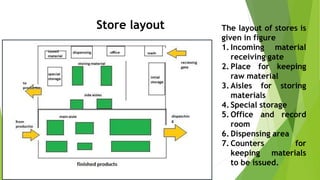
1. Pharmaceutical plant layout involves arranging departments and machinery to integrate machines, materials, and personnel for efficient production while following safety and regulatory requirements.
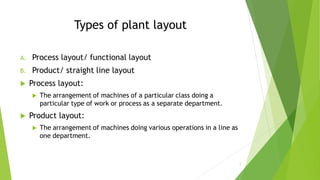
2. There are two main types of layouts - process layout which groups similar machines together and product layout which arranges machines in the order of operations.
3. Effective planning of production involves selecting the process, materials, and equipment; determining the layout; and creating routing sheets and schedules to optimize resource usage and meet production targets.