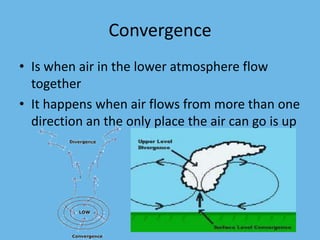
This document discusses various cloud formation and precipitation processes including: adiabatic temperature change caused by air compression/expansion; orographic lifting where winds force air up mountains cooling it; frontal wedging where warm/cold air collide forming storms; convergence where air flows together upward; localized convective lifting forming warm air pockets called thermals; stability based on air density differences; condensation requiring saturated air; the types and heights of clouds; vertical cloud development enhancing movement; fog forming over land or sea; cold/warm cloud precipitation mechanisms; and rain, snow, sleet, glaze and hail depending on atmospheric temperatures.