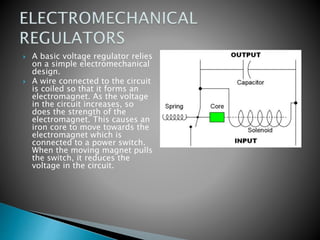
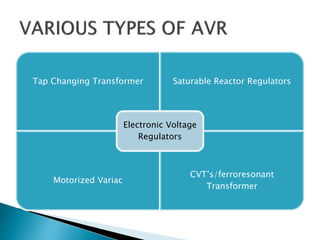
Here are the key characteristics of a good inverter:
- Sinusoidal output voltage waveform
- High gain
- Controllable output voltage and frequency
- Low power requirement for control circuitry
- Low cost
- Long working life
- Semiconductor devices with minimal switching and conduction losses