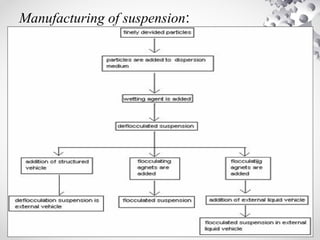
This document provides information about pharmaceutical suspensions. It defines a suspension as a coarse dispersion where an insoluble solid active ingredient is uniformly dispersed throughout an external aqueous or non-aqueous liquid phase. Suspensions are formulated when drugs are insoluble, to mask bitter tastes, increase stability, or achieve sustained release. Key factors in formulating stable suspensions include particle size, shape, wettability, and use of suspending agents to decrease interparticle attraction and impart viscosity. Proper manufacturing controls suspension quality.