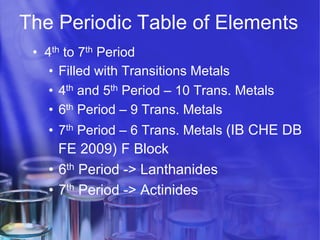
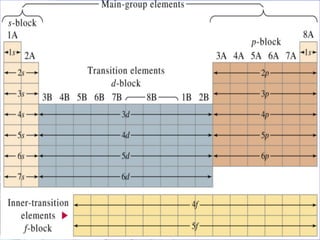
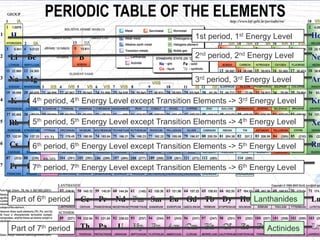
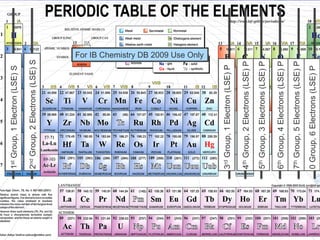
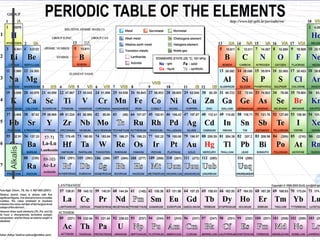
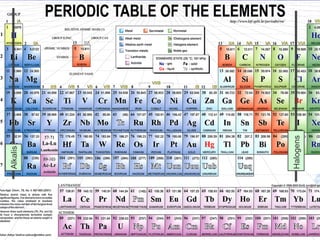
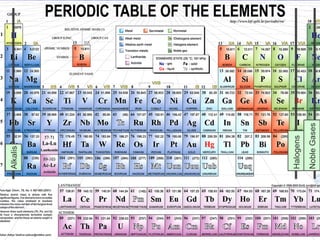
The document discusses key aspects of the periodic table, including its structure, properties of different groups of elements, and how position on the table relates to electron configuration and chemical properties. It provides details on the alkali metals, halogens, and noble gases groups, describing their physical and chemical characteristics. Examples are given of elements in each group to illustrate trends in properties.