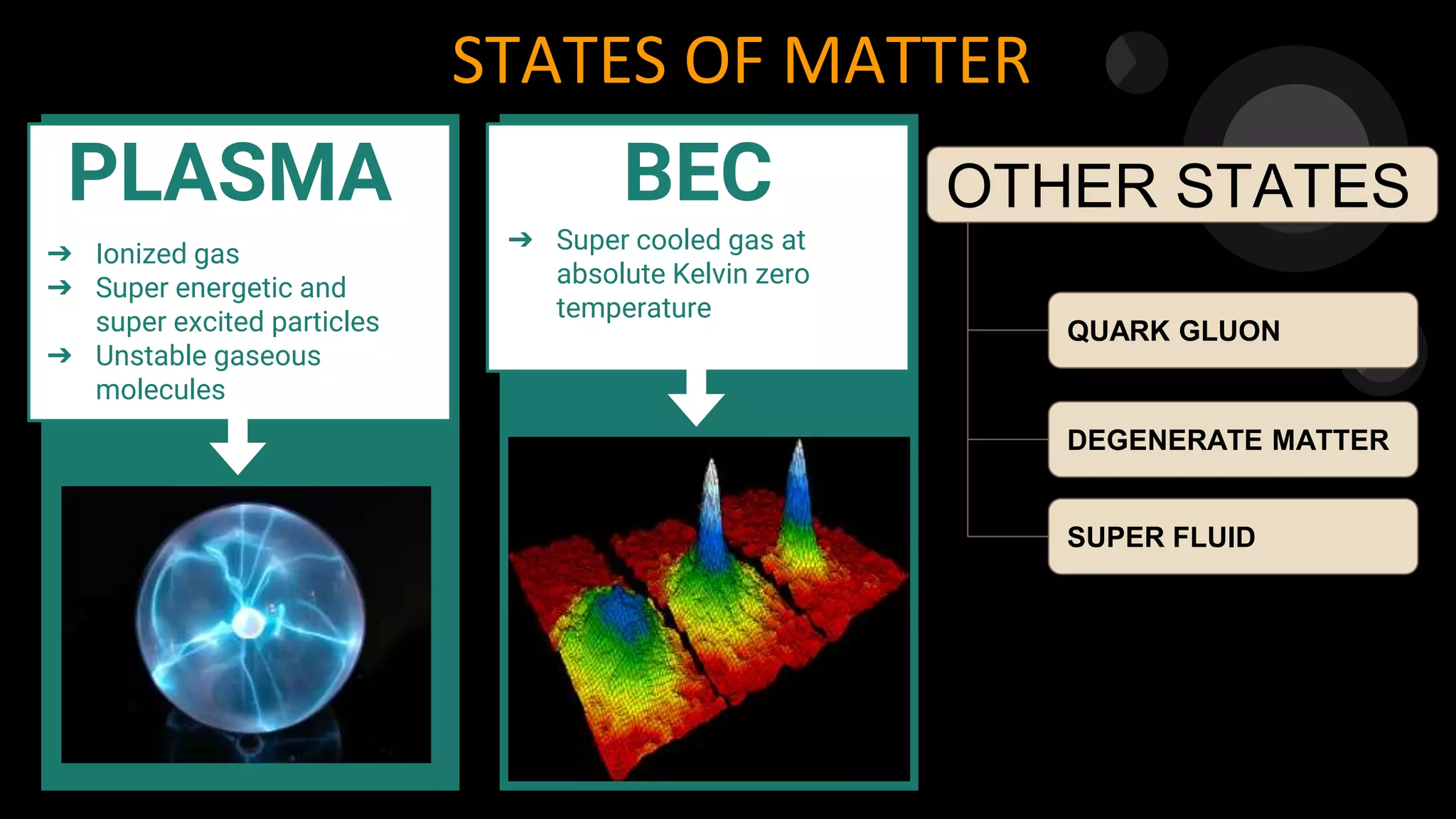
The document discusses the nature of matter, its characteristics, and classification into solids, liquids, and gases, based on physical state and chemical composition. It explains the behavior of particles in different states, temperature effects, and processes such as melting, boiling, and evaporation. Additionally, it covers concepts like latent heat, interconversion of states, and factors affecting evaporation.