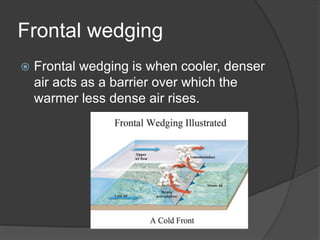
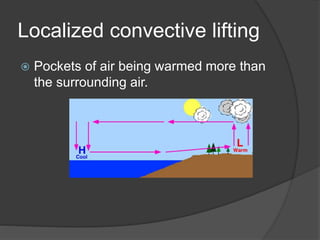
This document discusses various types of cloud formation and precipitation processes. It describes adiabatic temperature changes that can occur without heat exchange, as well as orographic and frontal lifting caused by air flowing over elevated land or cooler air. It defines convergence as air flowing together to cause lifting. It also outlines high, middle, and low cloud types, as well as vertical cloud development. Processes like condensation, the Bergeron process, and collision-coalescence are discussed in relation to cloud precipitation. Rain, snow, sleet, glaze and hail are also defined.