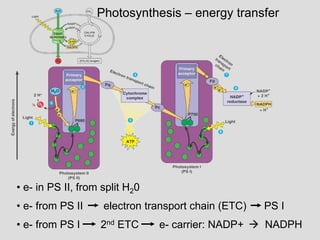
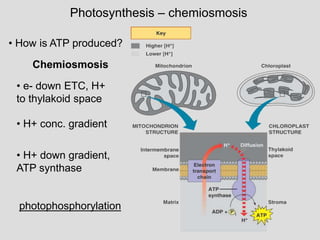
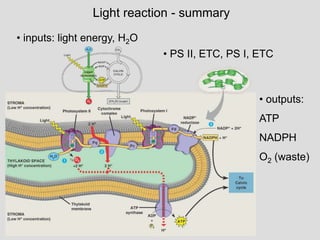
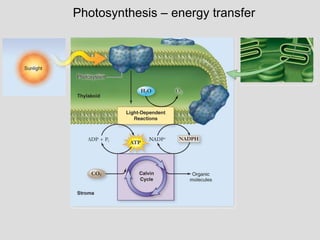
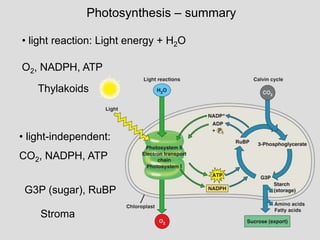
Photosynthesis uses light energy, carbon dioxide, and water to produce oxygen and energy-rich organic compounds like glucose. It occurs in two stages - the light-dependent reactions where light energy is captured to make ATP and NADPH, and the light-independent reactions where CO2 is incorporated into organic compounds through the Calvin cycle. Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll and other pigments that absorb light for use in the photosystems. The energy from light drives electron transport and chemiosmosis to produce ATP, then electrons are transferred to NADP+ to form NADPH. These products fuel the Calvin cycle to reduce CO2 into glucose using the energy from ATP and NADPH.



![Photosynthesis - overview
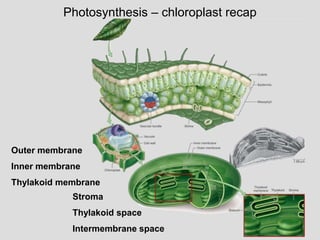
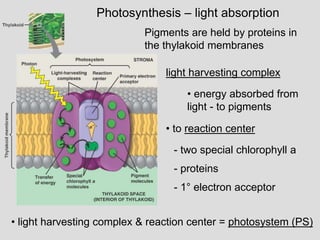
– thylakoid membrane
– thylakoid space
– stroma
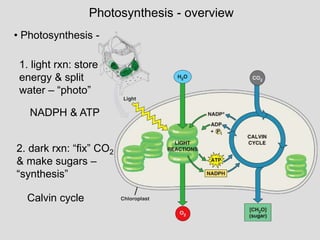
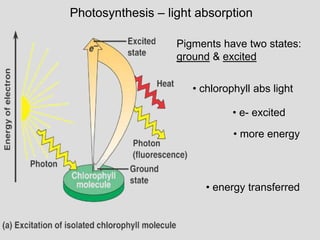
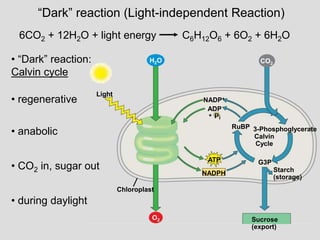
• light reactions: • dark reactions:
Light
H2O
Chloroplast
Light
Reactions
NADP+
P
ADP
+
ATP
NADPH
O2
Calvin
Cycle
CO2
[CH2O]
(sugar)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/photosynthesis-1-130808054515-phpapp01/85/Photosynthesis-1-9-320.jpg)
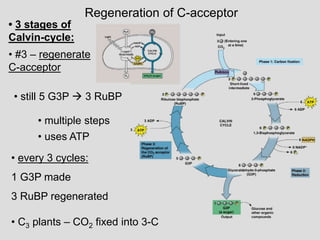
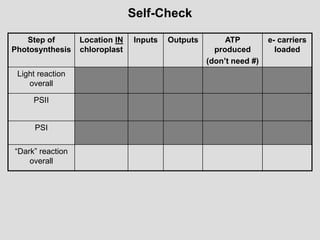
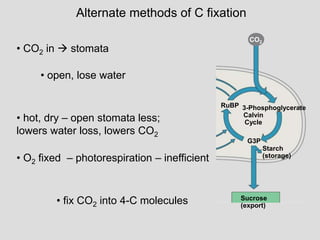

![Lecture 3 Summary
1. Photosynthesis Overview (Ch. 8)
- Purpose
- Redox reactions
- Electron carriers & sugars
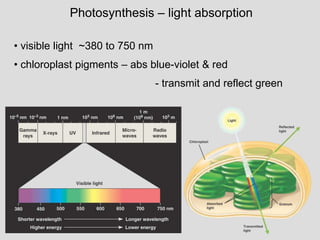
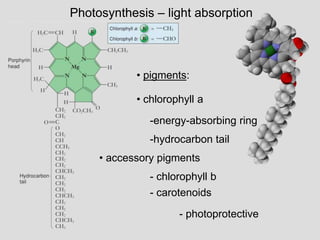
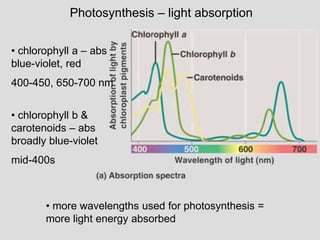
2. Light (Ch. 8)
- Absorption pigments
- Light spectra/wavelengths
3. Locations of steps, inputs/outputs, purpose, description (Ch. 8)
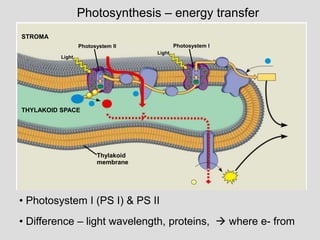
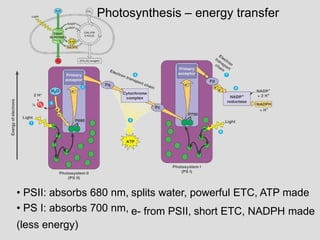
- PSI vs. PS II
- Whole light reaction [includes chemiosmosis]
- “dark” reaction/Calvin cycle [3 steps]
4. Alternate modes of photosynthesis (Ch. 8)
5. Photosynthesis context (Ch. 8)
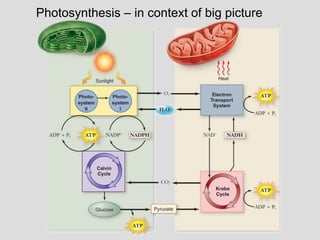
- Uses for products
- Relationship of cell respiration and photosynthesis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/photosynthesis-1-130808054515-phpapp01/85/Photosynthesis-1-32-320.jpg)