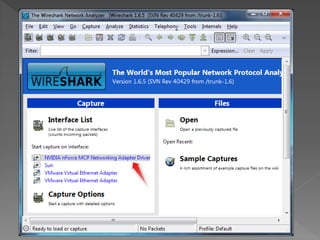
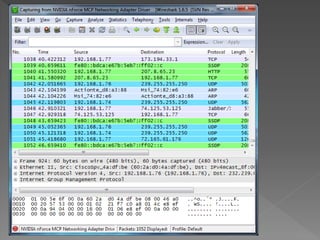
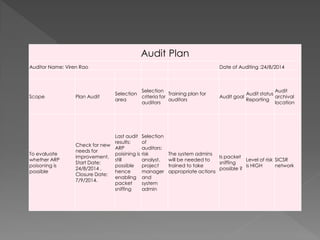
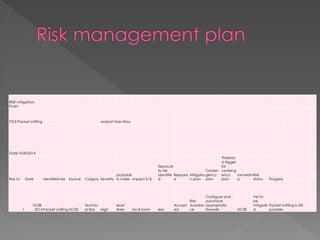
The document discusses packet sniffing and its implications on network security, specifically focusing on ARP spoofing vulnerabilities in the SICS network. It highlights the use of Wireshark for capturing packets, the risk assessment process, and the need for effective mitigation strategies, including the configuration of switches for better security. Various methods for addressing ARP poisoning are evaluated, with recommendations for actions to enhance security and reduce risks.