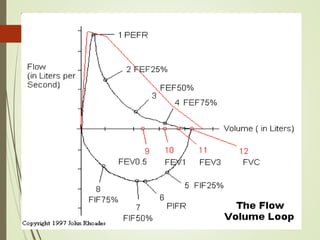
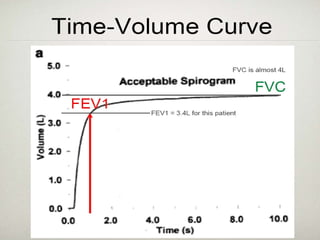
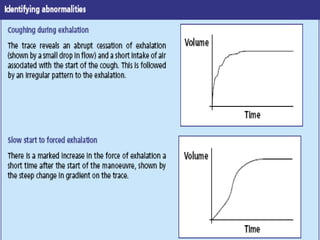
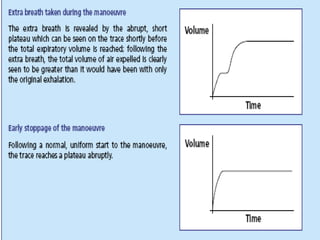
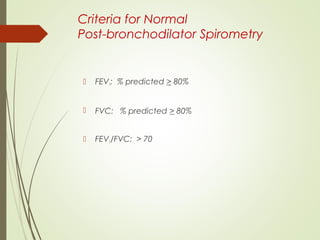
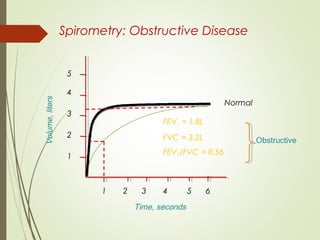
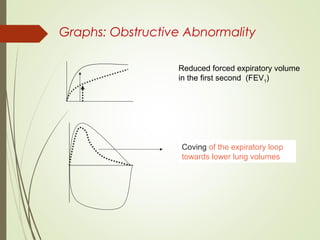
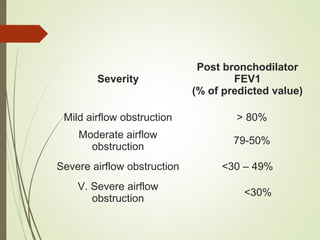
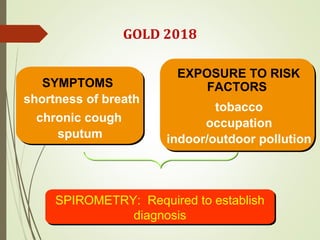
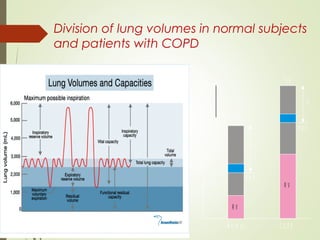
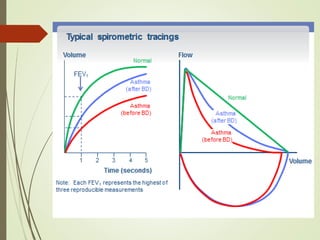
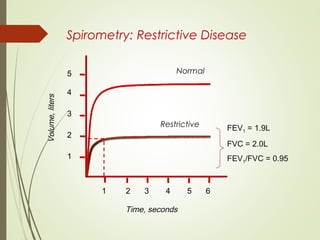
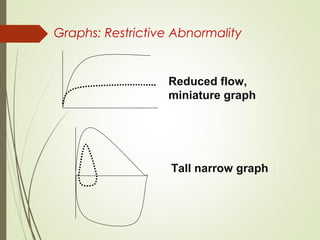
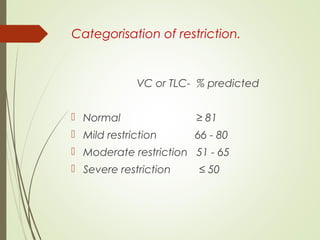
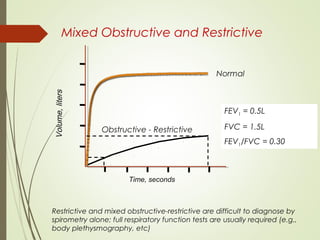
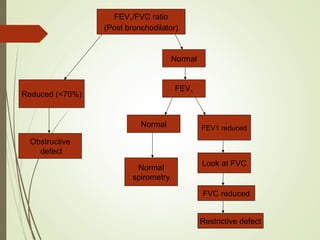
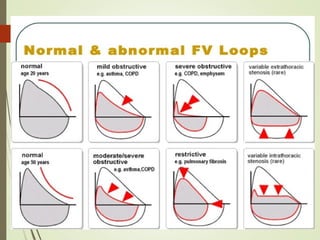
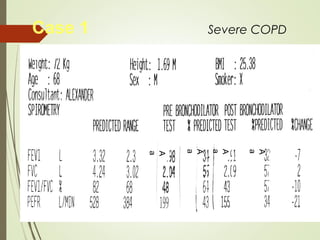
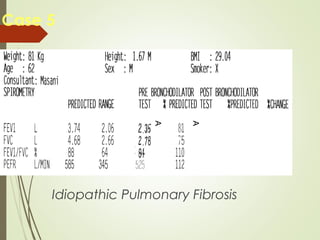
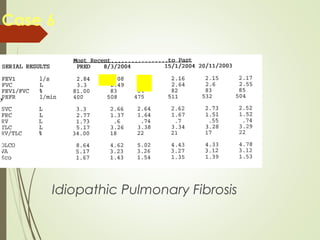
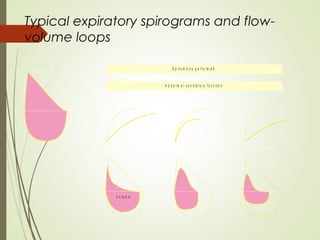
Spirometry is a simple lung function test that measures how much air a person can exhale from their lungs after taking a deep breath. It can help diagnose and monitor conditions like asthma and COPD. The test involves blowing into a mouthpiece to measure exhaled volumes like FEV1 and FVC. The ratio of FEV1/FVC is used to identify obstructive or restrictive lung abnormalities. A reduced ratio below 70% indicates obstruction, while reduced volumes but a normal ratio suggest restriction. Spirometry is a valuable tool for physicians to assess respiratory conditions but should be interpreted along with clinical history and examination findings.