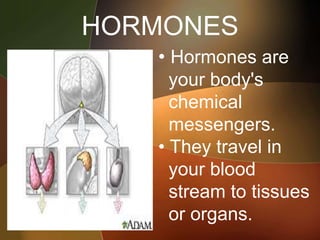
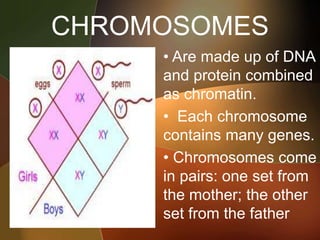
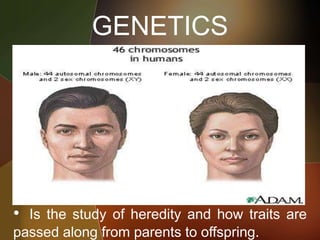
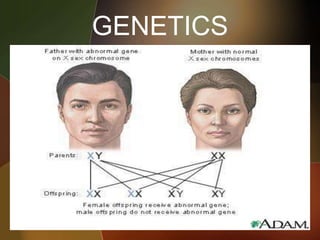
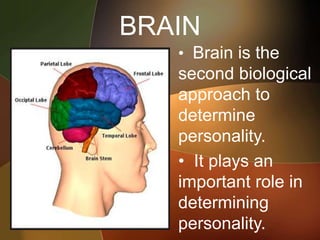
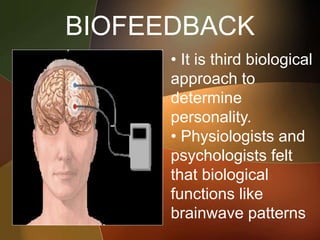
The document discusses the key foundations of personality, including biological, cultural, family, social and situational factors. It defines personality as the totality of qualities and traits that make a person unique. The biological foundations discussed include heredity, brain structures, hormones, enzymes, and physical features. Cultural, family and social factors also influence personality development. Freud's psychodynamic theory involving the id, ego and superego is summarized. The document concludes by outlining the six foundations of personality: mental, emotional, social, physical, moral and spiritual.