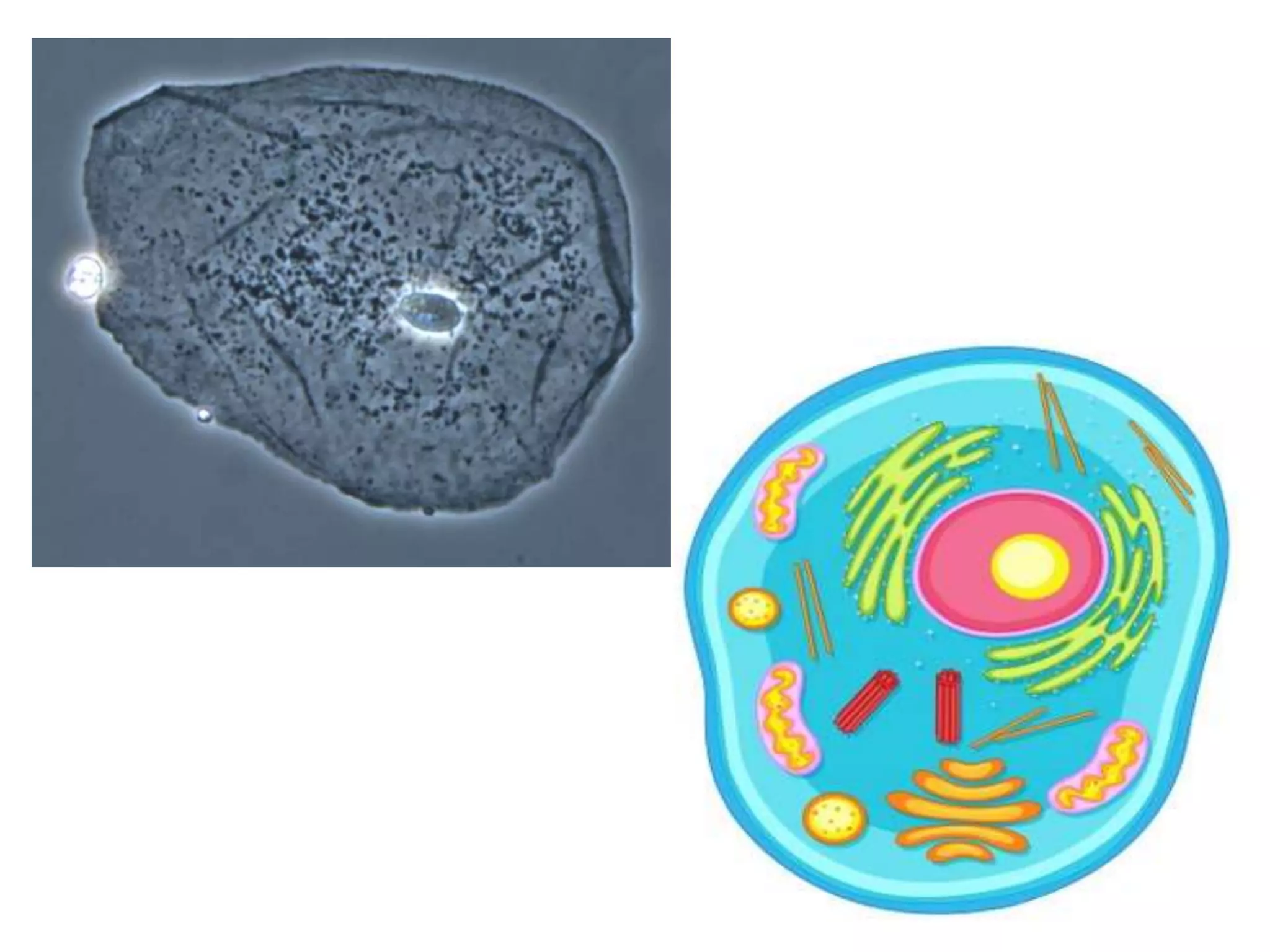
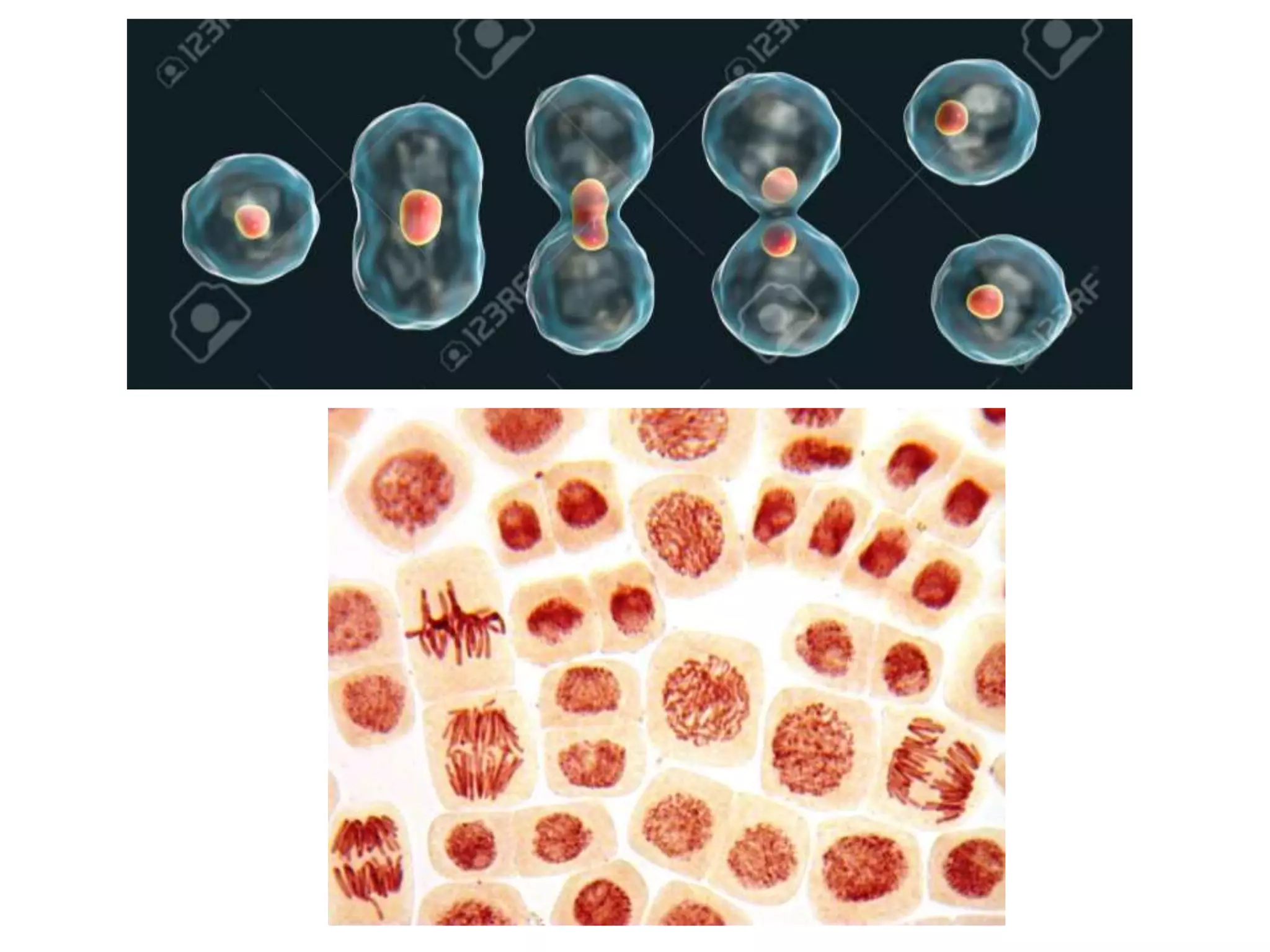
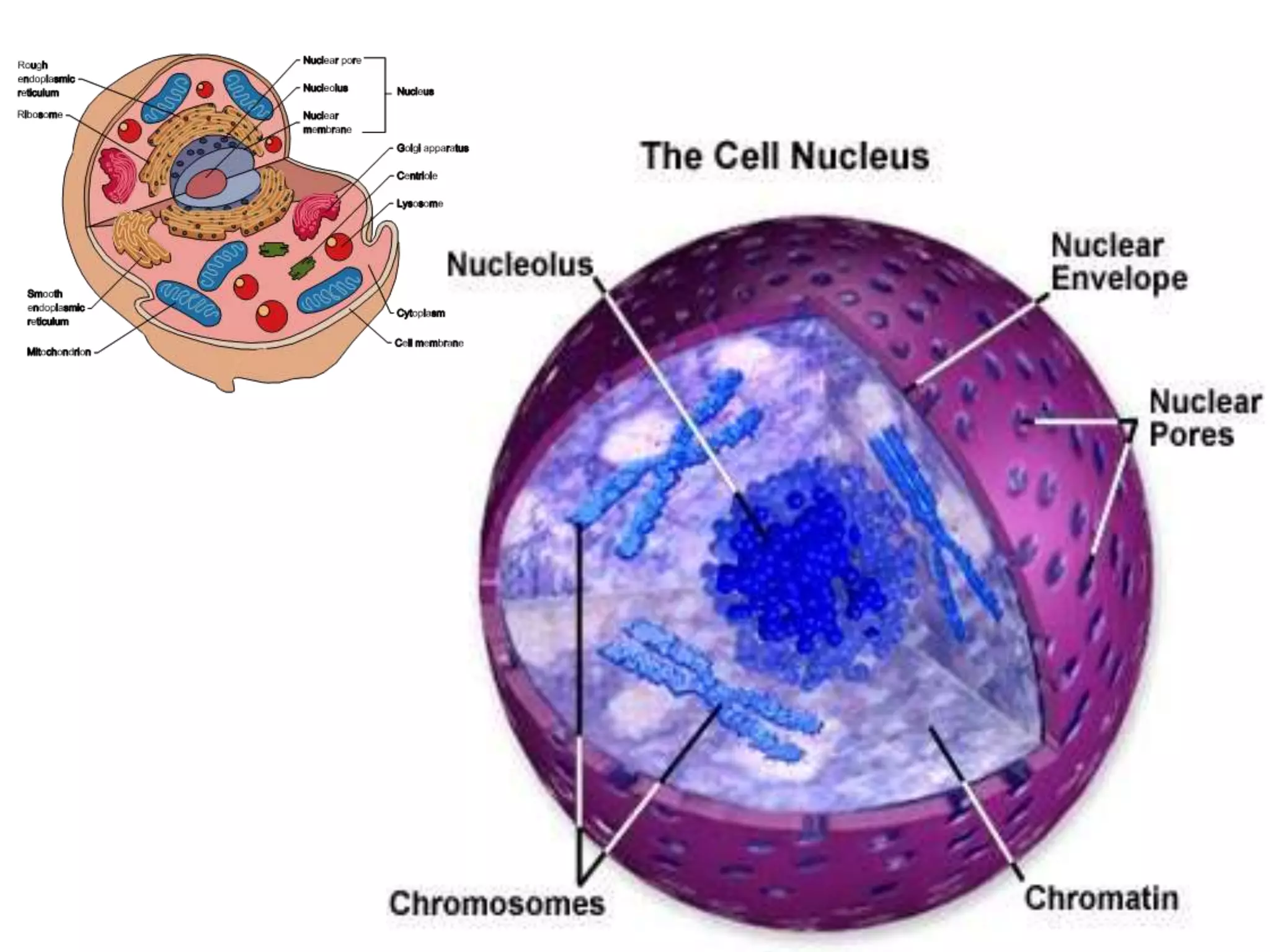
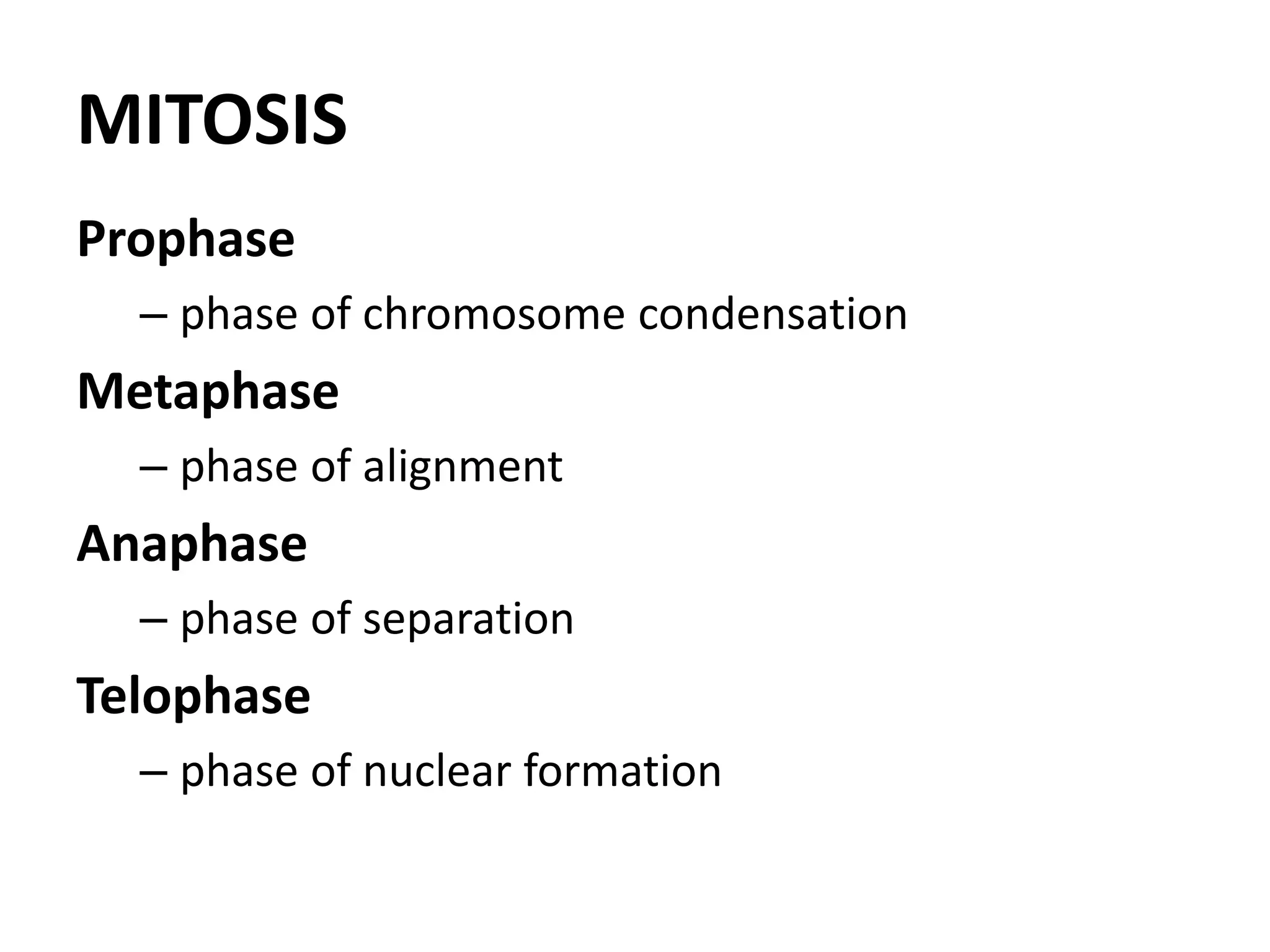
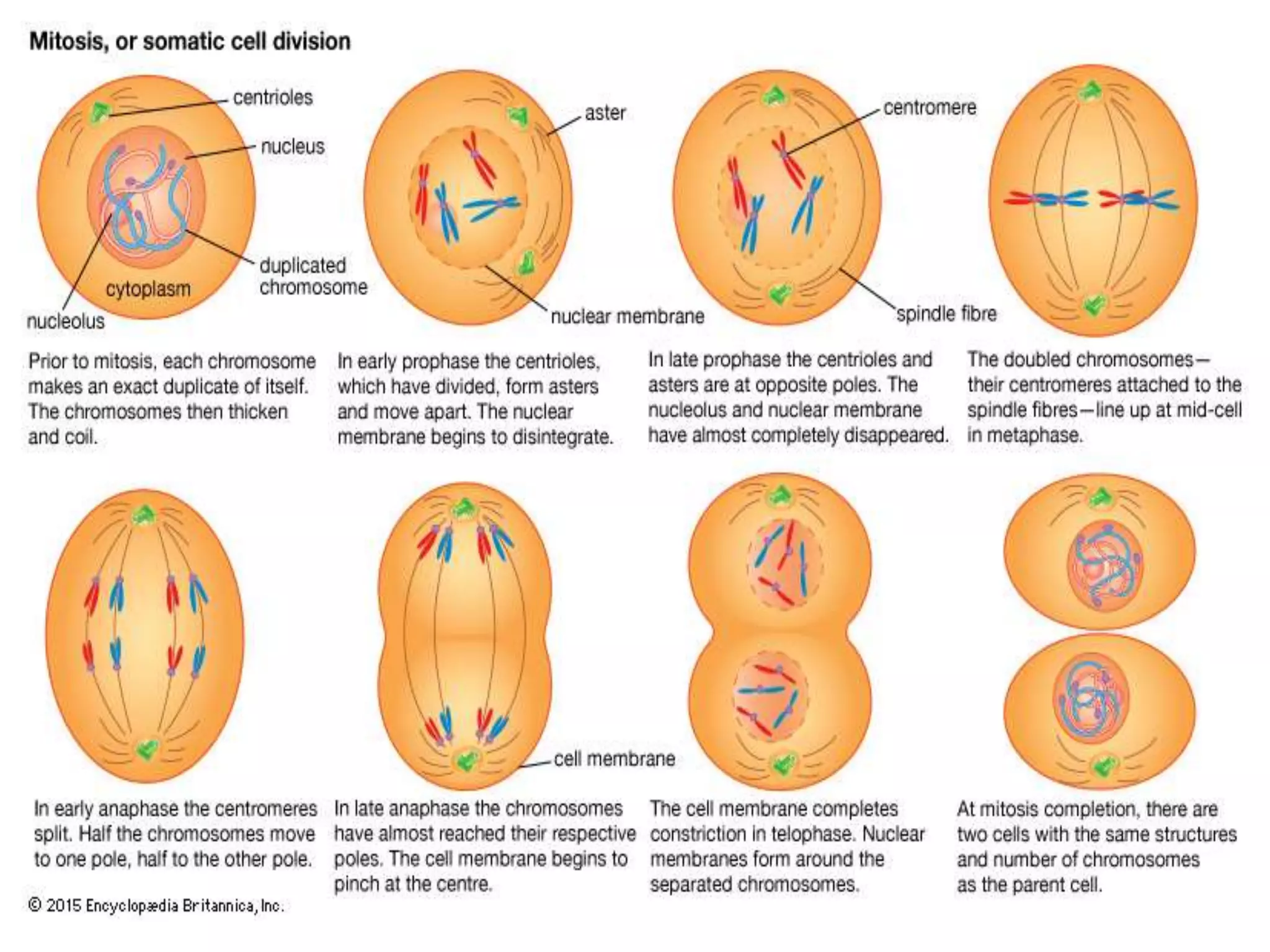
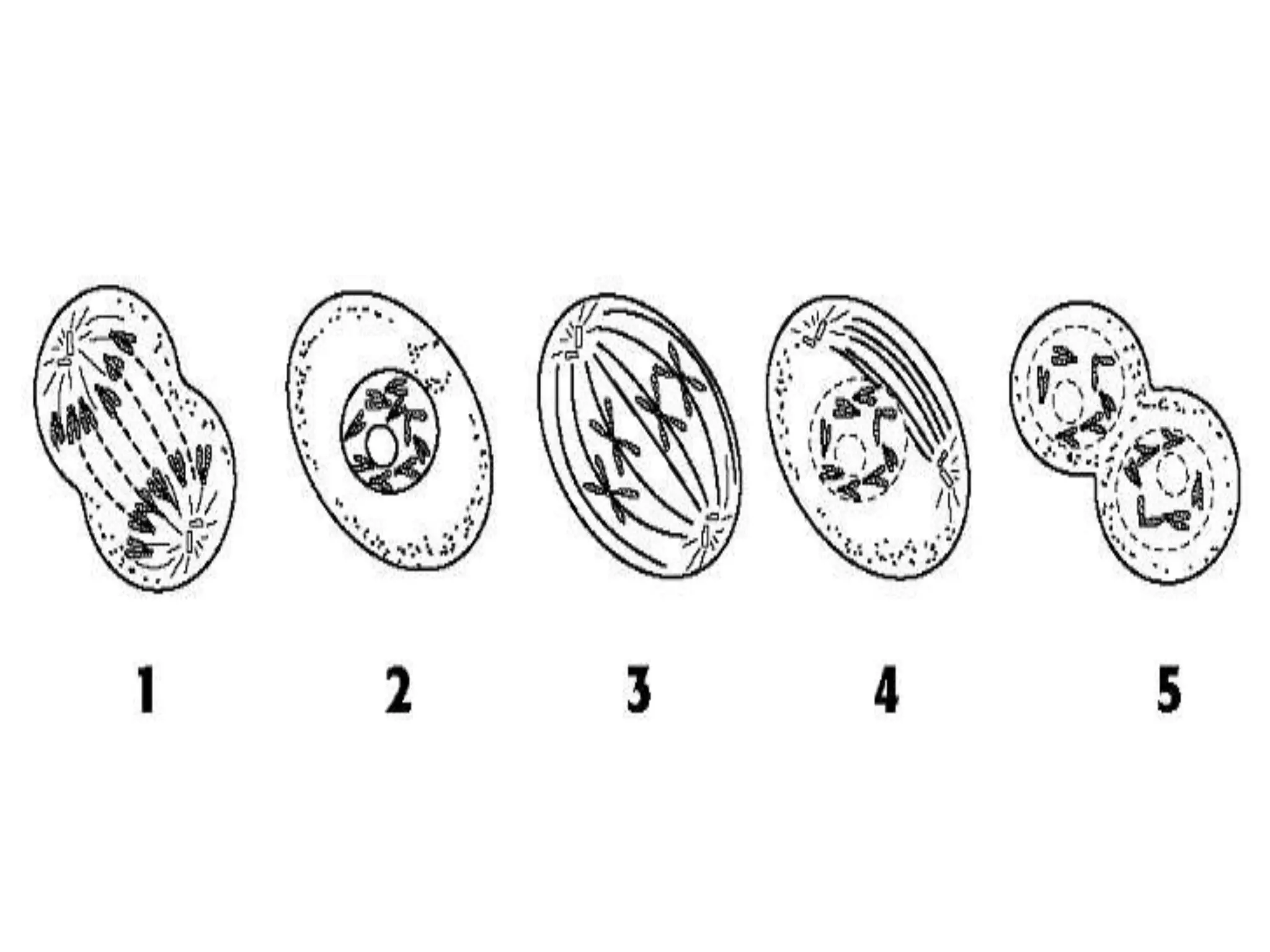
The document discusses cell division and the cell cycle. It defines cell division as the process where a cell divides into two daughter cells. The key stages of the cell cycle are interphase, where the cell grows and DNA replicates, and mitosis, where the cell divides. Mitosis is further broken down into prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Prophase involves chromosome condensation and nuclear envelope breakdown. Metaphase aligns chromosomes at the center. Anaphase separates sister chromatids. Telophase reforms the nuclei and divides the cytoplasm.