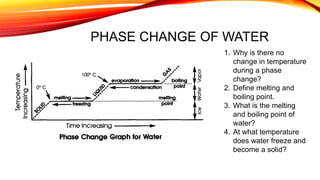
The document discusses the four states of matter - solid, liquid, gas, and plasma - and phase changes between states. It describes the particle behavior and properties of each state. Solids have a definite shape and volume, with particles tightly packed in a regular pattern that vibrate in place. Liquids have a definite volume that takes the shape of their container, with particles close together that can slide past one another. Gases have no definite shape or volume, with particles well separated and moving freely at high speeds. Plasma is similar to gas but with electrically charged particles. Phase changes are physical changes between these states that involve the absorption or release of heat energy as particles speed up and move farther apart or slow down and move