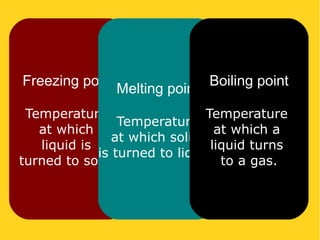
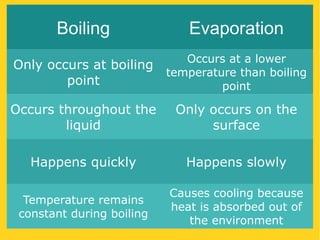
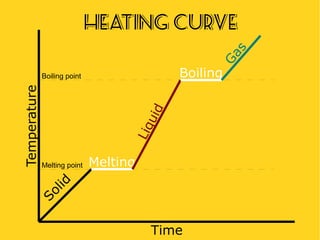
The document discusses the states of matter—solid, liquid, and gas—and their properties based on the kinetic molecular theory. It explains how temperature affects the physical condition of substances, detailing phase changes such as melting, evaporation, and solidification. Key concepts include diffusion, Brownian motion, and the relationship between particle energy and state changes.