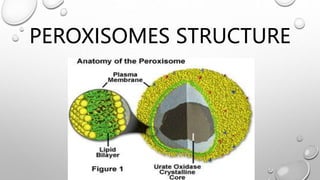
Peroxisomes are organelles found in the cytoplasm of almost all eukaryotic cells that are involved in many important metabolic functions. They contain enzymes for fatty acid oxidation and breakdown of hydrogen peroxide. Mutations in peroxisome genes can cause serious diseases by disrupting these metabolic pathways. While peroxisomes produce their own enzymes, the genes for these enzymes are located in the cell nucleus. The enzymes are transported to peroxisomes with the help of targeting sequences and receptor proteins.