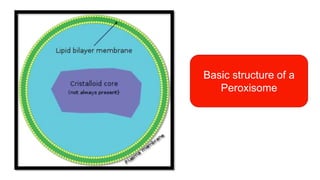
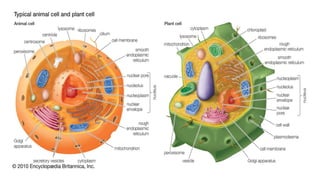
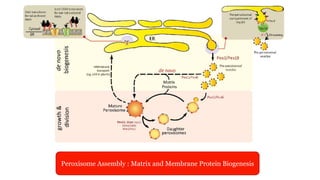
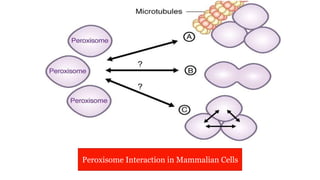
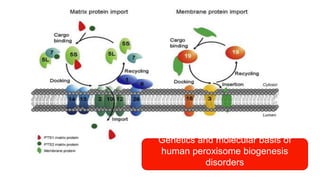
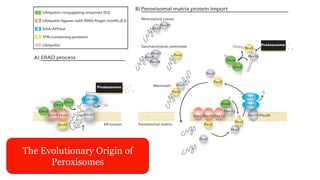
Peroxisomes are oxidative organelles that metabolize long-chain fatty acids and reactive oxygen species, playing crucial roles in cellular lipid metabolism and brain function. They were first identified in 1954 and are involved in various metabolic processes, including plasmalogen biosynthesis and bile acid production. Peroxisome biogenesis involves specific proteins called peroxins and interacts dynamically with other organelles like mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum.