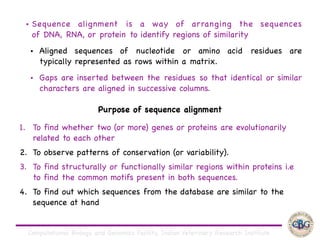
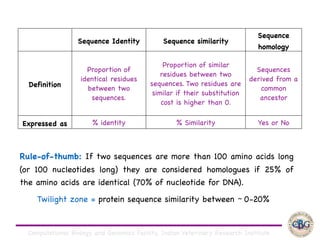
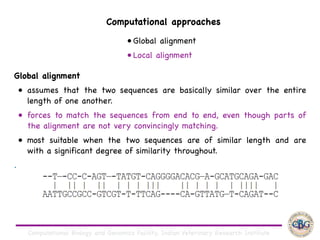
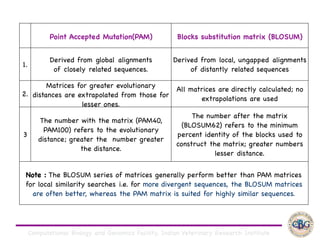
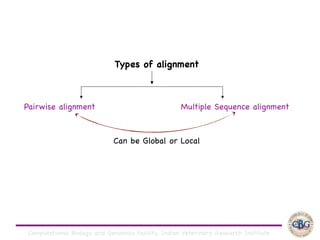
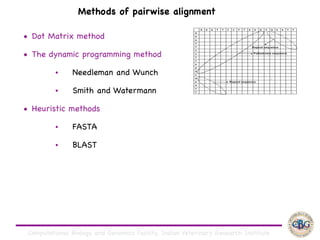
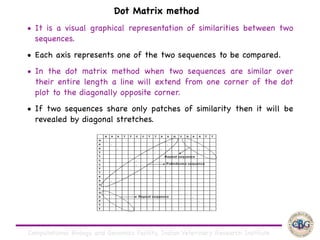
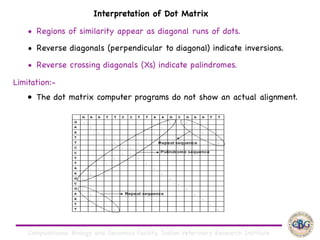
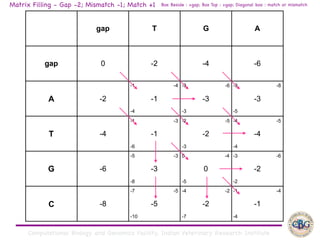
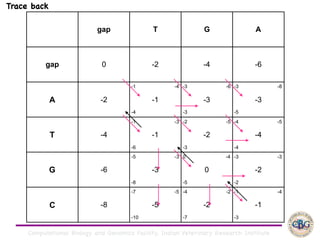
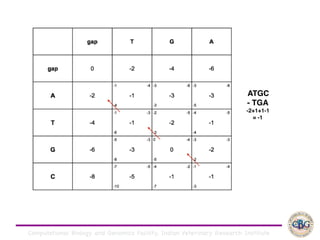
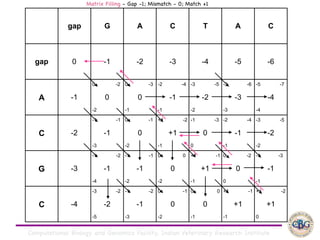
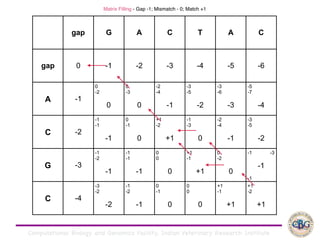
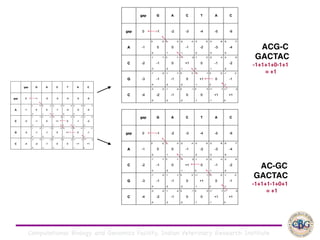
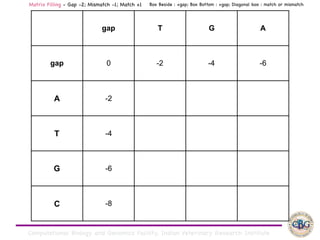
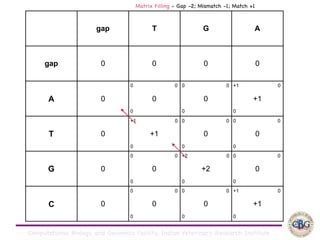
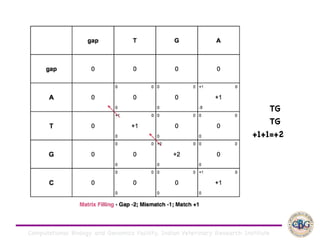
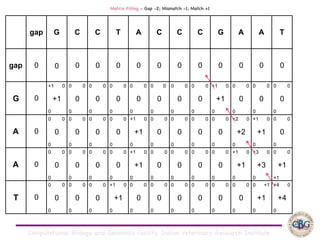
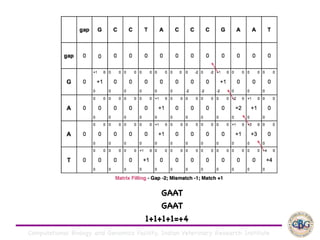
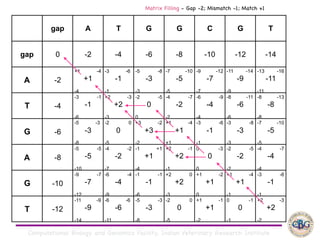
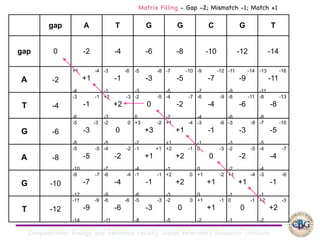
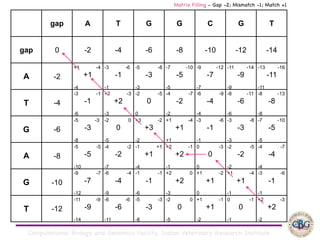
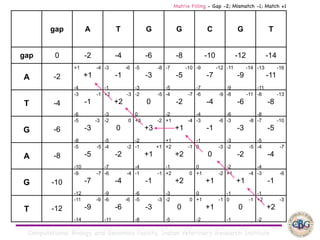
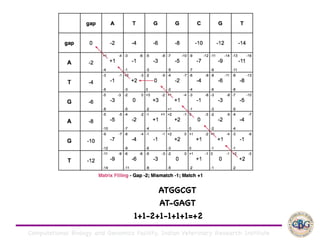
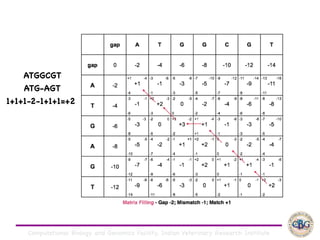
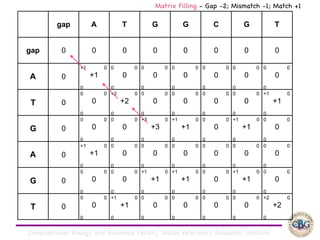
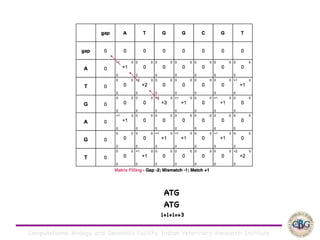
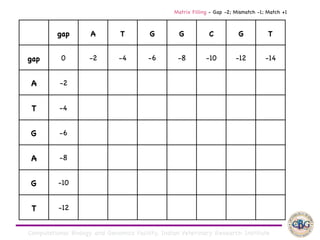
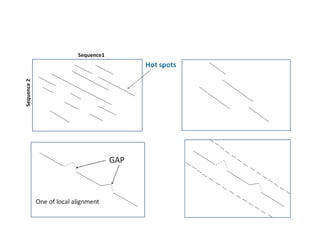
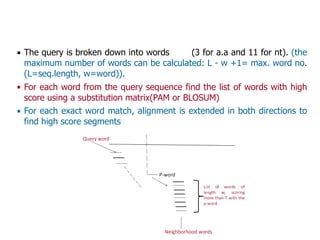
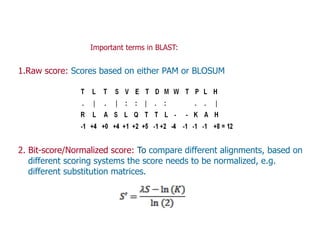
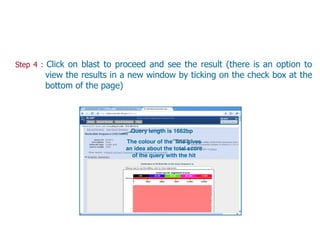
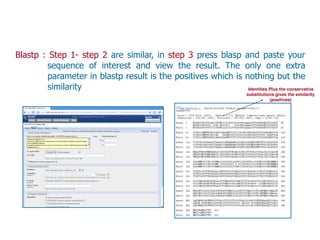
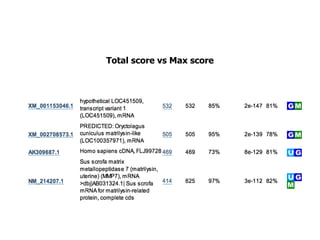
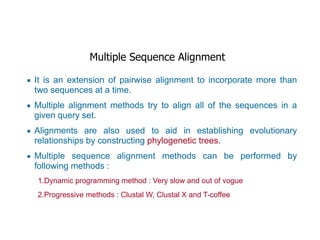
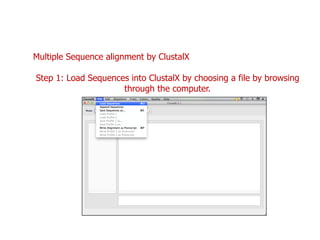
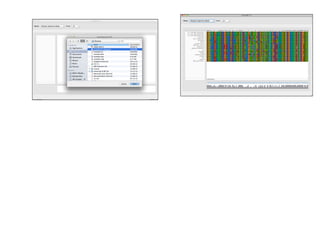
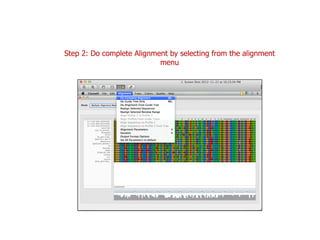
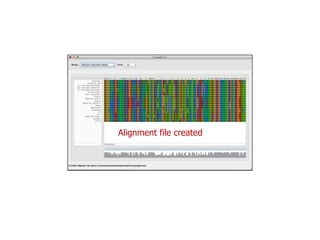
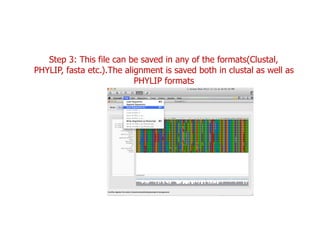
Sequence alignment involves arranging DNA, RNA, or protein sequences to identify regions of similarity. It is used to determine if sequences are evolutionarily related, observe patterns of conservation, and find similar regions within proteins. The key steps are representation of sequences in a matrix, insertion of gaps, and use of scoring schemes like PAM and BLOSUM matrices to identify the best alignment. Global alignment forces alignment over full sequence lengths while local alignment identifies short, well-matching segments. Algorithms like Needleman-Wunsch and Smith-Waterman use dynamic programming to calculate optimal pairwise sequence alignments.