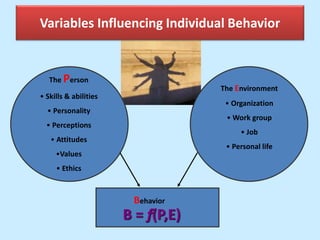
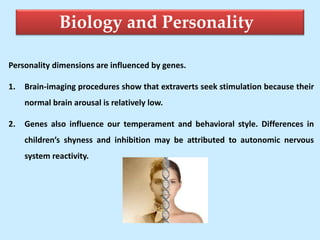
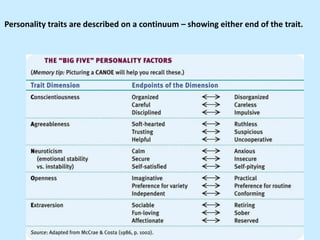
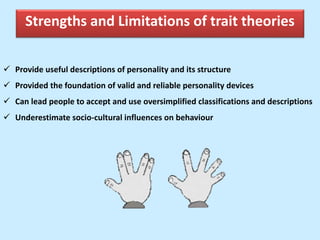
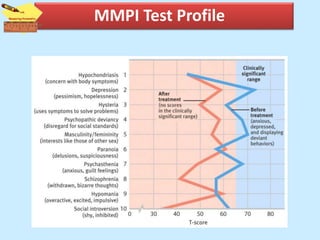
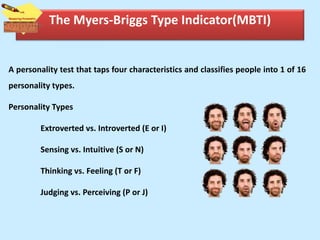
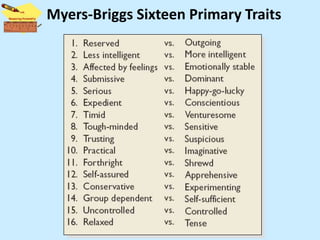
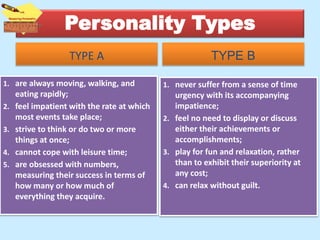
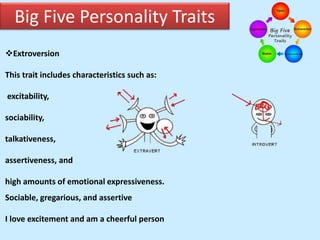
The document discusses personality from several perspectives. It defines personality as a relatively stable set of characteristics that influence individual behavior. It notes personality is influenced by both hereditary/biological factors and environmental factors. Several theories of personality are mentioned, including trait theory, psychodynamic theory, and humanistic theory. Methods of measuring personality include subjective self-report measures like questionnaires and interviews, as well as more objective measures like ratings and projective tests. Key aspects of personality like the Big Five traits and a teacher's role in student personality development are also summarized.