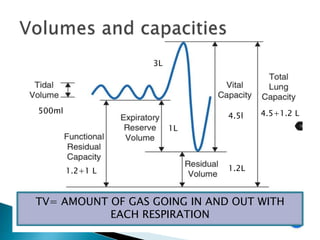
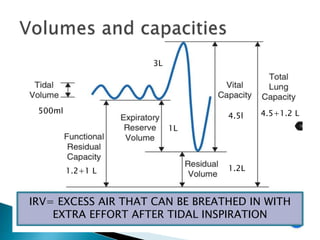
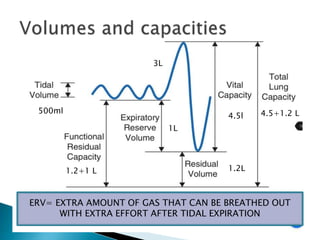
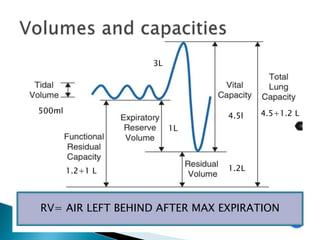
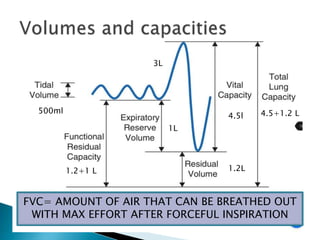
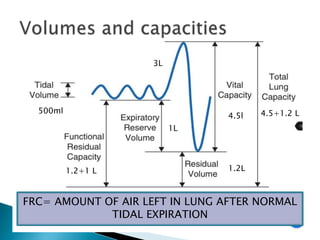
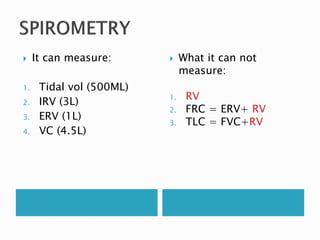
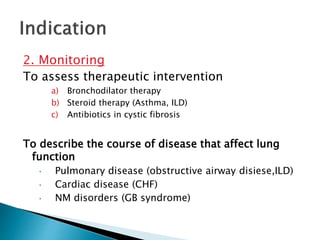
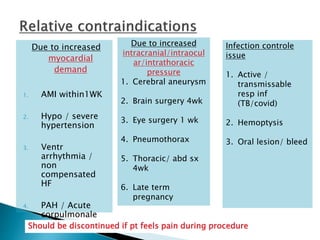
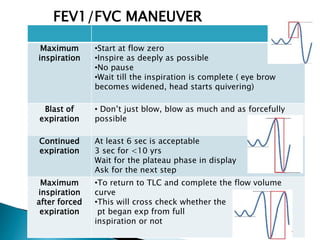
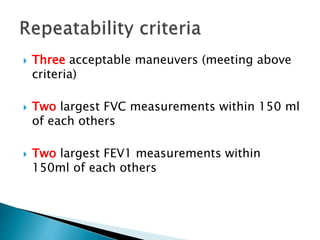
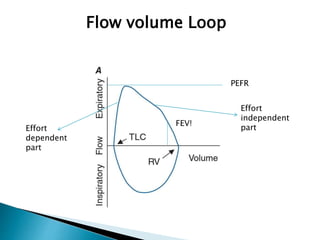
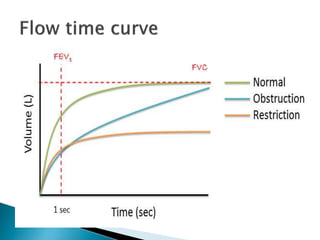
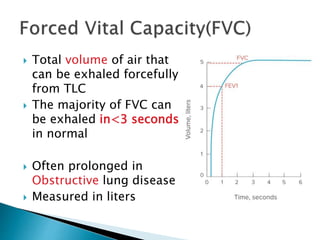
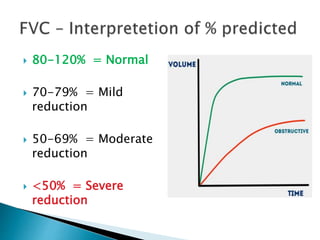
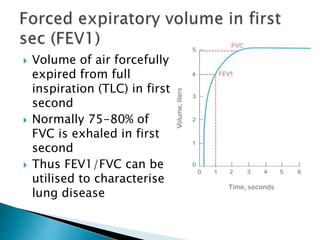
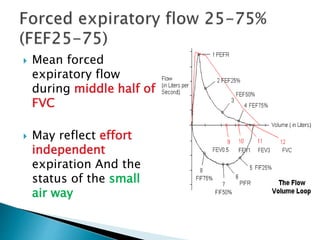
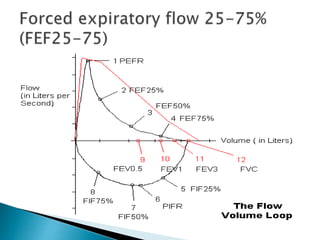
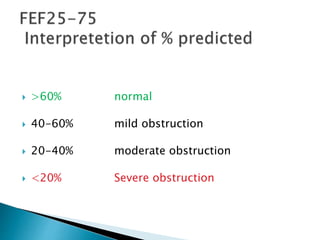
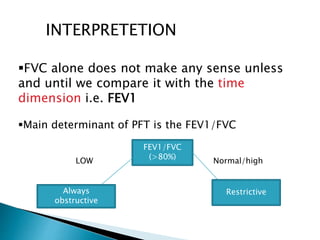
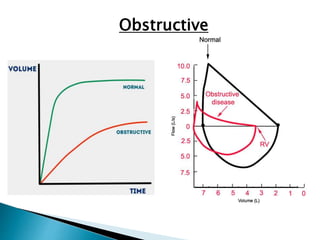
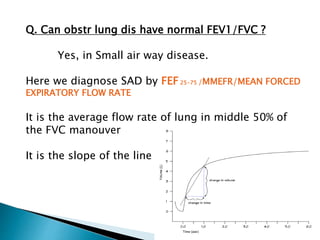
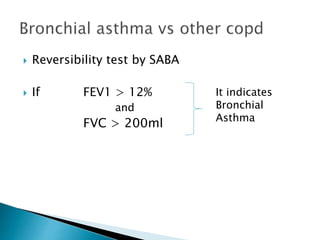
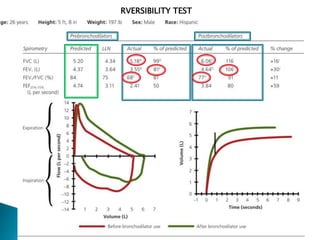
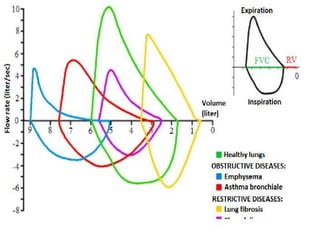
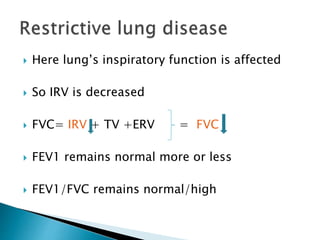
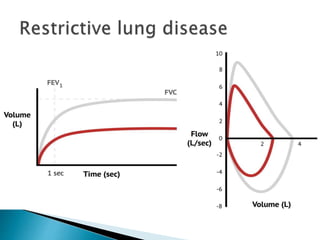
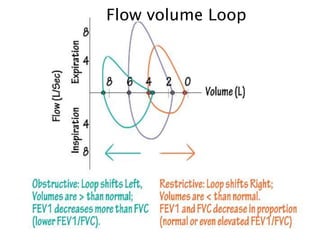
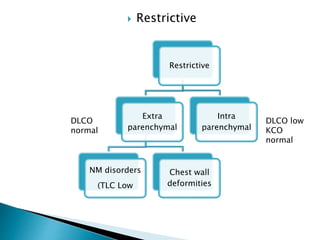
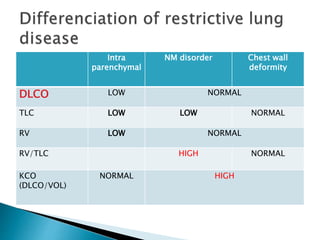
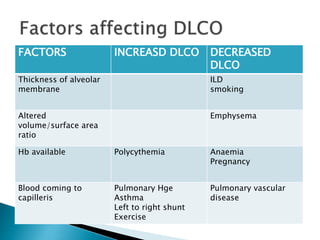
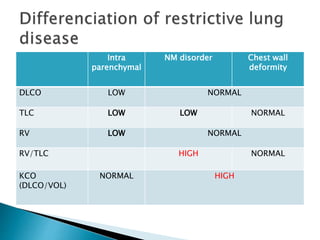
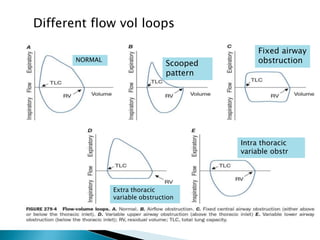
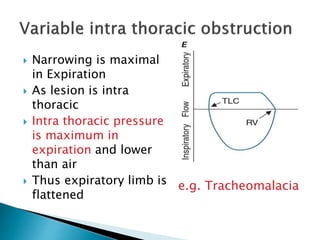
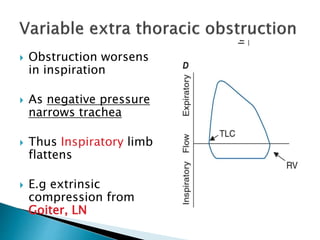
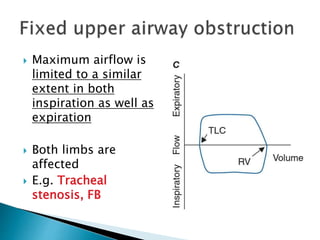
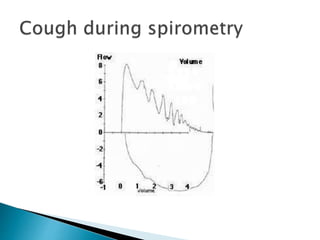
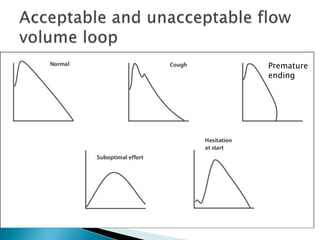
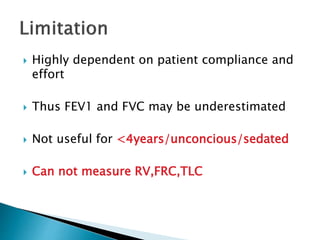
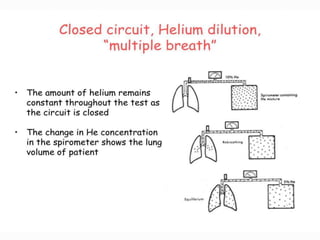
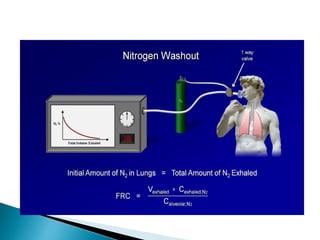
The document outlines various pulmonary function tests (PFTs) used to evaluate lung function, including spirometry, gas exchange tests, and assessments of lung compliance and muscle strength. It discusses the relevance of these tests in diagnosing respiratory conditions, evaluating treatment efficacy, and monitoring patient progress. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of proper technique and calibration in conducting these tests to ensure accurate results.