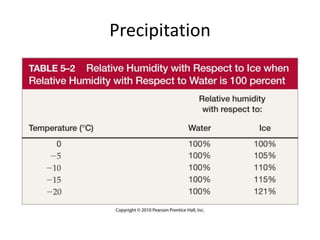
The Bergeron process describes how precipitation forms in clouds. It involves the properties of supercooled water and ice crystals. Supercooled water droplets remain liquid below freezing temperatures until they contact an ice nucleus. Ice crystals grow more easily than liquid droplets because water vapor pressure is lower above ice. This causes ice crystals to grow at the expense of water droplets, producing snow or other forms of precipitation.