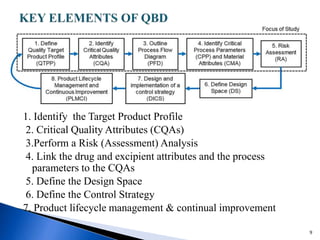
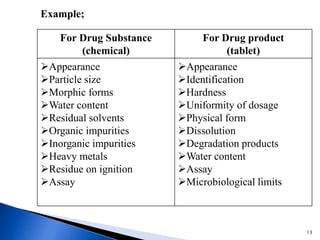
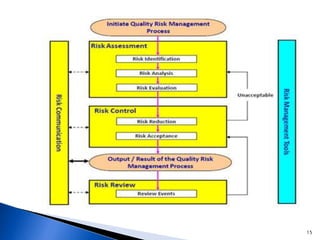
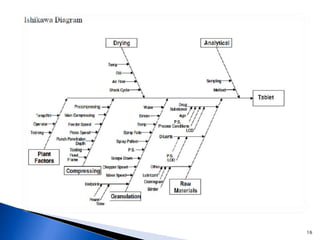
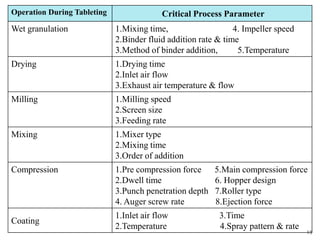
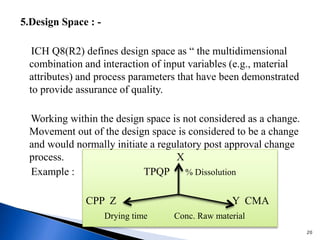
The document discusses Quality by Design (QbD) in the pharmaceutical industry. It defines QbD and outlines its key benefits, including higher product quality assurance, cost savings, and regulatory flexibility. The main elements of QbD are described as identifying target quality profiles, critical quality attributes, risk assessment, linking attributes and parameters to quality, defining a design space and control strategy. QbD facilitates innovation and continuous improvement across a product's lifecycle.