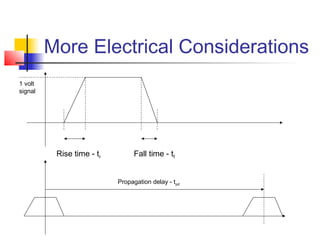
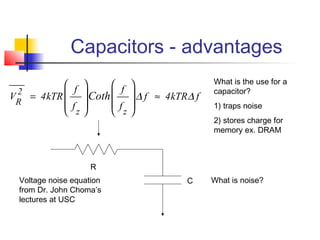
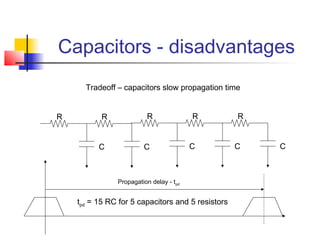
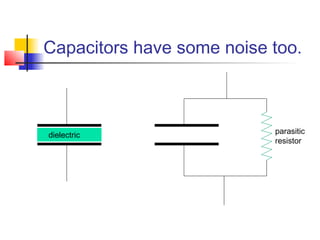
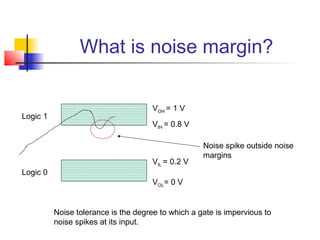
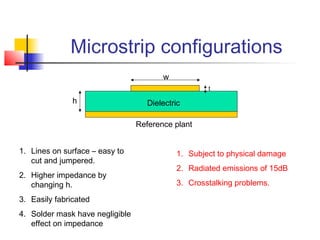
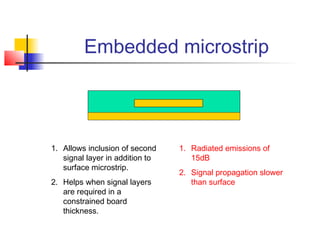
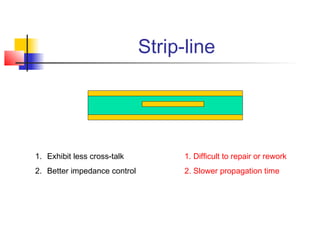
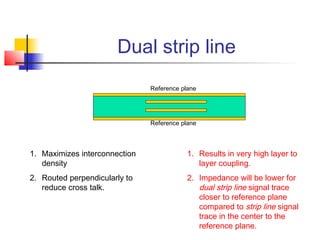
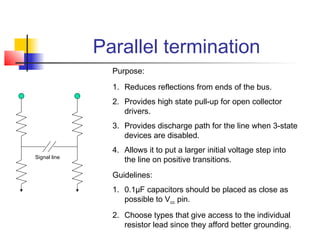
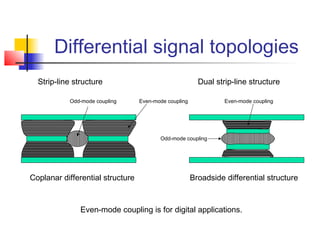
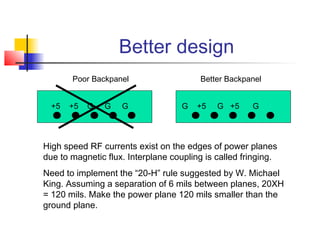
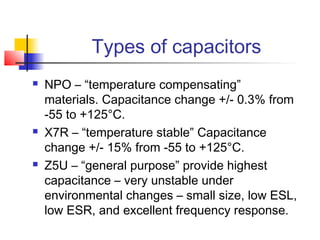
This document discusses the design of high performance printed circuit boards. It covers topics such as PCB design flow, mechanical design considerations, electrical considerations like impedance and noise, capacitor advantages and disadvantages, microstrip and signal trace configurations, cross-talk control techniques, termination methods, and guidelines for layout and EMI reduction. The goal is to minimize delays, noise, and reliability issues through careful mechanical and electrical design.