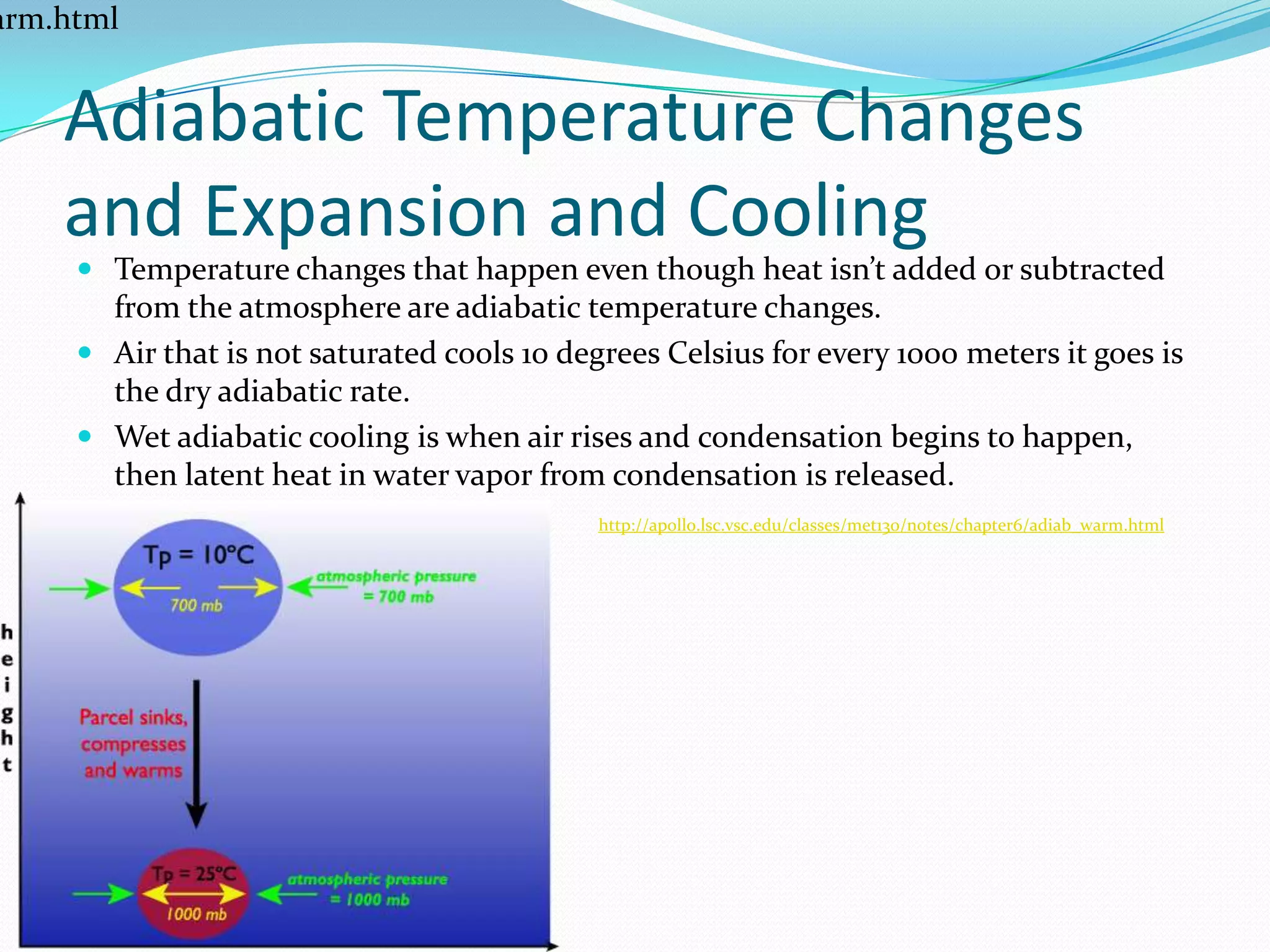
This document discusses various meteorological concepts related to cloud formation and precipitation. It covers topics like adiabatic temperature changes, orographic lifting, frontal wedging, convergence, stability, condensation, different cloud types classified by height and form, fog, precipitation processes in warm and cold clouds, and types of precipitation including rain, snow, sleet, glaze and hail. Each section provides a brief definition or explanation of the term and includes a link to an external reference site for more information.