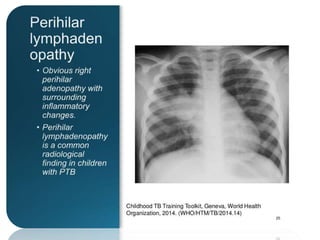
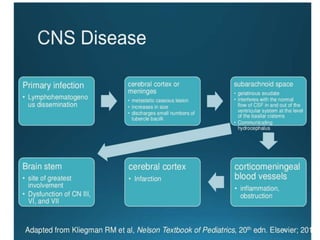
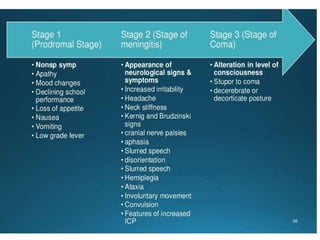
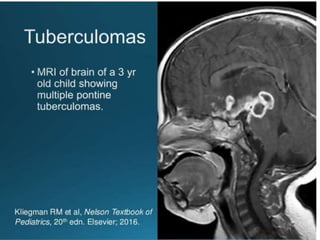
- Childhood tuberculosis is challenging to diagnose due to difficulties in confirming infection status and obtaining bacteriological confirmation.
- Risk of developing active TB is highest in the first two years of life, with disseminated disease and mortality also more common in young children.
- Diagnosis relies on clinical features, radiology, tuberculin skin testing, and bacteriological confirmation through sputum/gastric aspirate sampling and culture.
- Treatment guidelines in India recommend 6 months of chemotherapy for all childhood contacts of active TB cases, and clinically diagnosed cases can now begin treatment if confirmation testing is negative.