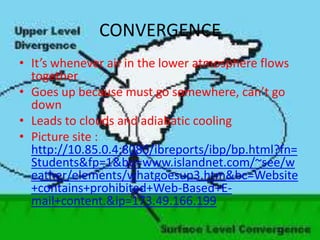
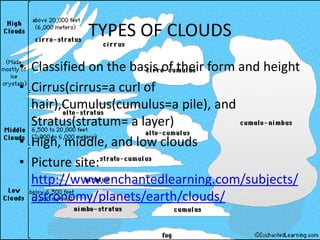
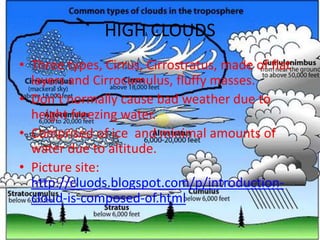
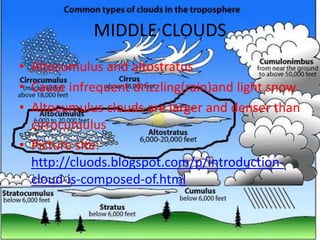
This document summarizes different types of clouds and precipitation. It describes various cloud formation processes like adiabatic cooling, orographic lifting, and frontal wedging. It explains high, middle, and low clouds like cirrus, altostratus, and stratus clouds. Different precipitation processes are outlined, such as warm cloud precipitation through coalescence and cold cloud precipitation using the Bergeron process. Sleet, glaze, hail, rain, and snow are defined. The document is intended to provide an overview of clouds and precipitation types and formation mechanisms.