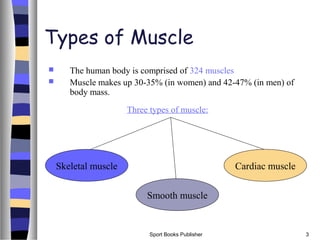
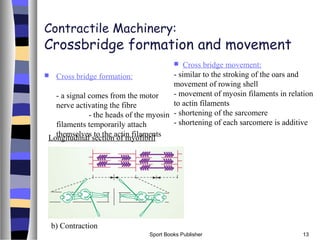
This document discusses the structure and function of the three main types of muscle in the human body: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. It describes the microscopic structure of skeletal muscle including sarcomeres, actin and myosin filaments, and the sliding filament model of contraction. It also outlines the macroscopic components of skeletal muscle including muscle fibers, fiber bundles, and muscle bellies. Finally, it discusses the coordinated action of agonist, antagonist, synergist and fixator muscles to produce movement.