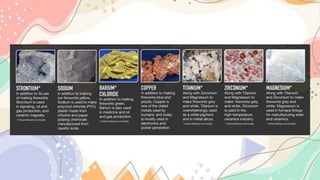
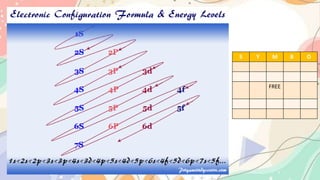
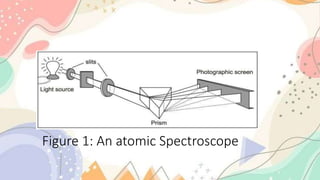
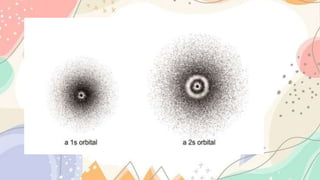
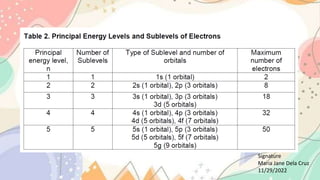
The document discusses the electronic structure of matter, detailing the composition of atoms and how metal salts produce characteristic colors in flames during tests. It explains the Bohr model of the atom, including energy levels and electron transitions, and introduces the quantum mechanical model as a more accurate representation of electron behavior. Key concepts include flame tests, atomic spectra, and the contributions of physicists like De Broglie, Schrödinger, and Heisenberg to atomic theory.