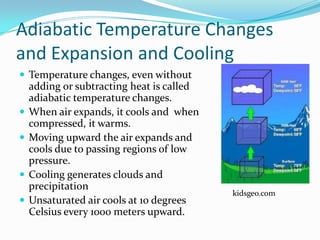
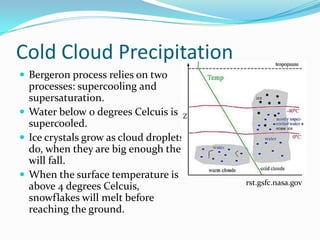
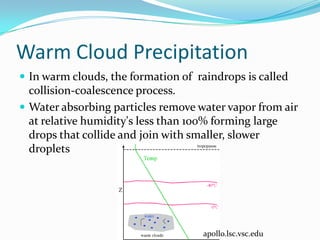
This document discusses various types of clouds and precipitation. It describes how temperature changes can cause air to expand and cool through adiabatic processes. Different lifting mechanisms like orographic lifting and convergence can cause air to rise and form clouds. Clouds are classified by height into high, middle, and low clouds and by form. Precipitation occurs through collision-coalescence in warm clouds and the Bergeron process in cold clouds. Rain, snow, sleet, glaze and hail are also explained.