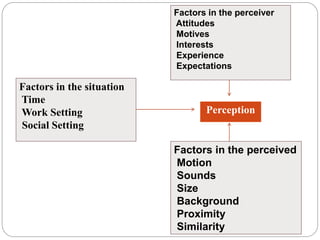
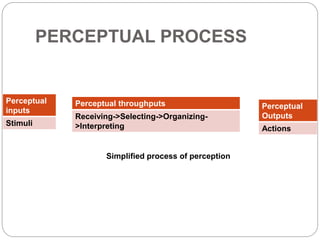
This document discusses perception and defines it as the process by which people select, organize, interpret, and respond to information from their environment. It notes that perception differs between individuals based on their past experiences and values. Perception influences behavior, as people act based on their perceptions rather than objective reality. The document outlines factors that influence perception, including characteristics of the perceiver, the perceived object/person, and the situation. It also discusses common perceptual distortions and the multi-step perceptual process of receiving inputs and forming outputs.