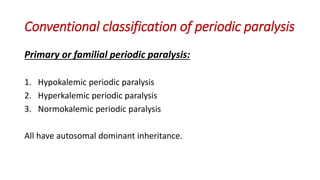
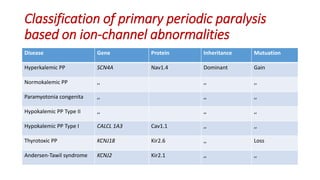
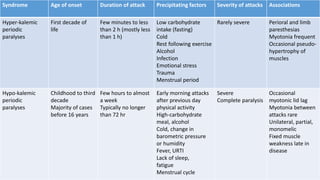
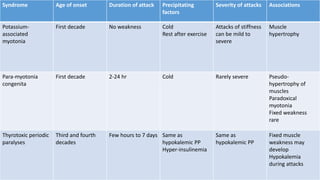
Periodic paralysis is defined by episodic, short-lived skeletal muscle weakness, which can be classified into primary (hereditary) and secondary (due to identifiable causes) types. The document details the pathophysiology, epidemiology, classification, and clinical approach to diagnosing and treating various forms of periodic paralysis, noting that serum potassium levels play a crucial role in diagnosis and management. Treatment options vary by type but are aimed at preventing attacks and addressing underlying causes.