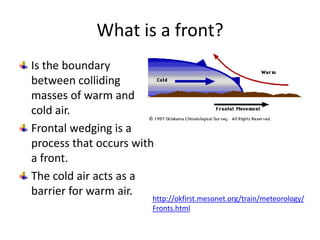
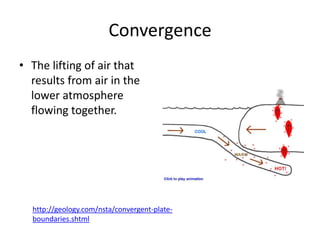
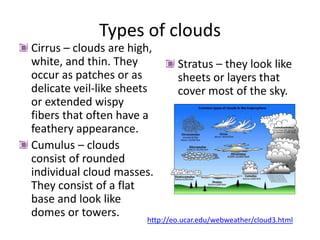
This document discusses various cloud formation processes and types of precipitation. It explains concepts like adiabatic temperature changes, orographic and frontal lifting, convection, condensation, and the formation of cirrus, stratus, cumulus clouds. It also discusses high, middle, low clouds, clouds with vertical development, fog, and types of precipitation including rain, snow, sleet, glaze and hail.