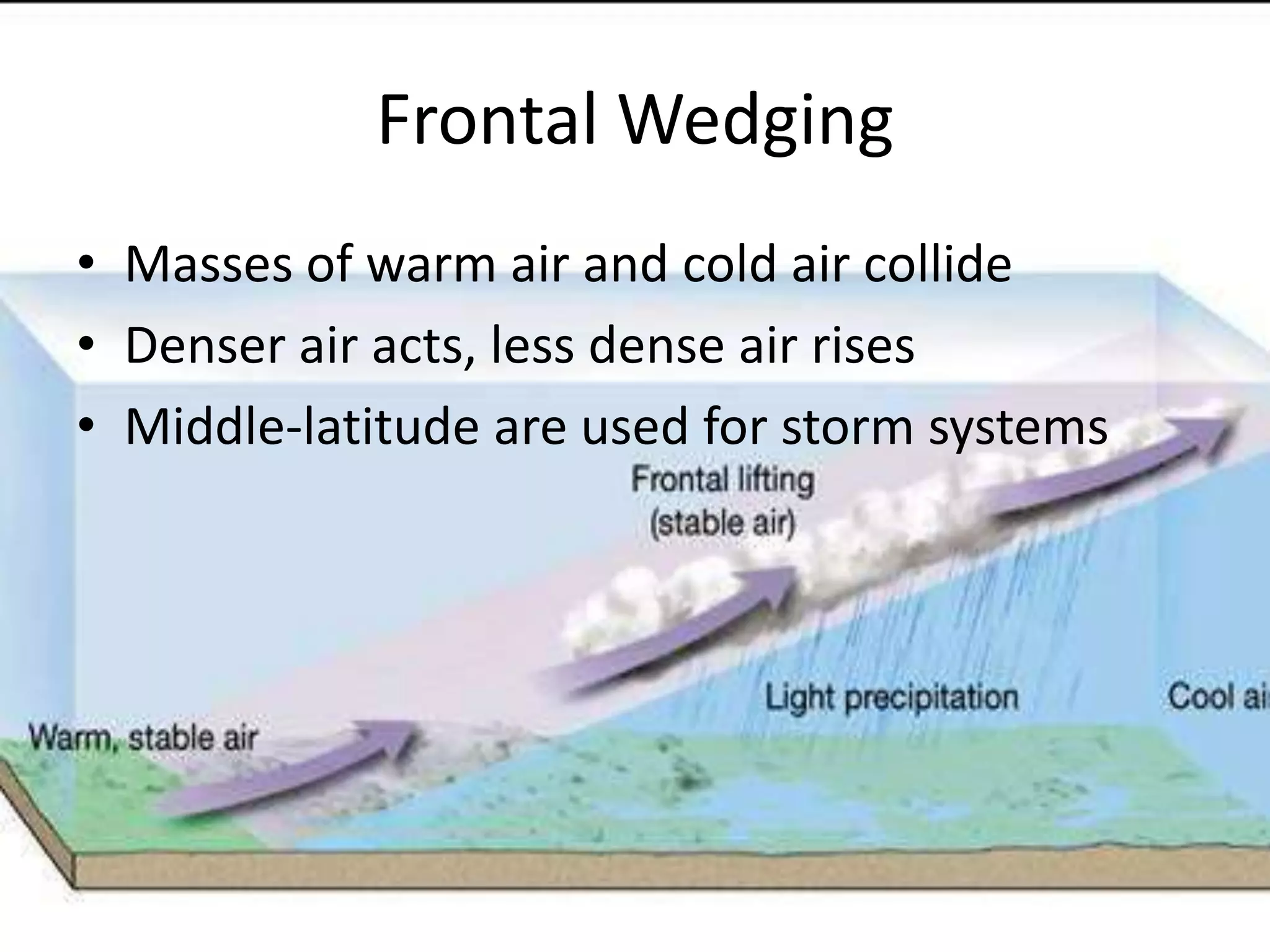
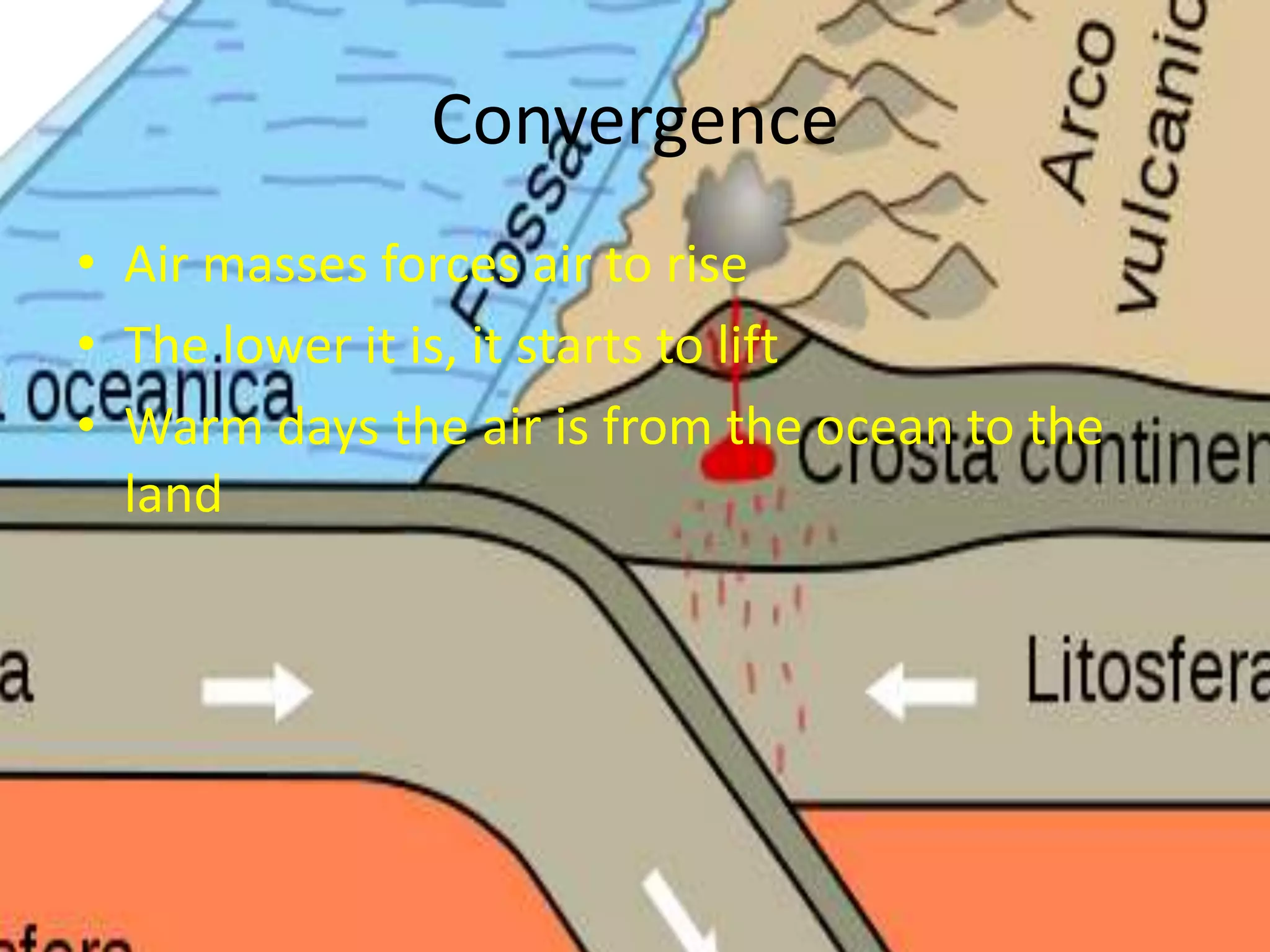
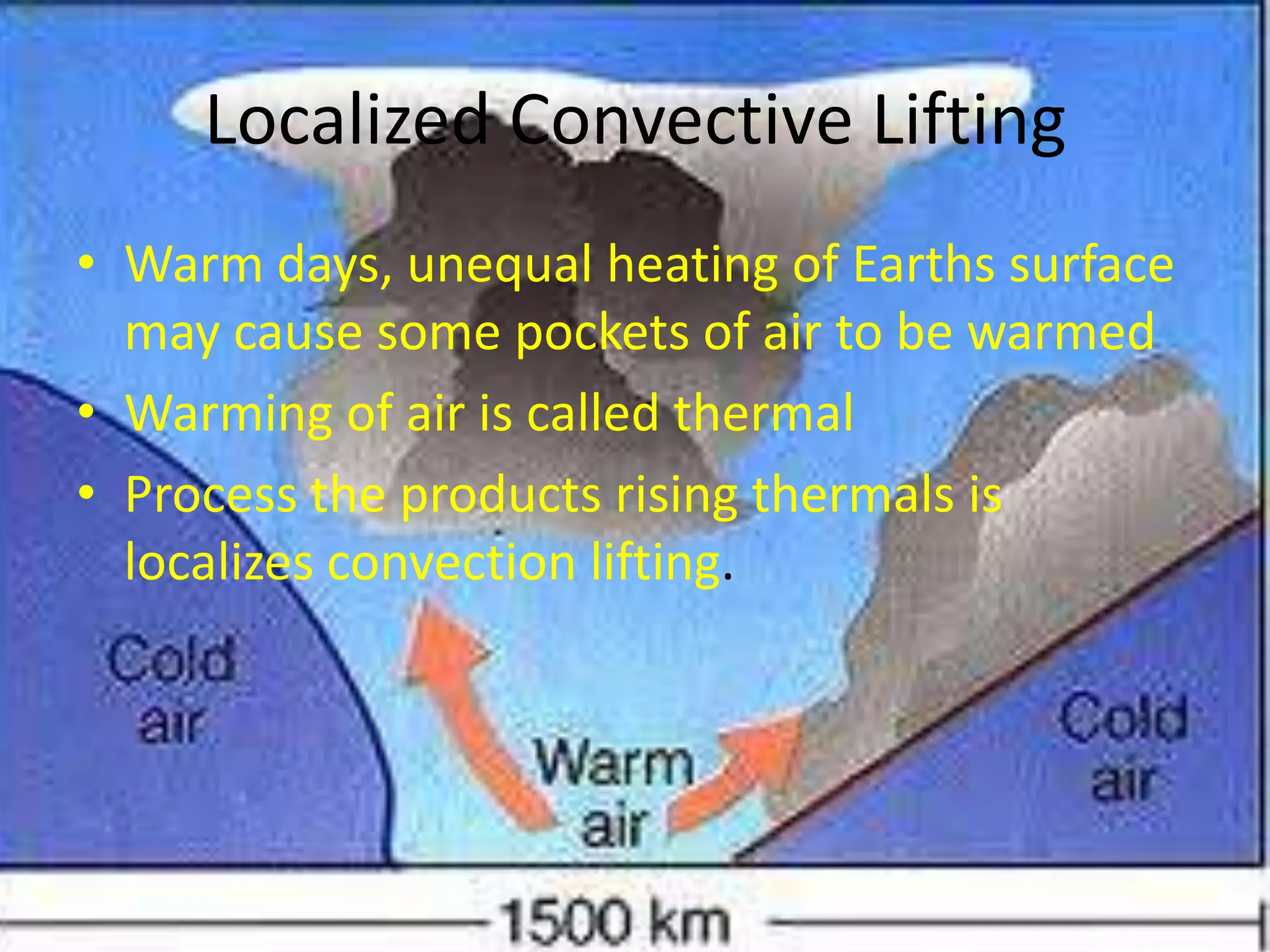
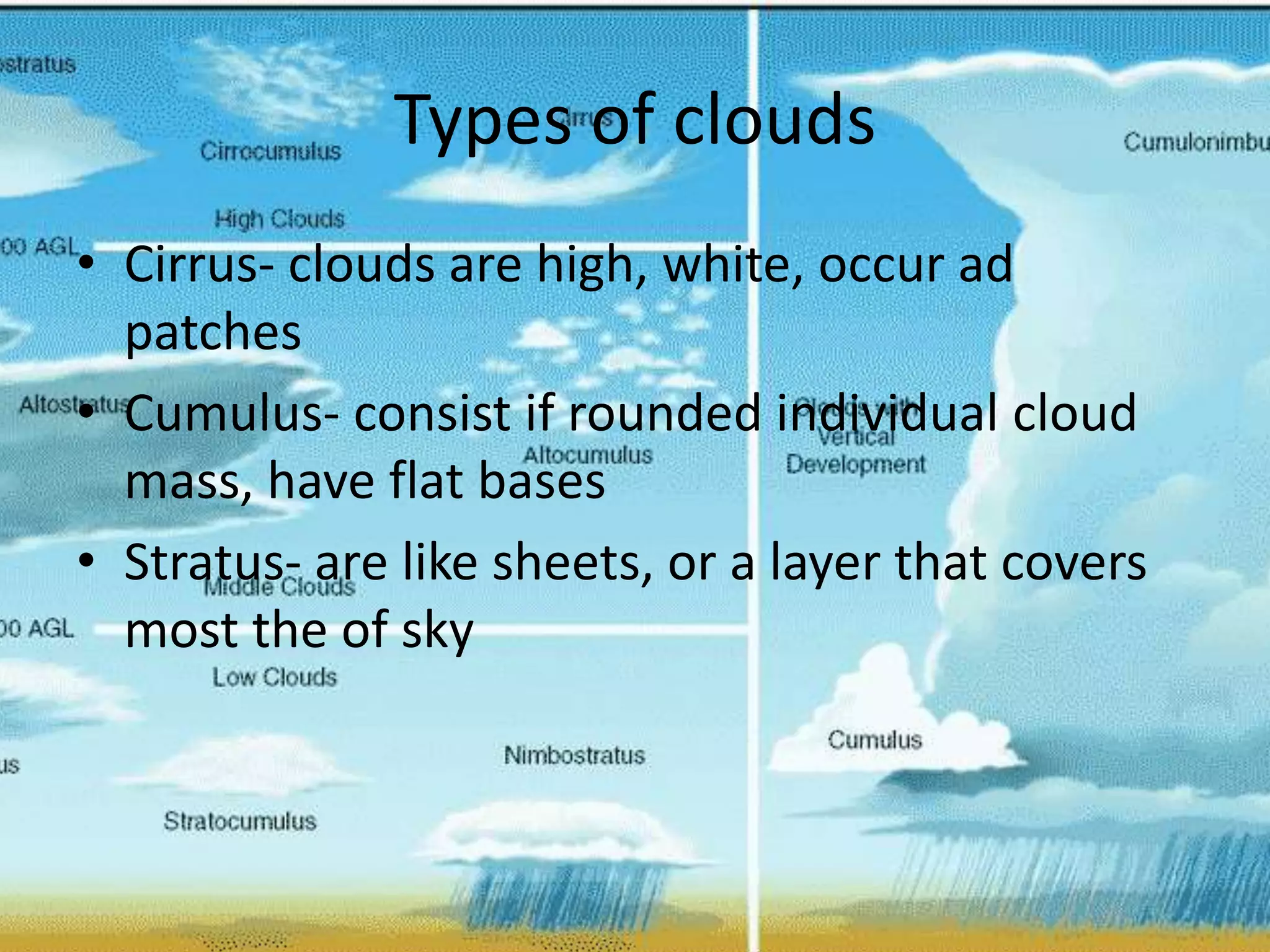
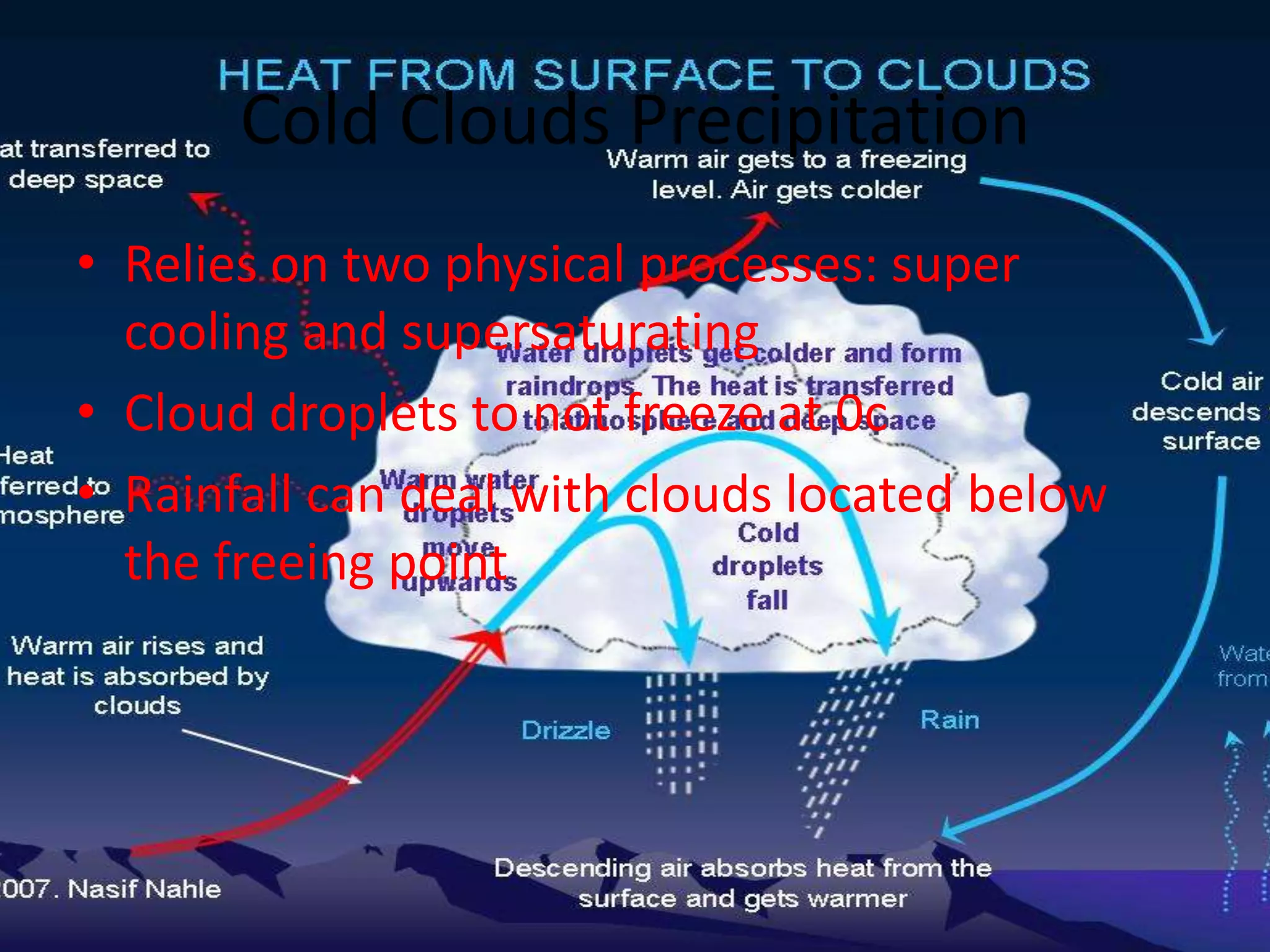
This document discusses various types of clouds and precipitation. It describes how different lifting mechanisms like orographic lifting and frontal wedging can cause clouds to form. It explains the temperature changes that occur during adiabatic expansion and cooling. It also outlines the different categories of clouds based on height (high, middle, low clouds) and discusses fog, rain, snow, sleet and hail.