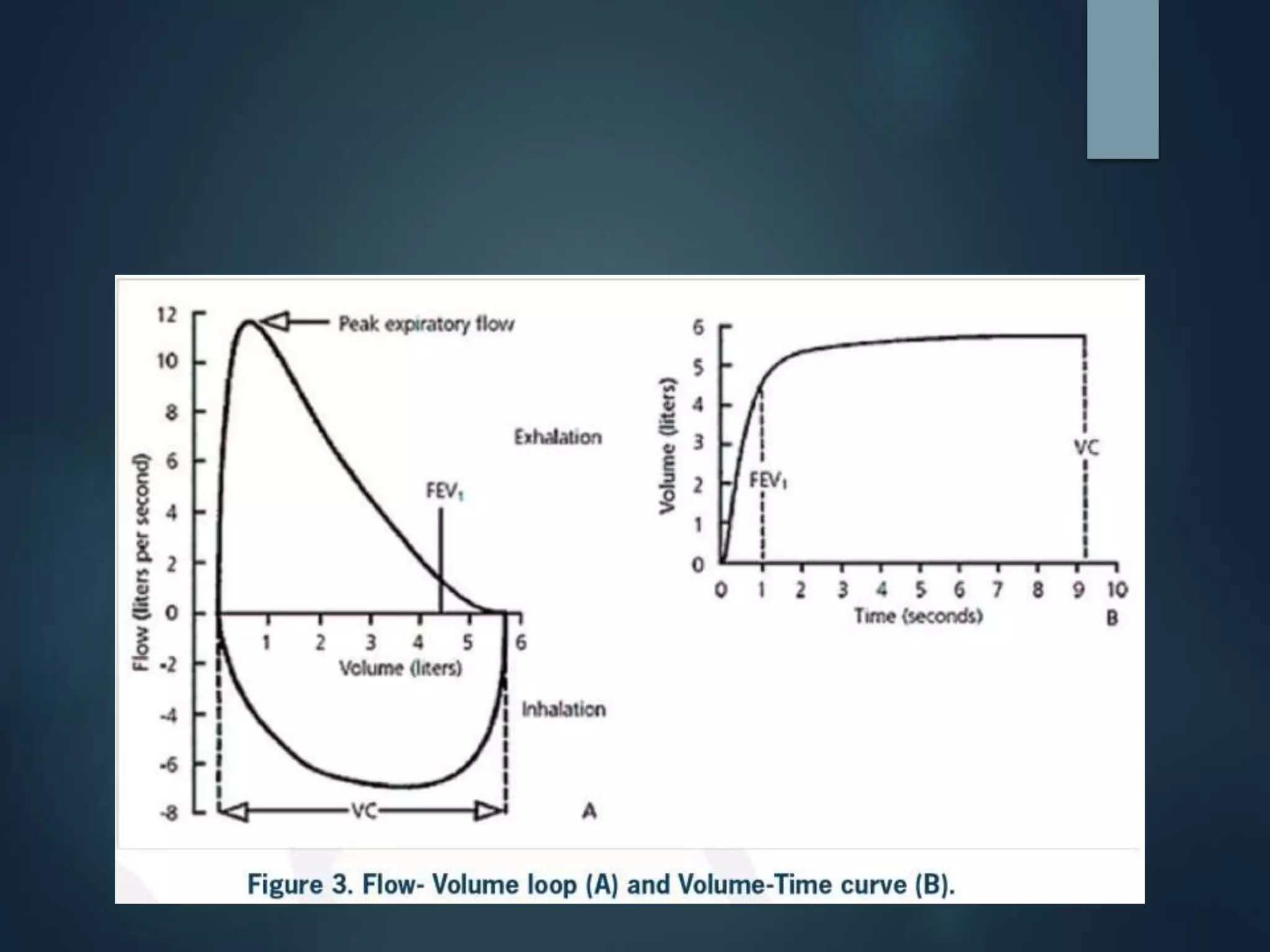
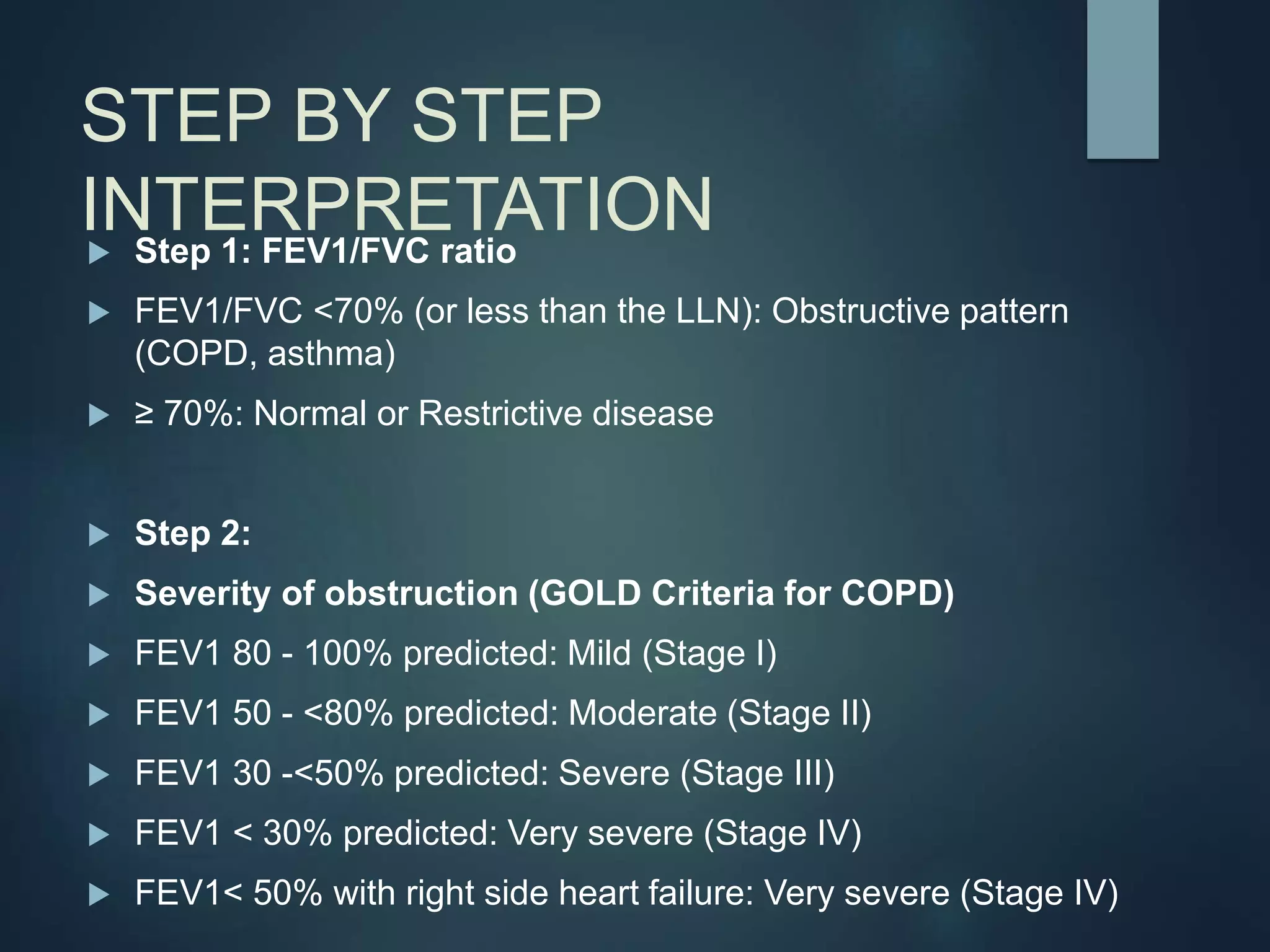
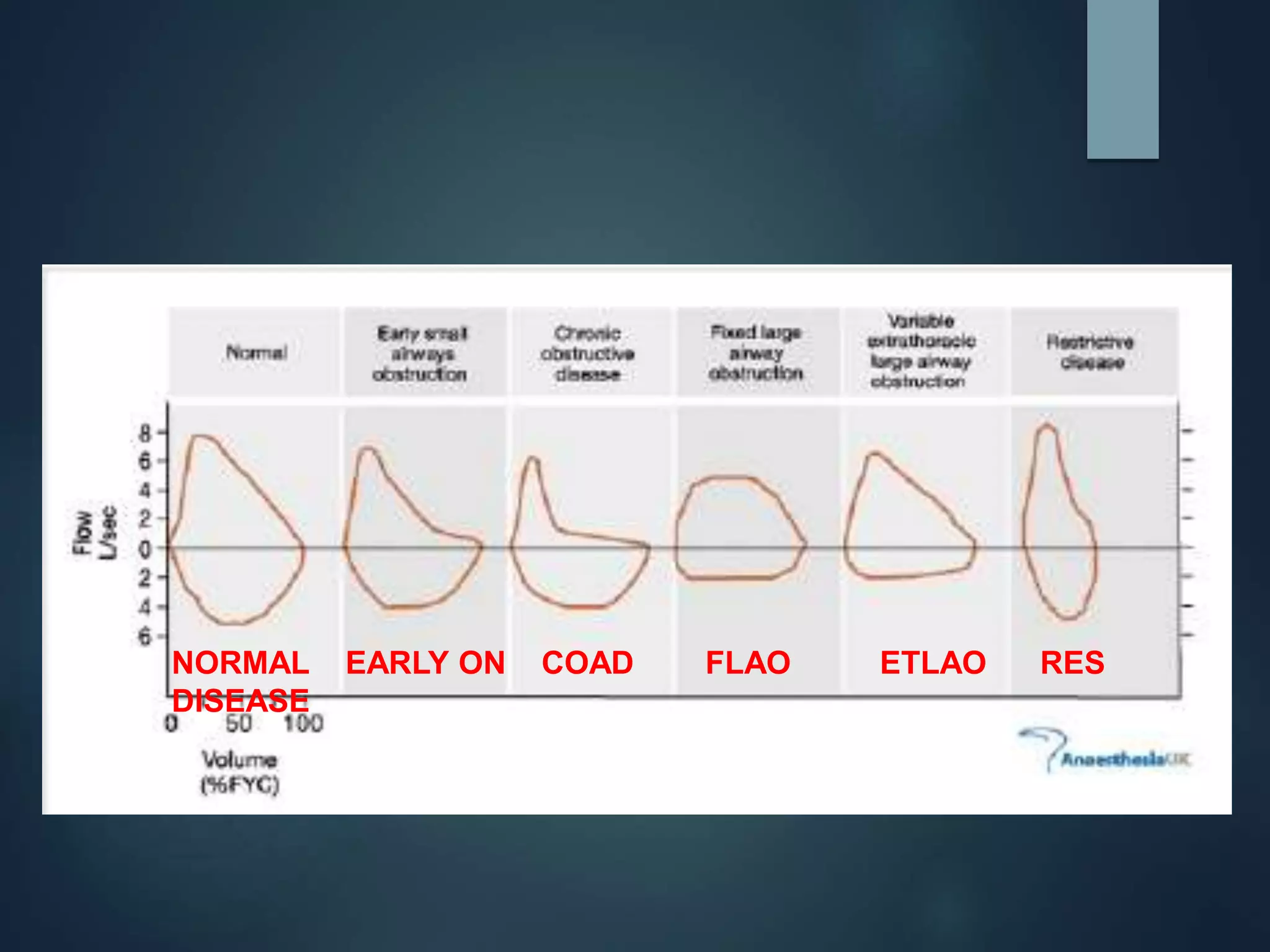
A pulmonary function test (PFT) evaluates lung function through spirometry, lung volume measurements, diffusion capacity, and exercise tests. Spirometry measures how much air the lungs can hold and how fast it can be exhaled. The FEV1/FVC ratio identifies airflow obstruction. Severity of obstruction is classified based on FEV1 percentages. A bronchodilator response helps distinguish asthma. Total lung capacity evaluates restriction. The DLCO measures gas exchange and identifies emphysema. PFTs provide a window into lung function and the nature of respiratory disorders.