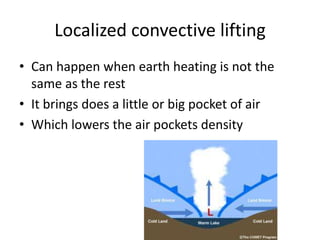
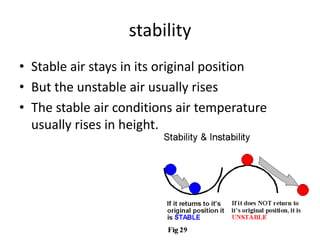
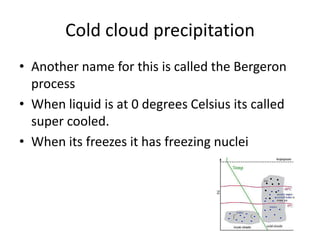
This document discusses various types of clouds and precipitation. It explains processes like adiabatic temperature changes, orographic and frontal lifting that cause clouds to form. The document categorizes clouds by height as high, middle and low clouds. It also discusses different types of precipitation like rain, snow, sleet and hail. The key roles of condensation and freezing in the formation of clouds and precipitation are outlined.