This document discusses various theories of personality including:
- Genes and environment determine personality. Genes influence traits like nervous system and hormones while culture and social groups shape behavior.
- Myers-Briggs categorizes personalities along introversion/extroversion, sensing/intuition, thinking/feeling, and judging/perceiving scales.
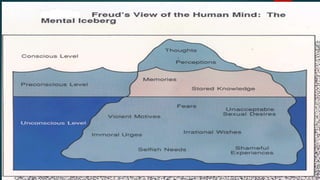
- Jung focused on the conscious and unconscious mind shaping personality. A healthy personality balances spirit, mind and body with ability to adapt.