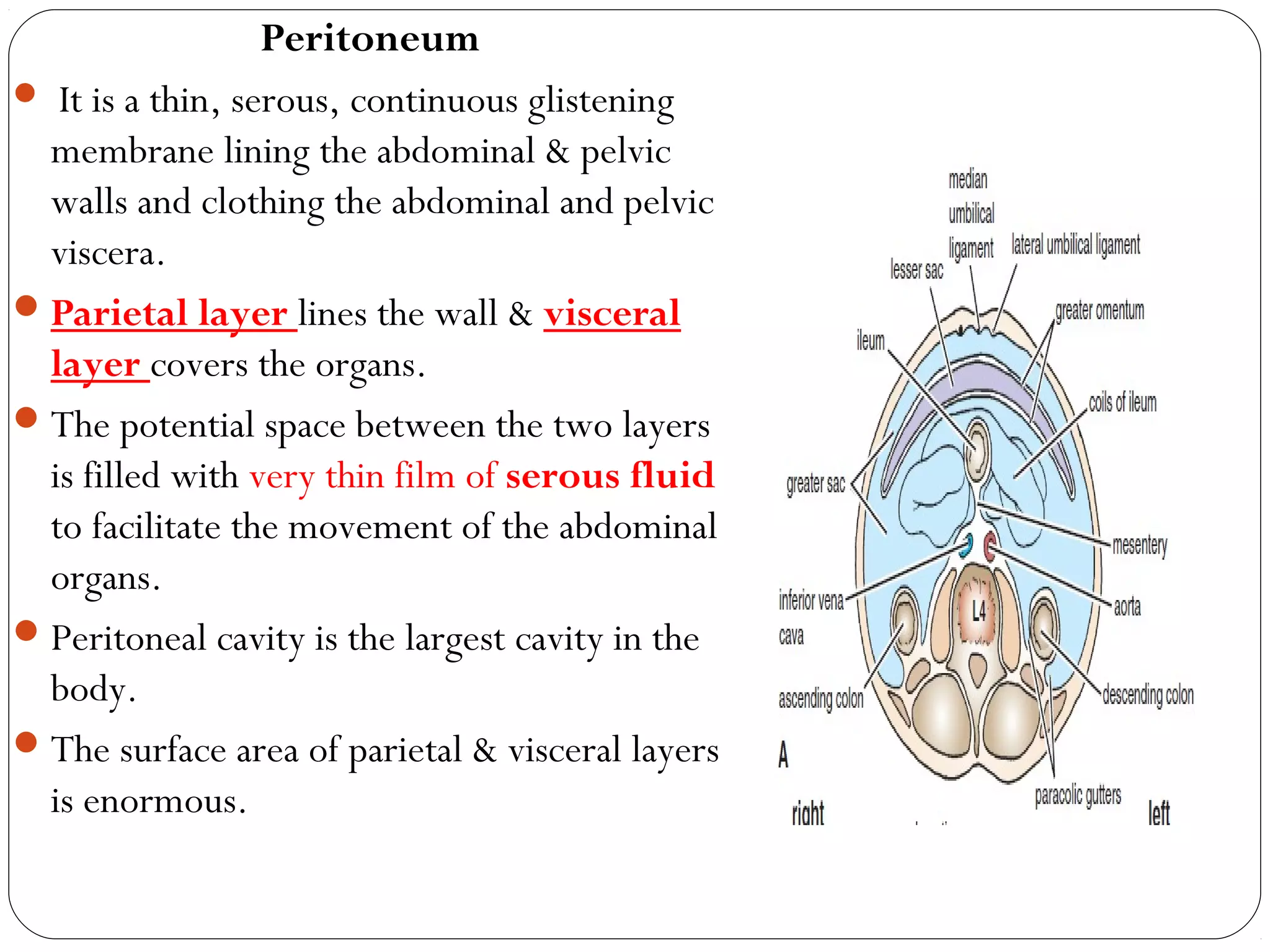
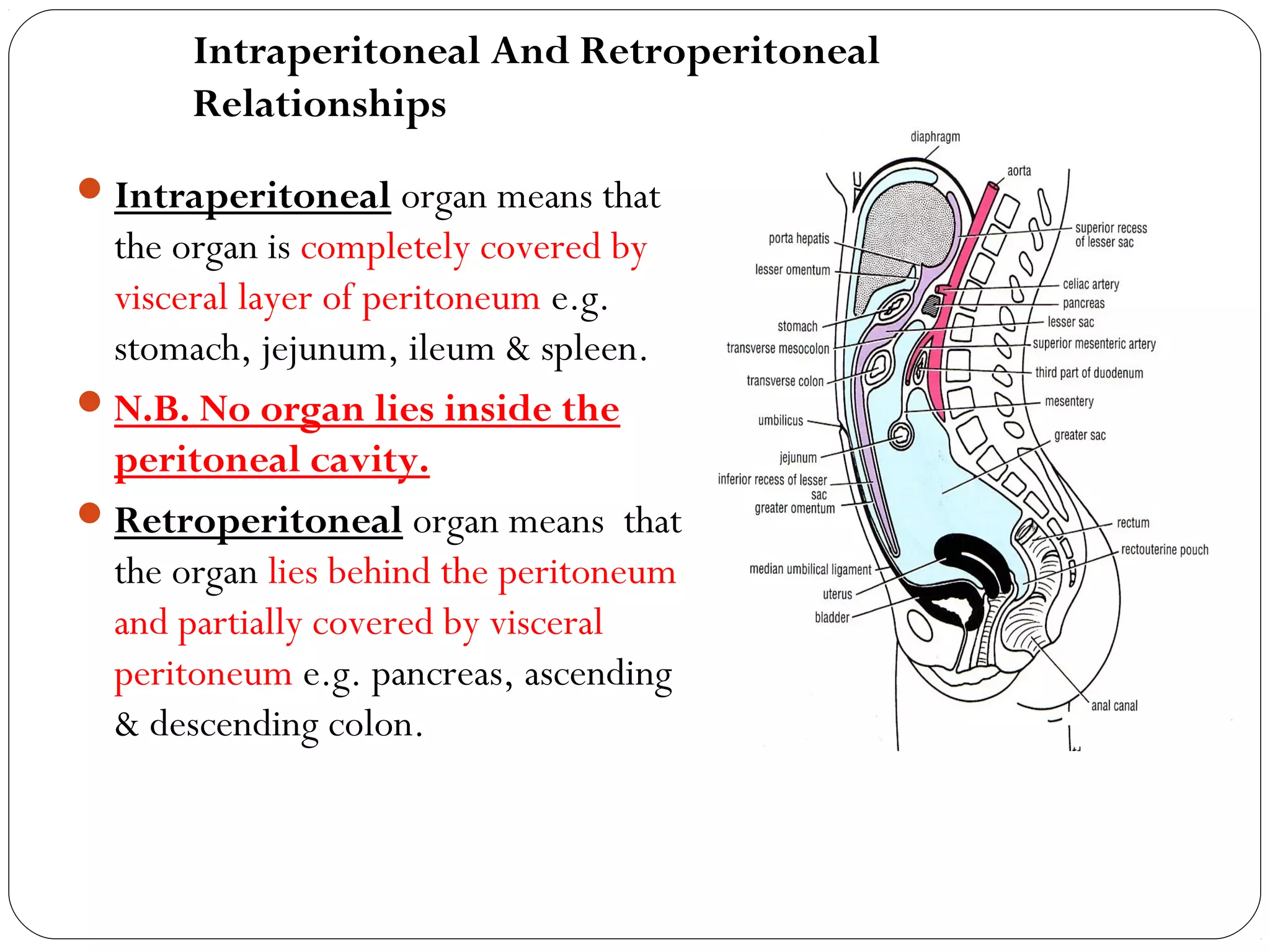
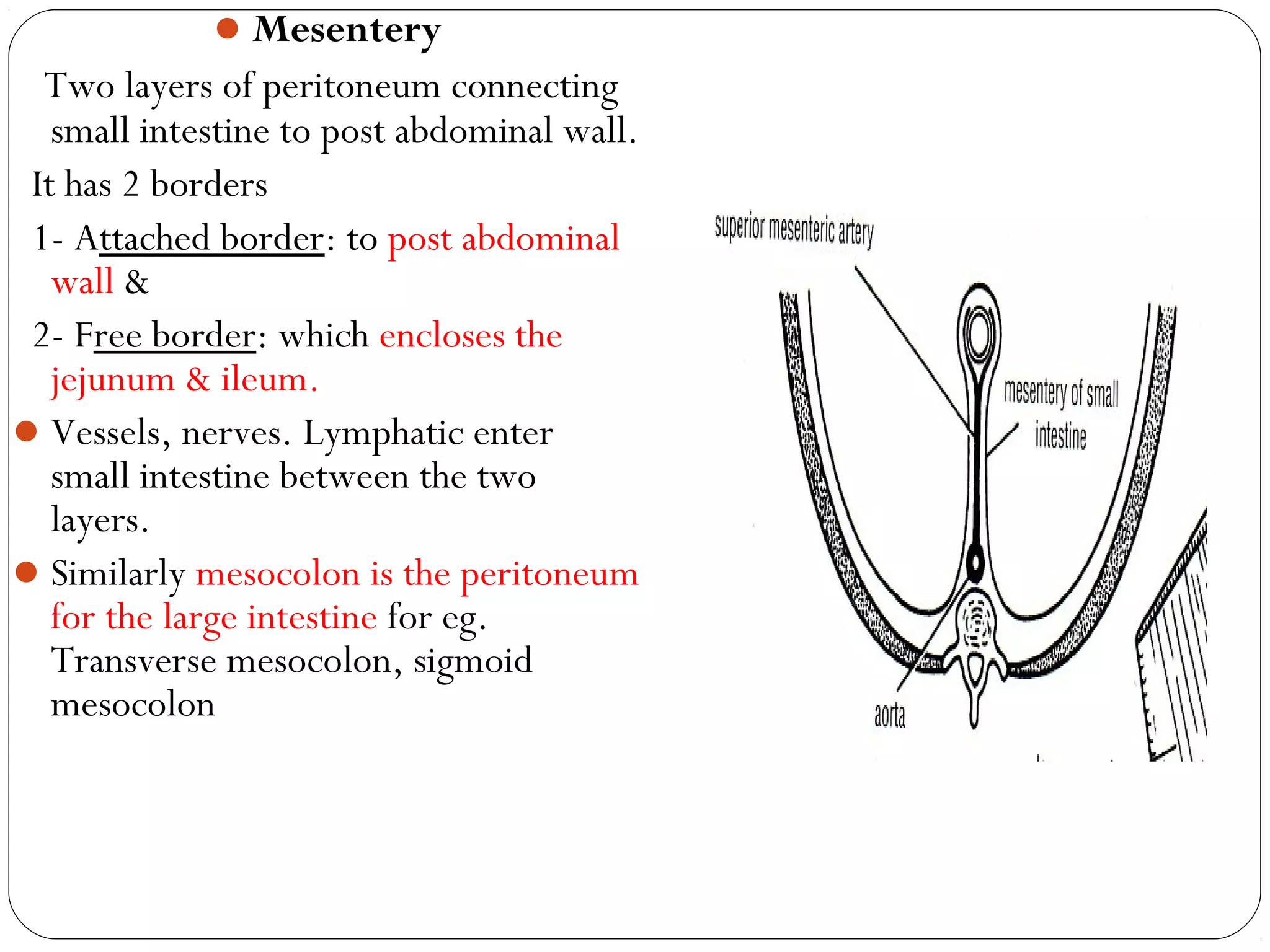
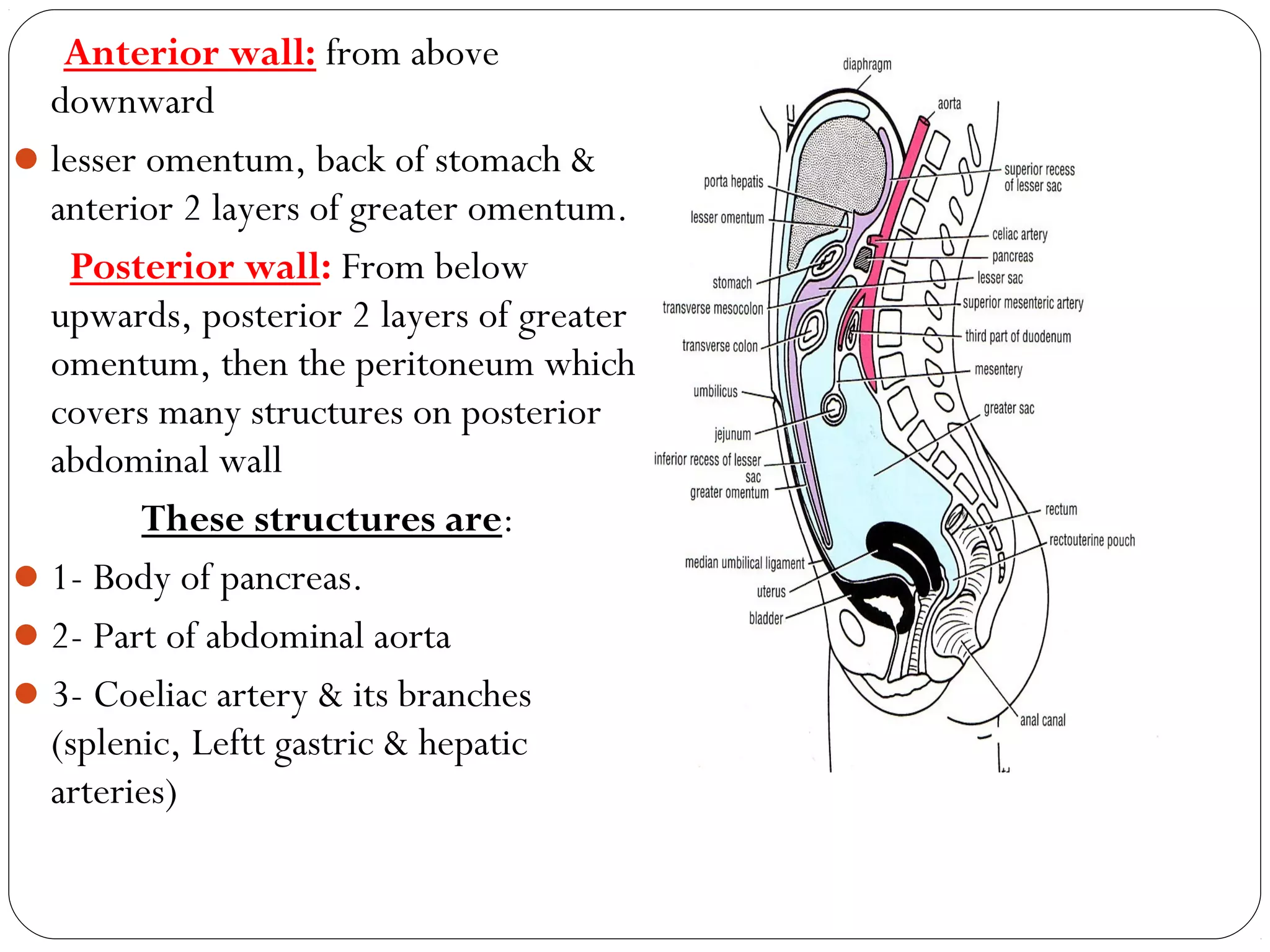
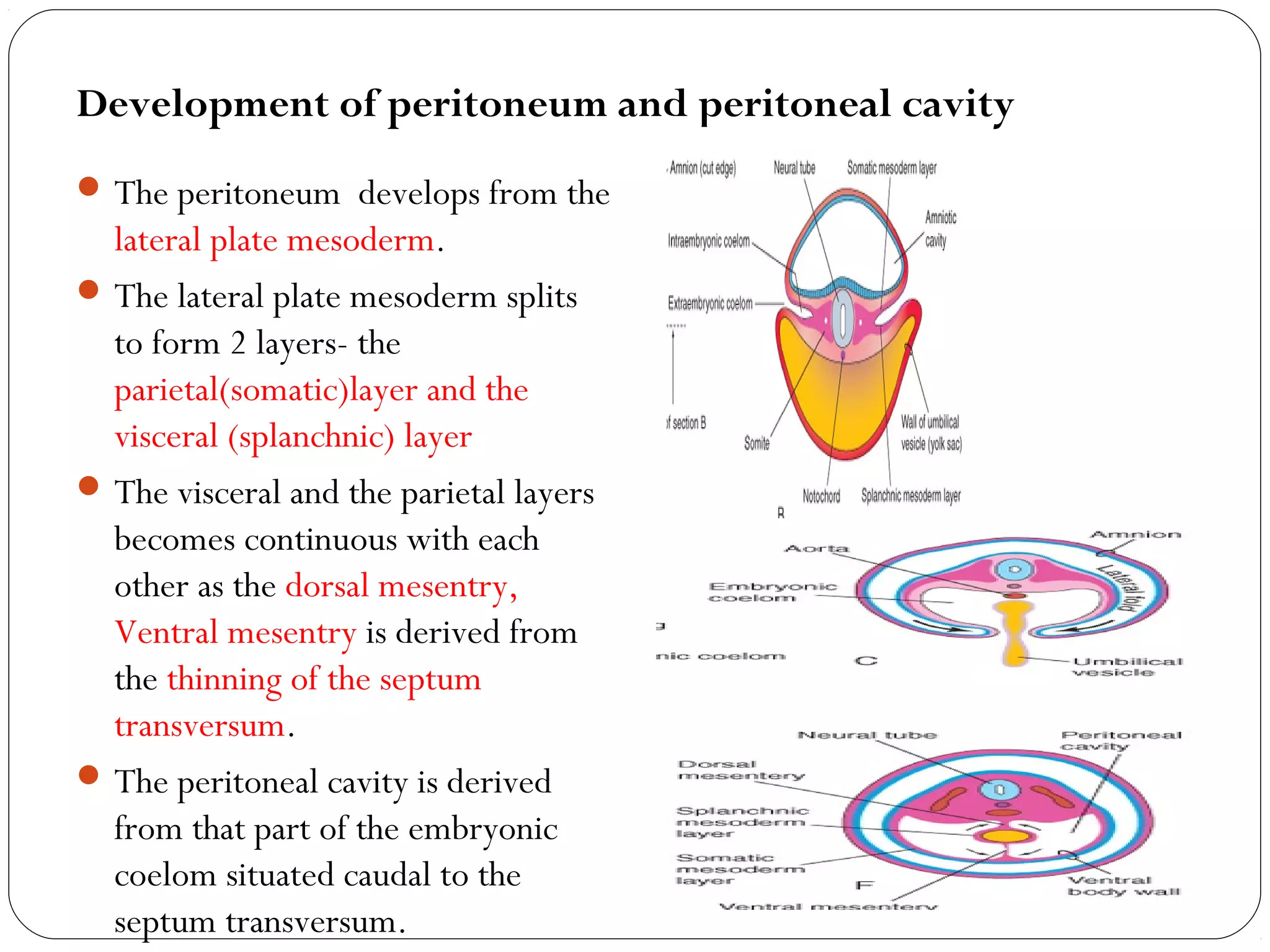
The peritoneum is a serous membrane that lines the abdominal cavity and covers abdominal organs. It consists of a parietal layer lining the abdominal wall and a visceral layer covering the organs. The potential space between these layers, called the peritoneal cavity, contains a thin film of fluid. The peritoneal cavity is divided into the greater and lesser sacs. The peritoneum has several functions including suspending organs, fixing some organs in place, storing fat, and secreting fluid to allow organ movement. It develops from lateral plate mesoderm and is innervated by thoracic and lumbar nerves. Clinical applications of the peritoneum include peritonitis, ascites, peritoneal dialysis, and internal