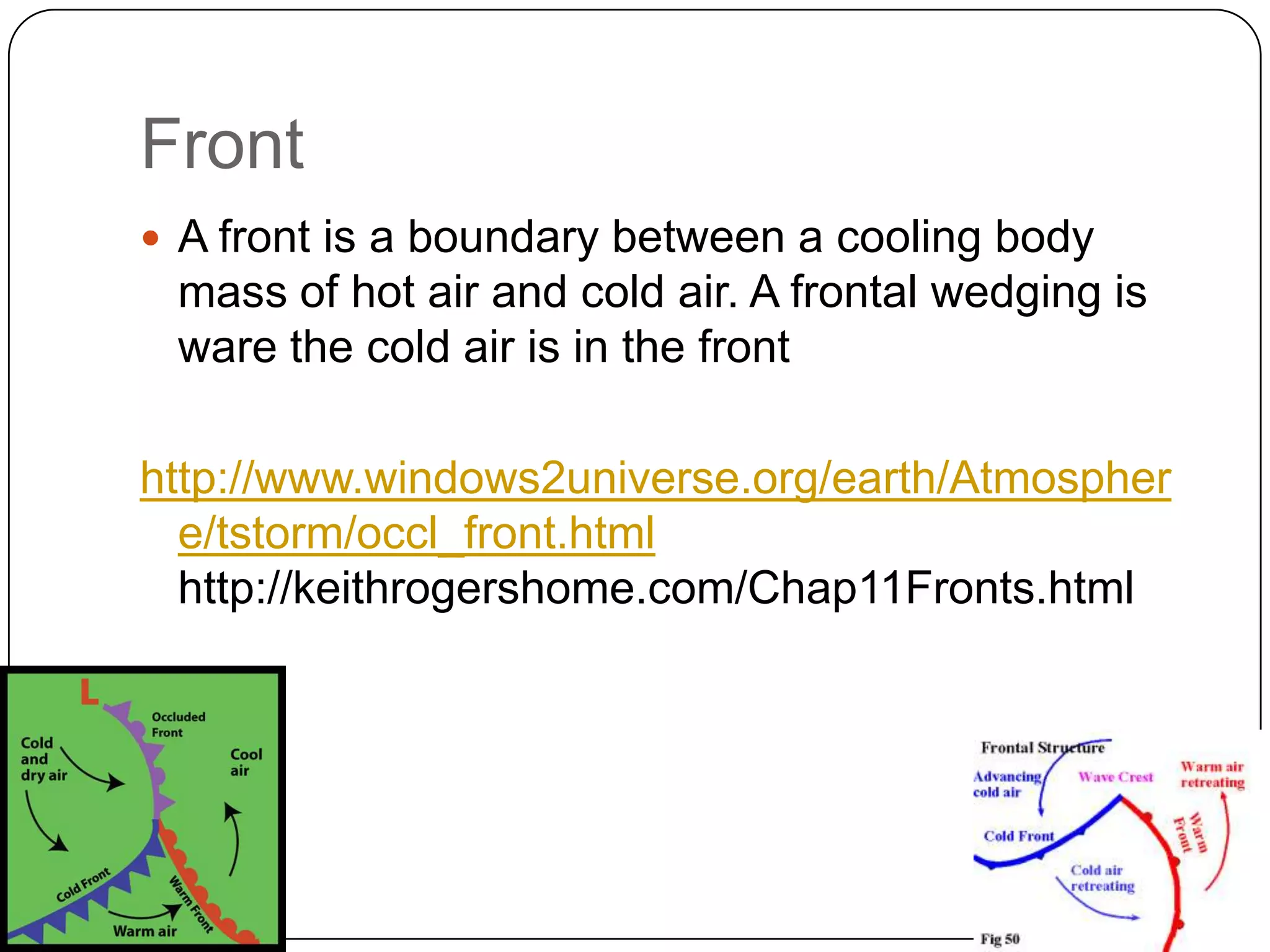
1) When air rises it cools through adiabatic expansion and condenses water vapor to form clouds like cirrus, cumulus, and stratus at different heights.
2) Orographic lifting occurs when air is forced to higher elevations over rising terrain, cooling and potentially causing precipitation.
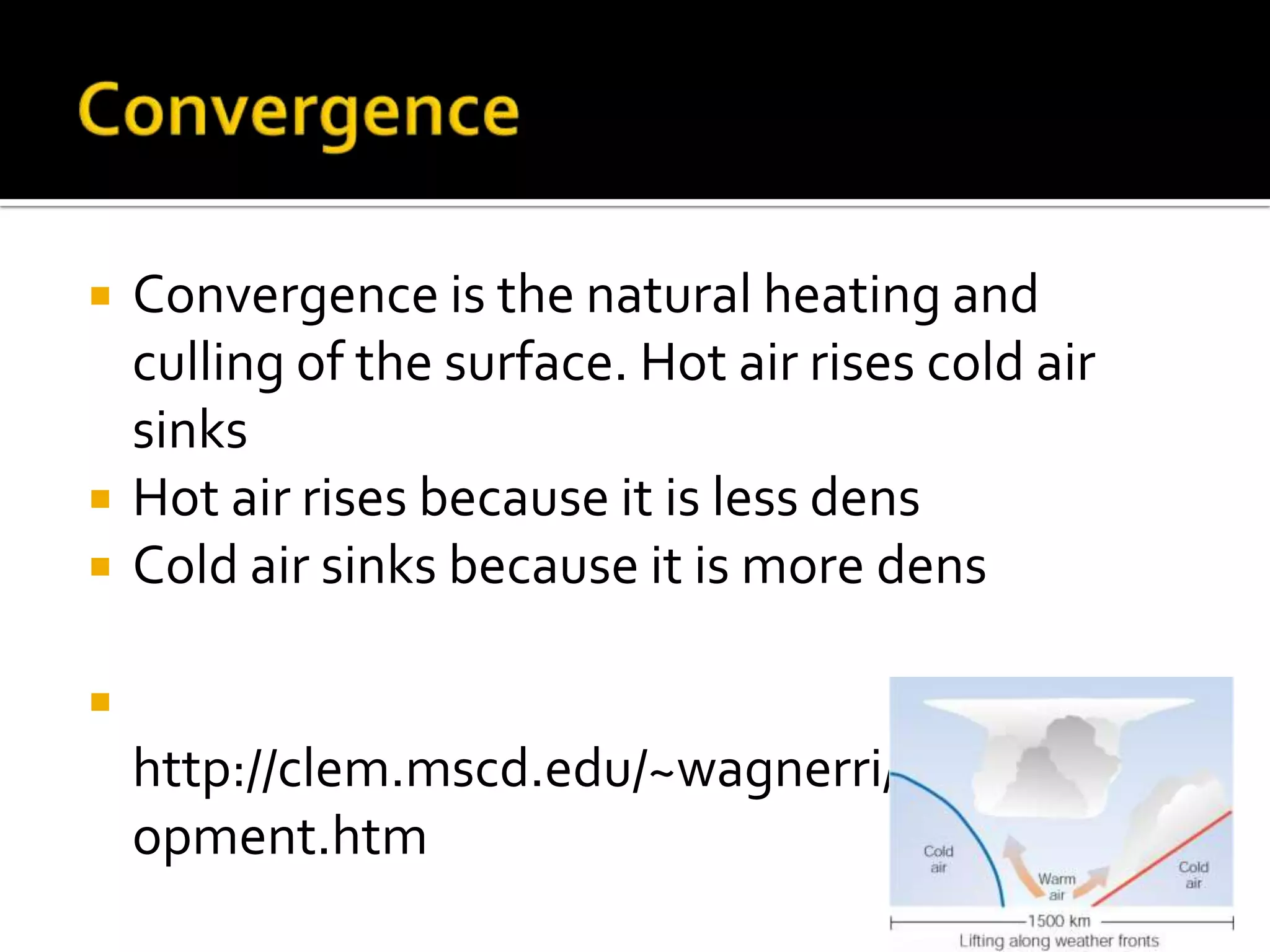
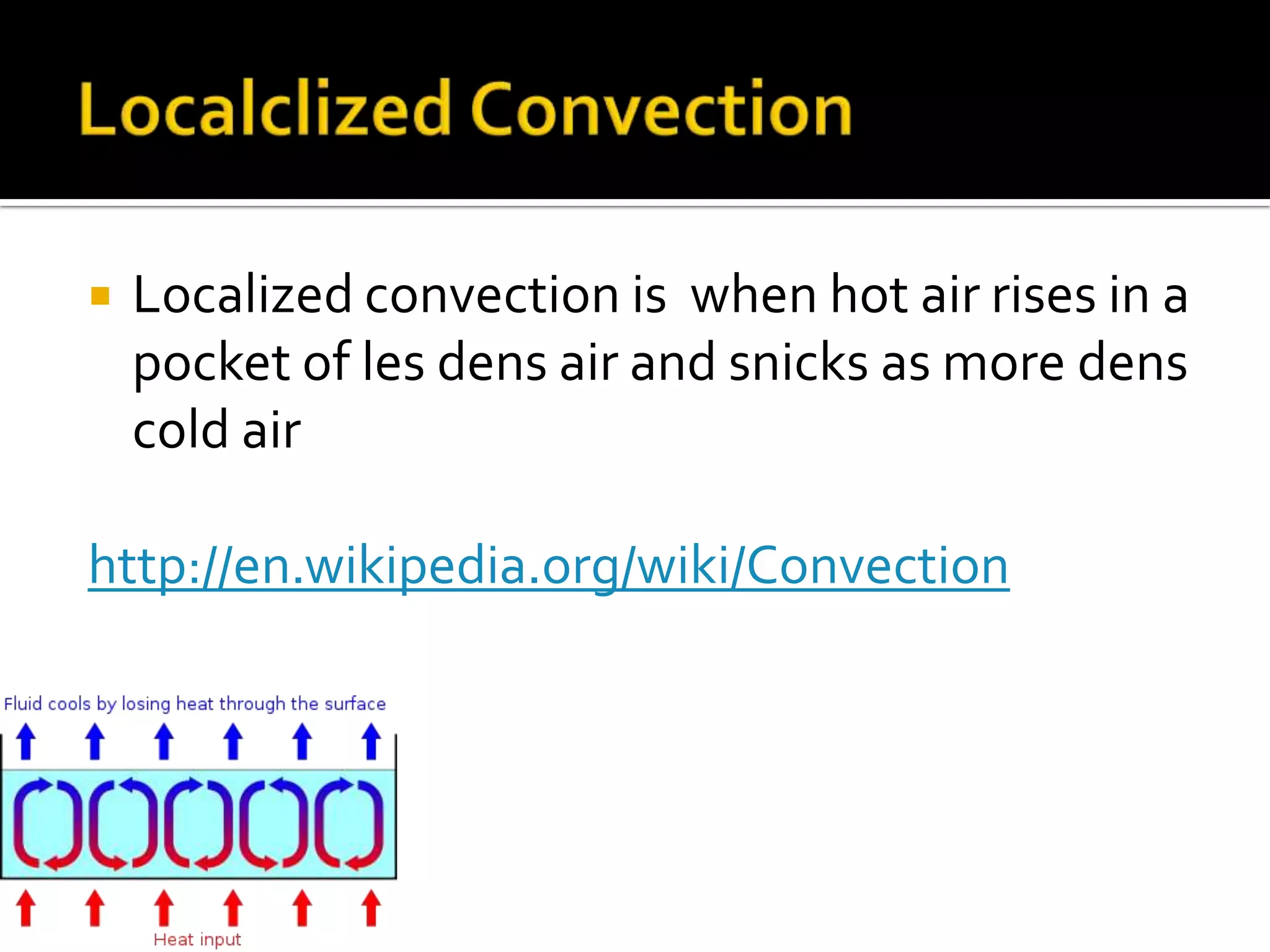
3) Convergence draws in surrounding air which rises then sinks, heating and cooling in localized areas and potentially causing convection storms.