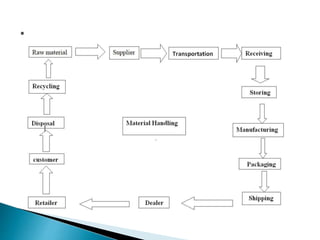
Production management involves planning, organizing, and controlling activities related to converting raw materials into finished goods. It includes functions like product selection, process planning, facility location, capacity planning, production planning and control, inventory control, quality control, and maintenance. The key aspects of production management are selecting the right production process, maintaining optimal inventory levels, and efficiently planning production activities to meet demand while minimizing costs.