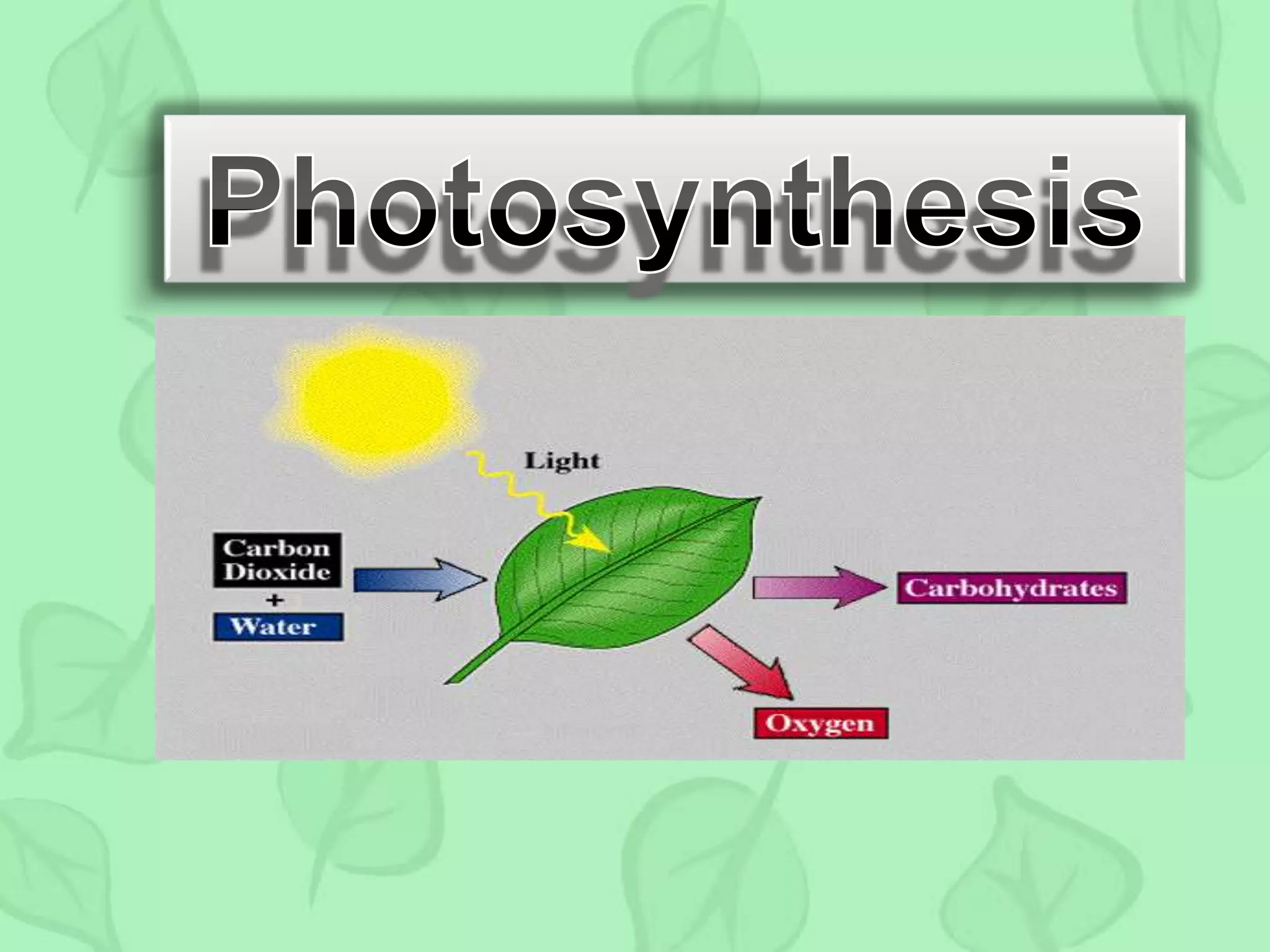
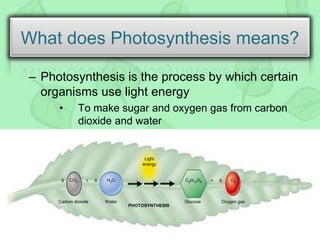
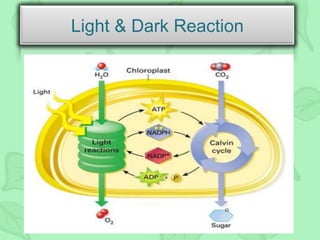
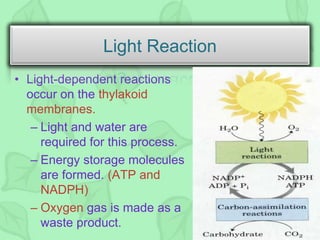
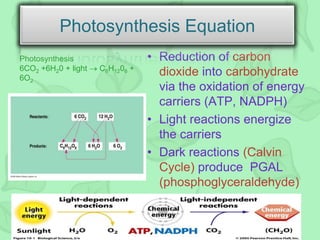
The document outlines the history and process of photosynthesis, detailing contributions from early scientists like Van Helmont, Priestley, and Ingenhousz. It explains that photosynthesis occurs in chloroplasts, involving light-dependent reactions in the grana and dark reactions in the stroma, ultimately converting carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. Photosynthesis primarily serves to synthesize glucose and is crucial for reintroducing carbon into the biosphere and producing oxygen.