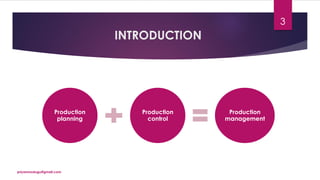
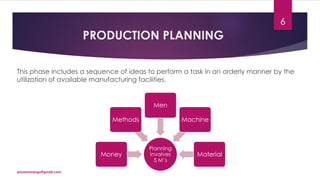
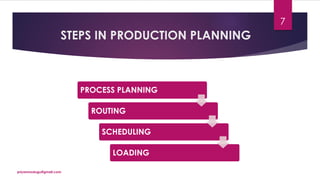
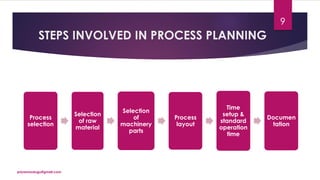
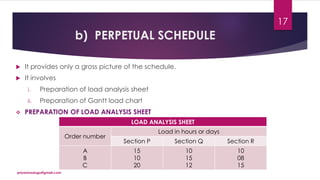
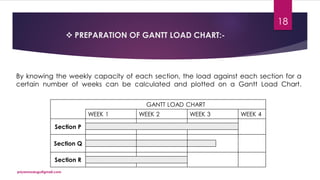
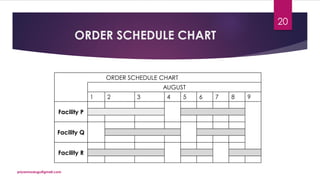
The document discusses production planning and control in manufacturing, highlighting the importance of coordinating men, materials, and machines to optimize efficiency and minimize costs. It outlines the processes of production planning, including process planning, routing, scheduling, loading, and control measures like dispatching, cost control, and quality control. The document emphasizes the need for detailed planning to ensure timely delivery and adherence to quality standards.