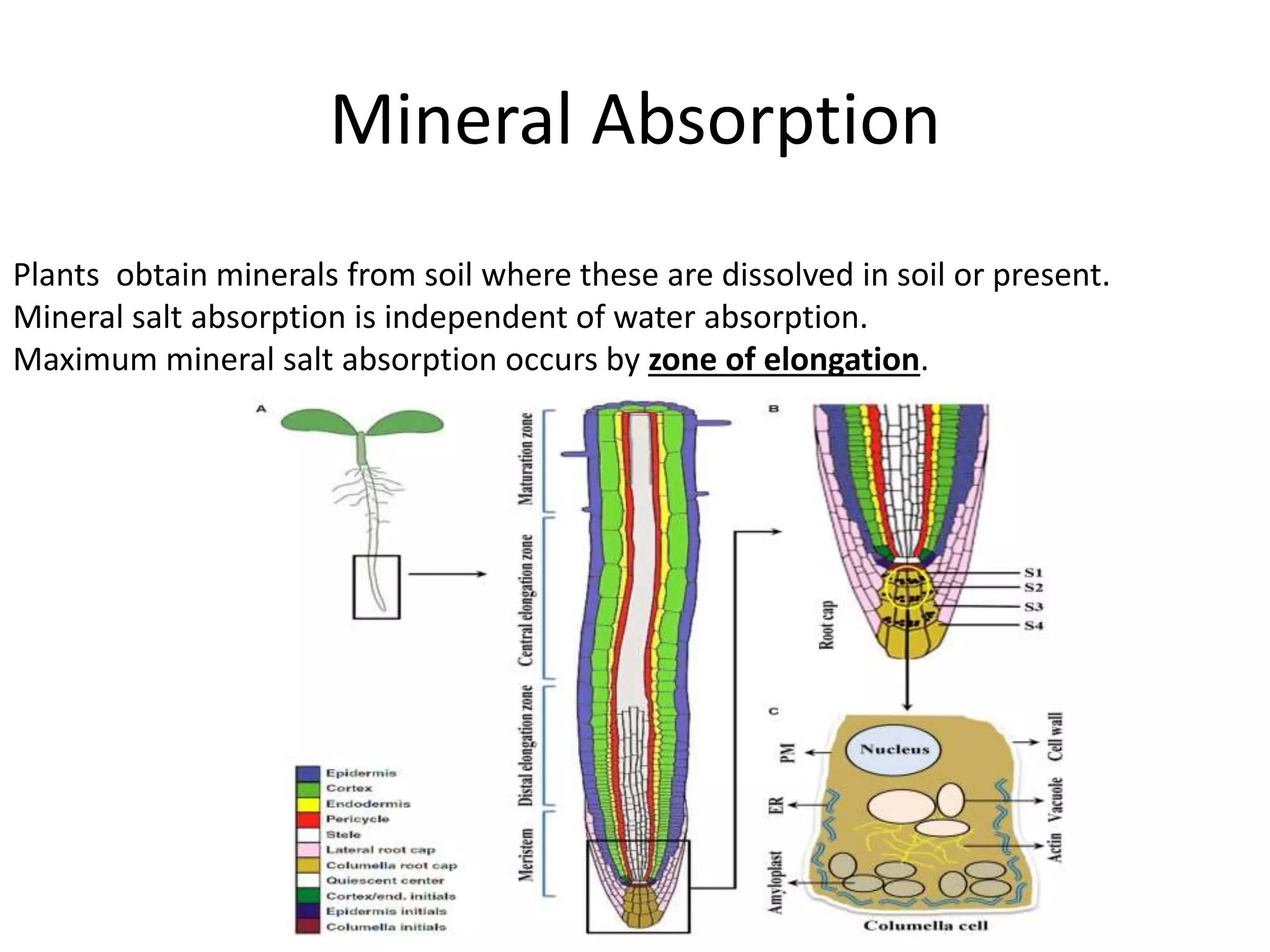
Plants absorb minerals from the soil in both passive and active transport mechanisms. Passive absorption follows concentration gradients through diffusion, mass flow with water, or ion exchange. Active transport requires metabolic energy to transport ions against their gradients using carrier proteins in the cell membrane. Minerals enter mostly through the zone of elongation in root cells. Common theories for passive absorption include mass flow, ion exchange, and diffusion. The carrier concept and cytochrome pump or protein-lecithin theories explain active absorption using carrier proteins and metabolic energy from respiration.