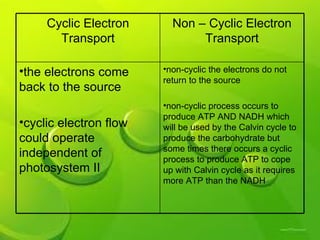
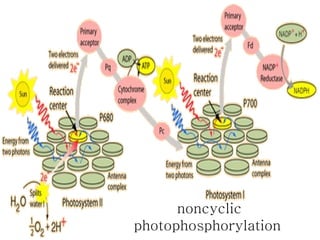
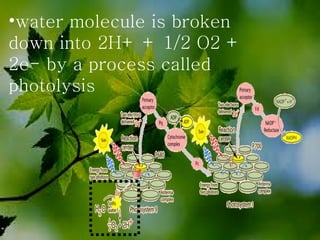
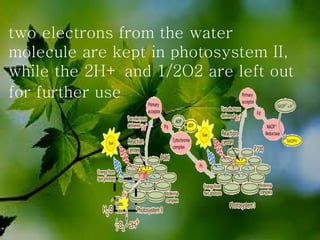
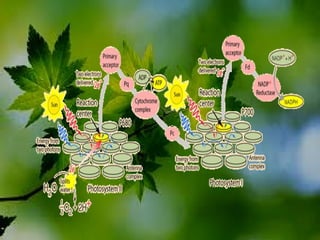
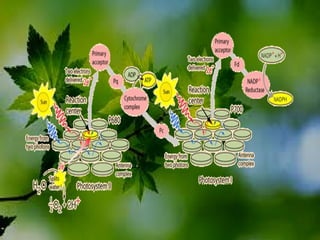
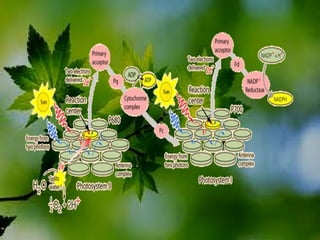
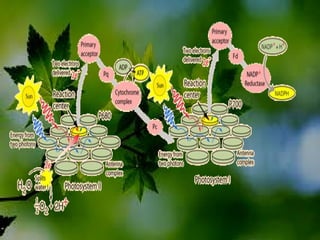
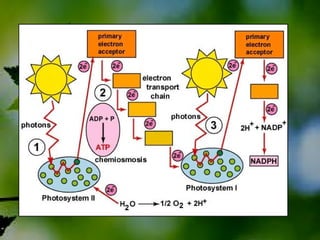
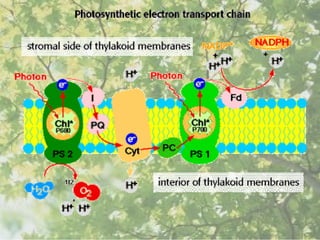
The document discusses the processes of non-cyclic and cyclic electron transport in photosynthesis, highlighting their roles in producing ATP and NADPH for the Calvin cycle. It explains the involvement of photosystems I and II, electron carriers, and the significance of photophosphorylation in energy conversion. Additionally, it notes how conditions in the chloroplast can lead to a shift from non-cyclic to cyclic electron flow when there's a deficit of ATP.