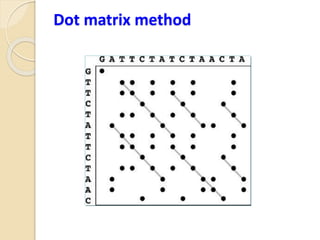
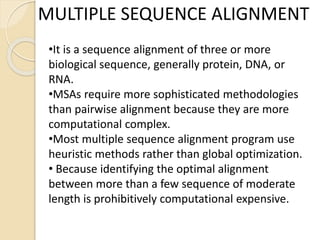
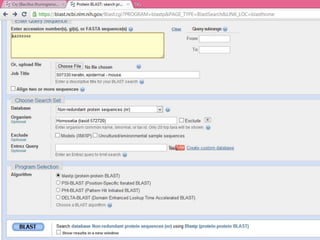
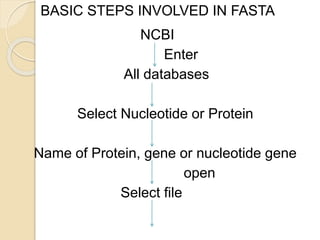
This document discusses various sequence alignment methods. It describes global alignment, which aligns two generally similar sequences over their entire length. Local alignment finds local regions of highest similarity between more divergent sequences. Pairwise alignment compares two sequences, while multiple sequence alignment handles three or more sequences using more sophisticated methods like progressive alignment and iterative alignment. Various online tools for sequence alignment are also mentioned, including BLAST, FASTA, and CLUSTAL Omega.