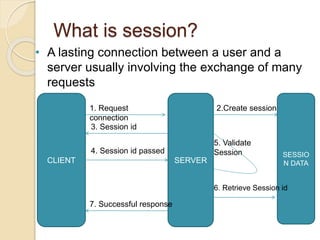
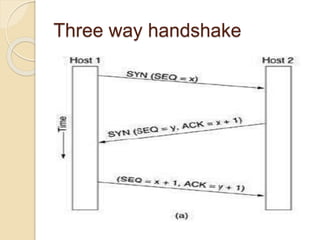
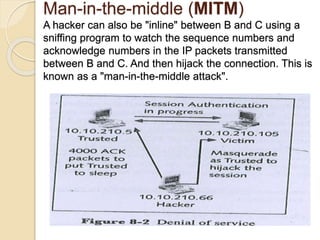
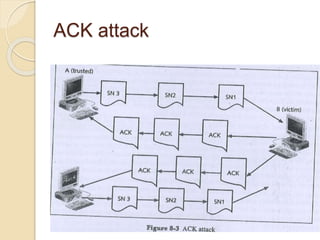
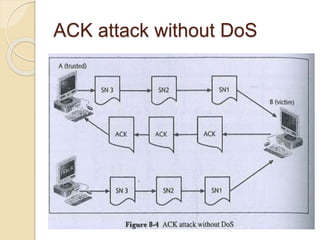
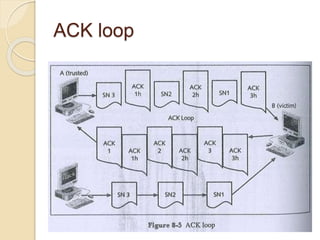
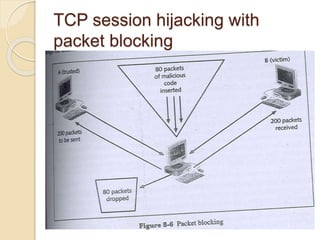
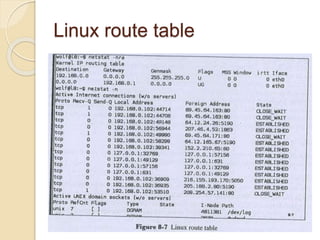
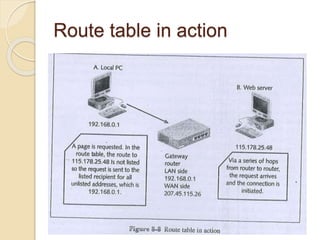
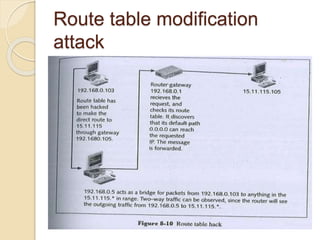
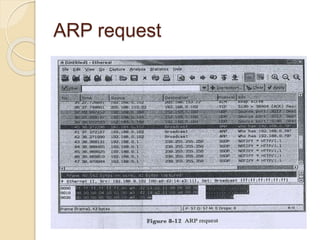
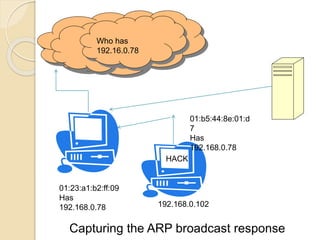
Session hijacking involves taking control of an authorized user's session by obtaining their session ID. There are several methods, including TCP session hijacking, which can be done through blind hijacking or man-in-the-middle attacks. TCP session hijacking with packet blocking modifies the route table or ARP table to intercept packets. Tools like Hunt can hijack sessions through ARP attacks. Prevention methods include encryption, as used in SSH and TLS, and storm watching to detect abnormal network traffic increases that could indicate hijacking.